Discover For the Life of the World / Yale Center for Faith & Culture
For the Life of the World / Yale Center for Faith & Culture

For the Life of the World / Yale Center for Faith & Culture
Author: Matthew Croasmun, Ryan McAnnally-Linz, Drew Collins, Miroslav Volf, Evan Rosa, Macie Bridge
Subscribed: 190Played: 10,760Subscribe
Share
© 2020-2028 Yale Center for Faith & Culture
Description
Seeking and living a life worthy of our humanity. Theological insight, cultural analysis, and practical guidance for personal and communal flourishing. Brought to you by the Yale Center for Faith & Culture.
244 Episodes
Reverse
Theologian Bo Karen Lee joins Ryan McAnnally-Linz to explore how the multiple layers of trauma—pandemic grief, racialized violence, intergenerational wounding, vicarious suffering—can be met by the resources of Ignatian spirituality and contemplative prayer. Writing and teaching at the intersection of Christian formation and social justice, Lee brings both scholarly precision and uncommon personal candor to one of the most urgent conversations in theology today.
"Trauma tends to isolate and alienate us from our siblings, our human siblings. But ironically, this witnessing of one another's pain is the source of healing. So it has the very opposite effect of what is needed for it to be healed."
In this conversation, Lee reflects on the spiritual journey from what one author calls "alarmed aloneness" toward becoming beloved—seen, held, and gazed upon with love. Together they discuss the overlapping layers of collective, personal, racialized, and intergenerational trauma shaping contemporary life; attachment theory and its parallels with spiritual formation; the Ignatian tradition of imaginative, contemplative prayer; the still face experiment and the theology of the loving gaze; and why the church has something singular to offer the trauma crisis of our time.
Episode Highlights
"We are quite sure we're alone in the world and no one really sees us, no one truly cares and no one can be trusted. You're alone, overwhelmed, and helpless."
"Trauma tends to isolate and alienate us from our siblings, our human siblings. But ironically, this witnessing of one another's pain is the source of healing. So it has the very opposite effect of what is needed for it to be healed."
"I need to be held, but it's this illusory figure that holds me, because I have shut myself off to the very things that could help me, because no one is to be trusted."
"I've seen too much hope, and too much beauty, and too much healing walking through the spiritual exercises that I can no longer despair that trauma has the final word."
"Gazing upon the God who gazes upon me with love. That is contemplative prayer."
About Bo Karen Lee
Bo Karen Lee is Associate Professor of Spiritual Theology and Christian Formation at Princeton Theological Seminary, where she teaches contemplative theology, Ignatian spirituality, and the relationship between prayer and social justice. A leading voice in the integration of trauma studies and Christian formation, she brings the Ignatian tradition into conversation with psychology, attachment theory, and the lived experience of racialized communities. Her work draws on the Spiritual Exercises of Ignatius of Loyola to offer resources for healing that are both theologically grounded and pastorally immediate. She directs retreatants in the nineteenth annotation of the Spiritual Exercises and works regularly with spiritual directors trained in the Ignatian tradition.
Helpful Links and Resources
Bessel van der Kolk, Traumatic Stress: The Effects of Overwhelming Experience on Mind, Body, and Society https://www.amazon.com/Traumatic-Stress-Overwhelming-Experience-Society/dp/1572300485
Bessel van der Kolk, The Body Keeps the Score https://www.besselvanderkolk.com/resources/the-body-keeps-the-score
Resmaa Menakem, My Grandmother's Hands https://www.resmaa.com/resources
Kathy Weingarten, Common Shock: Witnessing Violence Every Day https://www.kathyweingarten.com
David Fleming SJ, Draw Me Into Your Friendship https://www.amazon.com/Draw-Me-Into-Your-Friendship/dp/0912422904
Ignatius of Loyola, The Spiritual Exercises https://www.ignatianspirituality.com/ignatian-prayer/the-spiritual-exercises/
Edward Tronick, Still Face Experiment https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=apzXGEbZht0
Find a Spiritual Director https://www.ignatianspirituality.com/making-good-decisions/find-a-spiritual-director/
Show Notes
Trauma defined: "terror triggered by an inescapably stressful event that overwhelms existing coping mechanisms" — Bessel van der Kolk
Layers of trauma: collective pandemic grief, personal wounding, racialized violence, intergenerational encoding, vicarious/secondary trauma
Global pandemic as collective trauma — threat of death, forced isolation, planetary-scale overwhelm
Racialized trauma and AAPI hate incidents — one in five AAPI individuals reported a hate incident in the U.S. in a 15-month window (as of late 2021)
My Grandmother's Hands by Resmaa Menakem — racialized trauma encoded in bodies and communities https://www.resmaa.com/resources
Cumulative microaggressions — daily small injuries can produce PTSD-level effects over time; growing body of clinical literature
Secondary/vicarious trauma — hearing others' suffering reactivates unresolved wounds in caregivers and companions
"Double jeopardy" — Kathy Weingarten's term for caregivers whose own past traumas are reactivated while supporting others
Five professions at highest risk: clergy, health workers, teachers, police, journalists — context for the Great Resignation
"Alarmed aloneness" — the net effect of trauma: certainty that no one sees you, no one cares, no one can be trusted
"Trauma tends to isolate and alienate us from our siblings, our human siblings. But ironically, this witnessing of one another's pain is the source of healing."
The orphan image: a girl in a Middle Eastern orphanage draws a chalk mother around her fetal body — illusory comfort as portrait of traumatic isolation
Intergenerational trauma — encoded in DNA; personal testimony about learning her own mother was nearly killed as an infant, its echo across generations
Kintsugi as healing metaphor — the Japanese art of mending broken pottery with gold; grief before repair, not a race to be fixed
Robert Stolorow's concept: finding a "relational home" for traumatic suffering — the necessity of being witnessed
Ignatius of Loyola — 16th-century Spanish soldier wounded by cannonball; encountered the living Christ through Ludolph of Saxony's Vita Christi during convalescence
The Spiritual Exercises: a four-week manual for imaginative prayer — beloved and broken, walking with Christ through ministry, suffering, resurrection https://www.ignatianspirituality.com/ignatian-prayer/the-spiritual-exercises/
Ignatian contemplative prayer defined: "gazing upon the God who gazes upon me with love" — kataphatic, embodied, not requiring stillness or silence
Still Face Experiment (Edward Tronick) — infant distress when a loving mother goes blank; evidence that the gaze of love is neurologically and psychologically foundational https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=apzXGEbZht0
Attachment theory and spiritual formation — earned secure attachment: what unhealthy early bonding cannot provide, sustained relationship with God can
"I've seen too much hope, and too much beauty, and too much healing walking through the spiritual exercises that I can no longer despair that trauma has the final word."
Personal testimony: AAPI hate crimes, night terrors, contemplative prayer with a spiritual director; a vision of Mary, the wailing women, and the crucified Christ
"Bo, they killed me too" — Christ's words in a contemplative vision; solidarity as the beginning of bearable grief
Sartre's "hell is other people" reframed — parasitic dependence on others' approval vs. the freedom of knowing how God gazes upon you
Resources for beginning: David Fleming's Draw Me Into Your Friendship; finding a spiritual director trained in Ignatian spirituality; Jesuit retreat centers
#TraumaHealing #IgnatianSpirituality #ContemplativePrayer #ChristianFormation #SpiritualTheology #MentalHealthAndFaith #RacializedTrauma #AttachmentTheory #ForTheLifeOfTheWorld #YaleDivinity
Production Notes
This podcast featured Bo Karen Lee
Edited and Produced by Evan Rosa
Hosted by Evan Rosa
Production Assistance by Annie Trowbridge and Luke Stringer
A Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/about
Support For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
What happens when we stop treating the Bible as a sacred object and start paying attention to how we actually use it? In this conversation, theologian David Dault reflects on interpretation, responsibility, and the ethics of reading scripture in a fractured world.
In this episode with Evan Rosa, Dault reflects on interpretation, responsibility, and how readers shape the meaning and moral impact of the Bible.
Together they discuss the materiality of scripture, translation and betrayal, moral seriousness, scriptural reasoning across traditions, catastrophic love, and the ethical responsibility readers bear for how sacred texts are used.
Episode Highlights
“To assume that we know what a text is telling us is a matter of hubris.”
“The Bible doesn’t tell you to do anything. You as a reader decide what to do.”
“Violence is always an act of interpretation.”
“We never get to a place where everything is clean and everyone benefits.”
“We have to take responsibility for the violence we involve ourselves in.”
About David Dault
David Dault is a theologian, journalist, and media producer whose work explores religion, culture, ethics, and interpretation. He is Executive Producer and host of Things Not Seen: Conversations About Culture and Faith, a nationally distributed public radio program. He teaches in the Institute of Pastoral Studies at Loyola University Chicago. Dault’s scholarship focuses on hermeneutics, religion and media, and the ethical implications of how sacred texts are interpreted and used in public life. His book The Accessorized Bible examines the material forms, cultural framing, and interpretive communities that shape how people encounter scripture. He holds degrees in theology and religious studies and frequently writes and lectures on religion, politics, and culture.
Helpful Links And Resources
The Accessorized Bible, by David Dault https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300153125/the-accessorized-bible/
Things Not Seen: Conversations About Culture and Faith https://thingsnotseenradio.com
David Dault’s personal website https://www.daviddault.com/
Show Notes
The Accessorized Bible—material culture of scripture, design, marketing niches, and the ways the physical form of the Bible shapes how readers interpret and use it
Bible as object, medium, and cultural artifact; Marshall McLuhan and media theory—the form of a book shaping how ideas move between minds
Books as technologies of imagination and identity formation; reading as a kind of “magical” transfer of ideas from one mind into another
“To assume that we know what a text is telling us is a matter of hubris.” Interpretation requires caution, humility, and the recognition that texts exceed our control
Making the familiar strange again; recovering the power of scripture by refusing to domesticate it or assume we fully understand it
Franz Rosenzweig on preserving the alienness of sacred texts; debate with Martin Buber on translation and clarity
Translation as interpretation—translators inevitably carry values, ideologies, and cultural assumptions into the text
Harold Bloom’s Anxiety of Influence; interpreters “misread” texts in order to wrestle with their influence and generate new meaning
Reading scripture in community; trust, vulnerability, and shared responsibility among interpreters
Scriptural reasoning—Jews, Christians, and Muslims reading shared stories (Noah, Abraham, Moses) together without claiming mastery over the text
Tikkun olam—Jewish ethical tradition of “repairing the world”; the world is wounded and humans participate in its healing
Repentance and Repair—Rabbi Danya Ruttenberg on moral accountability, restitution, and the work of restoring relationships
Violence embedded in interpretation; moral action always involves choices about attention, resources, and responsibility
The “flashlight” metaphor—moral attention illuminating one suffering person while another need temporarily falls into shadow
Jairus’s daughter and the woman with the hemorrhage—competing moral urgencies in the Gospels
“We never get to a place where everything is clean and everyone benefits.” Moral action always involves tragic limitation and competing responsibilities
Levinas and infinite responsibility; the ethical demand arising from the face of the person before us
Moral seriousness versus performative irony; resisting discourse driven by trolling, spectacle, and dopamine-driven outrage
A Bible Is A Book—dismantling the assumption that sacred texts themselves command moral action
Steve Martin’s The Jerk and the phone book illustration; a sniper randomly selecting a name and deciding someone should die
“The Bible doesn’t tell you what to do.” Readers decide what moral actions follow from a text
Reader responsibility; refusing the excuse “the Bible told me to,” recognizing moral agency belongs to interpreters
Scripture as “accessory to a crime”—sacred texts used as cover for violence, exclusion, or cruelty
The Bible as platform—modular text shaped by study notes, editorial commentary, illustrations, and devotional framing
Study Bibles, children’s Bibles, niche-market editions; publishing strategies shaping the interpretive experience
Platform logic—similar to Facebook or Twitter; users curate meaning from a shared medium
Proof-texting and selective quotation; constructing entire moral worlds from isolated passages
Hannah Arendt on responsibility; loving the world enough to accept responsibility for it
James Baldwin leaving Paris after the Little Rock crisis; refusing comfort while others bear injustice
“Someone should have been there with her.” Baldwin’s recognition that solidarity requires leaving safety and standing beside the vulnerable
Catastrophic love—risking institutions, traditions, and comfort for the sake of vulnerable bodies
Matthew 25 ethics; encountering Christ among the hungry, imprisoned, and marginalized
Moral seriousness as daily practice; imperfect responsibility, persistent solidarity, doing what one can today and beginning again tomorrow
#Bible
#ChristianBible
#BiblicalInterpretation
#TheologyPodcast
#ChristianEthics
#Hermeneutics
#Scripture
#FaithAndCulture
#DavidDault
Production Notes
This podcast featured David Dault
Edited and Produced by Evan Rosa
Hosted by Evan Rosa
Production Assistance by Noah Senthil
A Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/about
Support For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Today we’re bringing you an episode with Esau McCaulley, from the Lenten season of 2023. Esau sees Lent as a practice of collective generational wisdom, passed down through centuries of sacramental rhythms—but as a contemporary reality, Lent is a spiritual rebellion against mainstream American culture.
He construes Lent as a season of repentance and grace; he points out the justice practices of Lent; he walks through a Christian understanding of death, and the beautiful practice of stripping the altars on Maundy Thursday; and he’s emphatic about how it’s a guided season of pursuing the grace to find (or perhaps return) to yourself as God has called you to be.
In his classic text, Great Lent, Orthodox priest and theologian Alexander Schmemann calls this season one of “bright sadness”—an important paradox that represents both Christian realism and hope.
Lent is not about gloom, self-loathing, performative penitence, or despair. Instead it brings us face to face with our human condition, reminding us that we did not bring ourselves into being and someday we will die, sober about the reality and banality of evil, and sorrowful in a way that leads back to joy.
Esau McCaulley is The Jonathan Blanchard Associate Professor of New Testament and Public Theology at Wheaton College, a contributing writer for the New York Times, and is author of many books, including children’s books. Notables are Reading While Black, a theology of Lent, and his latest: How Far to the Promised Land: One Black Family’s Story of Hope and Survival in the American South.
This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. For more information, visit tyndale.foundation.
About Esau McCaulley
Esau McCaulley is The Jonathan Blanchard Associate Professor of New Testament and Public Theology at Wheaton College, a contributing writer for the New York Times, and is author of many books, including children’s books. Notables are Reading While Black, a theology of Lent, and his latest: How Far to the Promised Land: One Black Family’s Story of Hope and Survival in the American South. Learn more at https://esaumccaulley.com/.
Show Notes
Lent: The Season of Repentance and Renewal — https://esaumccaulley.com/books/lent-book/
Commodifying our rebellion—the agency on offer is a thin, weakened agency.
Repentance, grace, and finding (or returning to) yourself
Examination of conscience
The Great Litany: “For our blindness to human need and suffering, and our indifference to injustice and cruelty. Except our repentance, Lord.”
The beauty of Christianity
“Liturgical spirituality is not safe. God can jump out and get you at any moment in the service.”
“The great thing about the, the, the season of Blend in the liturgical calendar more broadly is it gives you a thousand different entry points into transformation.”
Lent is bookended by death. Black death, Coronavirus death, War death.
Jesus defeated death as our great enemy.
“Everybody that I know and I care about are gonna die. Everybody.”
“I, as a Christian, believe that because we're going to die. our lives are of infinite value and the decisions that we make and the kinds of people we become are the only testimony that we have and that I have chosen to, to, in light of my impending death, put my faith in the one who overcame death.”
Two realities: We’re going to die and Jesus defeated death.
Stripping of the Altars on Maundy Thursday.
Silent processional in black; Good Friday celebrates no eucharist.
“I'm, like, the one Pauline scholar who doesn't like to argue about justification all of the time.”
Good Friday’s closing prayer: “Lord Jesus Christ, son of the living God, we pray you to set your passion cross and death between your judgment and our souls.”
“You end Lent with: Something has to come between God’s judgement and our souls. And that thing is Jesus.”
“Lent is God loving you enough to tell you the truth about yourself, but not condemning you for it, but actually saying that you can be better than that.”
Production Notes
This podcast featured Esau McCaulley
Edited and Produced by Evan Rosa
Hosted by Evan Rosa
Production Assistance by Macie Bridge, Luke Stringer, and Kaylen Yun.
A Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/about
Support For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Acknowledgements
This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of Blueprint 1543. For more information, visit http://blueprint1543.org/.
Work shapes identity, community, and meaning—but how should faith show up in professional life? Sociologist Elaine Ecklund discusses religion in the workplace, drawing on research conducted with co-author Denise Daniels.“I think our faith compels us to hope for and enact flourishing for everyone.”In this episode with Evan Rosa, Ecklund reflects on vocation, gender, authenticity, and principled pluralism in modern workplaces. Together they discuss workplace identity, gender discrimination, calling across occupations, boundaries around work, religion’s public role, and pluralism in professional life.Episode Highlights“I think our faith compels us to hope for and enact flourishing for everyone.”“People use their religion to bring justice to their workplaces.”“They don’t want to pretend they’re someone different.”“There are ways in which our faith traditions can put needed boundaries around our work.”“I am being fully who I am and I am oriented toward the other.”About Elaine EcklundElaine Howard Ecklund is a sociologist of religion and professor at Rice University, where she directs the Boniuk Institute for the Study and Advancement of Religious Tolerance. Her research focuses on religion in public life, science and faith, and workplace culture. She is the author or co-author of numerous books, including Religion in a Changing Workplace and Working for Better: A New Approach to Faith at Work (with Denise Daniels). Her work has been supported by the National Science Foundation and featured in major media outlets.Helpful Links And ResourcesWorking for Better: A New Approach to Faith at Work https://www.ivpress.com/working-for-betterReligion in a Changing Workplace https://academic.oup.com/book/58194Boniuk Institute for Religious Tolerance https://boniuk.rice.edu/Elaine Ecklund website https://elaineecklund.comShow NotesReligion and workplace lifeSociology of belief research backgroundStudying scientists and religionExpanding research beyond science workplacesCollaboration with Denise DanielsAcademic and practical faith-at-work booksDefining work as paid laborHonoring caregiving and volunteer labor“People don’t want to pretend they’re someone different.”Bringing whole selves to workCalling across occupational sectorsWorkplace autonomy and meaning“People use their religion to bring justice to their workplaces.”Faith creating boundaries around workGender dynamics in workplacesStory of hiding motherhood in academiaFragmentation and identity performance“There are ways in which our faith traditions can put needed boundaries around our work.”Church gender expectationsBilly Graham rule implicationsWork skills serving congregationsLiving in pluralistic societyPrincipled pluralism explained“I am being fully who I am and I am oriented toward the other.”Embrace, dignity, and learning from difference#FaithAndWork #ElaineEcklund #PrincipledPluralism #ReligionAndWorkplace #Vocation #GenderAndWork #HumanFlourishingProduction NotesThis podcast featured Elaine EcklundEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Noah SenthilA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Can faith sustain courage and openness in a polarized democracy? Former Ohio governor and presidential candidate John Kasich reflects on faith, fear, character, and public life amid deep political polarization and religious tension in America.“There is a certain comfort in knowing you have somebody who’s always in your corner.”In this conversation with Evan Rosa, Kasich reflects on personal faith shaped by tragedy, the search for purpose, and why character matters more than ideology in leadership. Together they discuss religious faith in American life, his experience running in the 2016 Republican presidential primaries, voting on character over beliefs, firm political commitments, open-minded perspective taking, his vision of a life worth living, and before the end of this conversation, you’ll find out his favorite Metallica song.Episode Highlights“There is a certain comfort in knowing you have somebody who’s always in your corner.”“You can be firm while at the same time looking at a point of view of somebody who’s diametrically opposed to you.”“I look for character. I don’t look for what somebody thinks about the Book of Revelation.”“Faith informs the way I think about things, but it doesn’t spell out what I’m going to do.”“If you begin to work together to solve a problem locally, it can actually create friendship.”About John KasichJohn Kasich is a former U.S. congressman, two-term governor of Ohio, and presidential candidate with more than four decades of experience in public service, media, and civic leadership. First elected to the Ohio State Senate at age 26, he later served 18 years in the U.S. House of Representatives before becoming governor in 2011. Kasich has authored six books exploring politics, faith, leadership, and civic responsibility, including his most recent, Heaven Help Us: How Faith Communities Inspire Hope, Strengthen Neighborhoods, and Build the Future. He is known for emphasizing character, dignity, and community-based solutions over ideological rigidity. Kasich frequently speaks on leadership, faith in public life, and democratic renewal, and continues to engage across political and cultural divides in pursuit of common purpose. Learn more and follow at https://johnkasich.com and https://twitter.com/JohnKasichShow NotesGrowing up Catholic, altar service, early religious formationTragedy in 1987, parents killed by drunk driver“Where do you stand vis-à-vis your eternal destiny?”Faith as ongoing window of questioning, not certaintyGod’s existence, care, and personal relationship“Faith itself is a gift. God has to act first.”Fear, loss, and the backstop of divine presence“You’ve got the most powerful being in all of history kind of got your back.”Faith shared as gift, not coercion or argumentVoting based on character, not doctrinal alignmentScripture informing decisions, not dictating policyRespect for the poor as moral baselineChristian nationalism and the question of objective truthPolitics and faith distinct, neither hostile nor coerciveSingles win games, local action over grand crusadesFaith communities as clubhouses for moral actionWorking locally dissolves partisan hostilityLife worth living as purpose, gifts, and contributionCharacter, integrity, and not taking advantage of othersFreedom from fear, boxes, and rigid identitiesKindness versus niceness as moral distinctionOpen-mindedness as antidote to boredom and fearCampaigning as test of endurance, character, and empathy“People wanted to know who you were more than your ideas.”Pursuing convictions while staying rooted in faith communitiesProduction NotesThis podcast featured John KasichEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Noah SenthilA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give#FaithAndPolitics#CharacterMatters#PublicFaith#CivicLife#CommonGood#JohnKasich
Mortality, fragility, forgiveness, and peace. Journalist and author Stan Grant offers a genre-bending work of prayer, memory, and theology shaped by fatherhood, Aboriginal inheritance, masculinity, and mortality.“I see this as a gift from God, a creator that allows us to find each other again.”In this conversation with Evan Rosa, Grant reflects on his 2025 book, Murriyang: Song of Time—his philosophical and spiritual exploration of the human place in the world and faith as lived experience rather than abstraction. He looks closely at his father’s life in order to come to terms with his own, the meaning of fatherhood and how to understand and forgive our fathers, masculinity and vulnerability, Aboriginal history and identity, masculinity and vulnerability, forgiveness and sacrifice, prayer and poetry, and the whole human experience of time and eternity.Episode Highlights“We inherit our father’s cups.”“We must forgive our fathers. It is the only way that we can forgive ourselves.”“We cannot survive without each other.”“Man is not made for history. History is made for man.”“ … to confront the beauty of that mortality—my father’s final gift to me is his death.”About Stan GrantStan Grant is an Australian journalist, author, and public intellectual of Wiradjuri, Kamilaroi, and Dharawal heritage. A former international correspondent and broadcaster, he has written widely on Indigenous identity, history, faith, and moral responsibility. Grant is the author of several acclaimed books, including Talking to My Country and Murriyang: Song of Time, which blends prayer, memoir, poetry, and theology. His work consistently resists abstraction in favor of embodied human experience, emphasizing forgiveness, attention, and the dignity of the human person. Grant has received national honors for journalism and cultural leadership and remains a leading voice in conversations about history, masculinity, faith, and what it means to live lives worthy of our shared humanity.Helpful Links and ResourcesMurriyang: Song of Time https://www.harpercollins.com.au/9781460763827/murriyang/Talking to My Country https://www.harpercollins.com.au/9781460752210/talking-to-my-country/Stan Grant official website https://www.stangrant.com.auShow NotesFathers and sons; inherited burden, sacrifice, and responsibility“We inherit our father’s cups”Christ in Gethsemane as archetype of father-son sufferingMasculinity as physical burden, scars, toughness“We must forgive our fathers. It is the only way that we can forgive ourselves and live in a world of forgiveness with the other.”Yindyamarra: respect, gentleness, quietness, forgivenessImprovisation and rehearsal; jazz as spiritual and artistic model“I have never written a second draft.”Second thought as artifice, hiding, dishonestyForgiveness of self before speaking; imperfection and risk“If silence is violence, then we have redefined the very nature of violence itself.”Giftedness of life; what is given and receivedGift exchange versus transaction in modern society“We offer the gift of ourselves to each other.”Murriyang as Psalter, prayer, song, contemplation of time and GodReading slowly; opening anywhere; shelter from modern noise“We cannot survive without each other.”One-person performance; no script, immediacy, intimacyMusic, poetry, time, mortality woven togetherFather’s body as history; sawmills, injuries, exhaustionChildhood memory of bath; “the water is stained black with blood”Mother’s touch; tenderness amid survivalLate-life renaissance; language recovery, teaching, honorsMurriyang (heaven) and Babiin (father) liturgical, prayerful, dialogical alternation throughout the textSt. Augustine: “What was God doing before he made time? He was making hell for the over-curious.”Is God in time? Or out of time?Speaking of eternity or timelessness still imputes the concept of time.“ The imaginative space of time itself, it reaches to an horizon. But what is beyond the horizon? For modernity, of course, time is the big story. To be modern is to reinvent time. It's to be new. Modernity and technology is all about taming time.”“Man is not made for history. History is made for man.”Attention, affliction, abstraction, and the loss of human touch“My father’s gift to me is his death.”Mortality as meaning; resisting transhumanismTime, modernity, instant life, collapsing spaceFragility, love, forgiveness, and beginning againEnding where we began#StanGrant#Murriyang#Fatherhood#Masculinity#Forgiveness#TimeAndFaith#HumanFlourishing#AustraliaProduction NotesThis podcast featured Stan GrantEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Noah SenthilA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Slavery did not end in the nineteenth century—it persists today, hidden in global supply chains, religious justifications, and systems of power. Kevin Bales and Michael Rota join Evan Rosa to explore modern slavery through history, psychology, and theology, asking why it remains so difficult to see and confront.“It’s time some person should see these calamities to their end.” (Thomas Clarkson, 1785)“There are millions of slaves in the world today.” (Kevin Bales, 2025)In this episode, they consider how conscience, power, and religious belief can either sustain enslavement or become forces for abolition. Together they discuss the psychology of slaveholding, faith’s complicity and resistance, Quaker abolitionism, modern debt bondage, ISIS and Yazidi slavery, and what meaningful action looks like today.https://freetheslaves.net/––––––––––––––––––Episode Highlights“There are millions of slaves in the world today.”“Statistics isn’t gonna do it. I need to actually show people things.”“They have sexual control. They can do what they like.”“Slavery is flowing into our lives hidden in the things we buy.”“We have to widen our sphere of concern.”––––––––––––––––––About Kevin BalesKevin Bales is a leading scholar and activist in the global fight against modern slavery. He is Professor of Contemporary Slavery at the University of Nottingham and co-founder of Free the Slaves, an international NGO dedicated to ending slavery worldwide. Bales has spent more than three decades researching forced labor, debt bondage, and human trafficking, combining academic rigor with on-the-ground investigation. His work has shaped international policy, influenced anti-slavery legislation, and brought global attention to forms of enslavement often dismissed as historical. He is the author of several influential books, including Disposable People and Friends of God, Slaves of Men, which examines the complex relationship between religion and slavery across history and into the present. Learn more and follow at https://www.kevinbales.org and https://www.freetheslaves.netAbout Michael RotaMichael Rota is Professor of Philosophy at the University of St. Thomas in Minnesota, where he teaches and researches in the philosophy of religion, moral psychology, and the history of slavery and religion. His work spans scholarly articles on the definition of slavery, the moral psychology underlying social change and abolition, and the relevance of theological concepts to ethical life. Rota is co-author with Kevin Bales of Friends of God, Slaves of Men: Religion and Slavery, Past and Present, a comprehensive interdisciplinary study of how religions have both justified and resisted systems of enslaving human beings from antiquity to the present day. He is also the author of Taking Pascal’s Wager: Faith, Evidence, and the Abundant Life, an extended argument for the reasonableness and desirability of Christian commitment. In addition to his academic writing, he co-leads projects in philosophy and education and is co-founder of Personify, a platform exploring AI and student learning. Learn more and follow at his faculty profile and personal website https://mikerota.wordpress.com and on X/Twitter @mikerota.––––––––––––––––––Helpful Links And ResourcesDisposable People by Kevin Baleshttps://www.ucpress.edu/book/9780520281820/disposable-peopleFriends of God, Slaves of Men by Kevin Bales and Michael Rotahttps://www.ucpress.edu/book/9780520383265/friends-of-god-slaves-of-menFree the Slaveshttps://www.freetheslaves.netVoices for Freedomhttps://voicesforfreedom.orgInternational Justice Missionhttps://www.ijm.orgTalitha Kumhttps://www.talithakum.info––––––––––––––––––Show Notes– Slavery named as a contemporary moral crisis obscured by twentieth-century abolition narratives– Kevin Bales’s encounter with anti-slavery leaflet in London, mid-1990s– “There are millions of slaves in the world today … I thought, look, that can’t be true because I don’t know that. I’m a professor. I should know that.”– Stories disrupting moral distance more powerfully than statistics– “There were three little stories inside, about three different types of enslavement … it put a hook in me like a fish and pulled me.”– United Nations documentation mostly ignored despite vast evidence– Decades of investigation into contemporary slavery– Fieldwork across five regions, five forms of enslavement– Kevin Bales’s book, Disposable People as embodied witness with concrete stories– “Statistics isn’t gonna do it. I need to actually show people things. There’s gonna be something that breaks hearts the way it did me when I was in the field.”– Psychological resistance to believing slavery touches ordinary life– Anti-Slavery International as original human rights organization founded in U.K. in 1839– Quaker and Anglican foundations of abolitionist movements– Religion as both justification for slavery and engine of resistance– Call for renewed faith-based abolition today– Slavery and religion intertwined from early human cultures– Colonial expansion intensifying moral ambiguity– Columbus, Genoa, and enslavement following failed gold extraction– Spanish royal hesitation over legitimacy of slavery– Las Casas’s moral conversion after refusal of absolution– “He eventually realized this is totally wrong. What we are doing, we are destroying these people. And this is not what God wants us to be doing.”– Sepúlveda’s Aristotelian defense of hierarchy and profit– Moral debate without effective structural enforcement– Power described as intoxicating and deforming conscience– Hereditary debt bondage in Indian villages– Caste, ethnicity, and generational domination– Sexual violence as mechanism of absolute control– “They have sexual control. They can beat up the men, rape the women, steal the children. They can do pretty much what they like.”– Three-year liberation process rooted in trust, education, and collective refusal– Former slaves returning as teachers and organizers– Liberation compared to Plato’s allegory of the cave– Post-liberation vulnerability and risk of recapture– Power inverted in Christian teaching– “The disciples are arguing about who’s the greatest, and Jesus says, the greatest among you will be the slave of all… don’t use power to help yourself. Use it to serve.”– Psychological explanations for delayed abolition– The psychological phenomenon of “motivated reasoning” that shapes moral conclusions– “The conclusions we reach aren’t just shaped by the objective evidence the world provides. They’re shaped also by the internal desires and goals and motivations people have.”– Economic self-interest and social consensus sustaining injustice– Quaker abolition through relational, conscience-driven confrontation– First major religious body to forbid slaveholding– Boycotts of slave-produced goods and naval blockade of slave trade– Modern slavery as organized criminal enterprise– ISIS enslavement of Yazidi women– Religious reasoning weaponized for genocide– “They said, for religious reasons, we just need to eradicate this entire outfit.”– Online slave auctions and cultural eradication– Internal Islamic arguments for abolition– Restricting the permissible for the common good– Informing conscience as first step toward action– Community sustaining long-term resistance– Catholic religious sisters as leading global abolitionists– Hidden slavery embedded in everyday consumer goods– “There’s so much slavery flowing into our lives which is hidden… in our homes, our watches, our computers, the minerals, all this.”– Expanding moral imagination beyond immediate needs– “Your sphere of concern has to be wider… how do I start caring about something that I don’t see?”– “It’s time some person should see these calamities to their end.” (Thomas Clarkson, 1785)––––––––––––––––––#ModernSlavery#FaithAndJustice#HumanDignity#Abolition#FreeTheSlavesProduction NotesThis podcast featured Kevin Bales and Michael RotaEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Noah SenthilA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Poet and essayist Carol Ann Davis (Fairfield University) joins Evan Rosa for a searching conversation on violence, childhood, and the moral discipline of attention in the aftermath of Sandy Hook. Reflecting on trauma, parenting, childhood, poetry, and faith, Davis resists tidy narratives and invites listeners to dwell with grief, healing, beauty, and pain without resolution.“I don’t believe life feels like beginnings, middles, and ends.”In this episode, Davis reflects on how lived trauma narrows attention, reshapes language, and unsettles conventional storytelling. Together they discuss poetry as dwelling rather than explanation, childhood and formation amid violence, image versus narrative, moral imagination, and the challenge of staying present to suffering.Episode Highlights“Nothing has happened at Hawley School. Please hear me. I have opened every door and seen your children.”“And that was what it is not to suffer. This is the not-suffering, happy-ending story.”“I’m always narrowing focus.”“I think stories lie to us sometimes.”“I think of the shooting as a nail driven into the tree.”“I’m capable of anything. I’m afraid I’m capable of anything.”“I tried to love and out of me came poison.”About Carol Ann DavisCarol Ann Davis is a poet, essayist, and professor of English at Fairfield University. She is the author of the poetry collections Psalm and Atlas Hour, and the essay collection The Nail in the Tree: Essays on Art, Violence, and Childhood. A former longtime editor of the literary journal Crazyhorse, she directs Fairfield University’s Low-Residency MFA and founded Poetry in Communities, an initiative bringing poetry to communities affected by violence. An NEA Fellow in Poetry, Davis’s work has appeared in The Atlantic, The American Poetry Review, Image, Agni, The Georgia Review, and elsewhere. Learn more and follow at https://www.carolanndavis.orgHelpful Links and ResourcesThe Nail in the Tree: Essays on Art, Violence, and Childhood https://www.tupelopress.org/bookstore/p/the-nail-in-the-tree-essays-on-art-violence-and-childhoodSongbird https://www.weslpress.org/9780819502223/songbird/Psalm https://www.tupelopress.org/bookstore/p/psalmAtlas Hour https://www.amazon.com/Atlas-Hour-Carol-Ann-Davis/dp/1936797003Carol Ann Davis official website https://www.carolanndavis.orgShow NotesCarol Ann Davis recounts moving to Newtown, Connecticut just months before Sandy Hook, teaching a course at Fairfield University when news of the shooting first breaksHer young children attended a local elementary schoolConfusion, delay, and the unbearable seconds of not knowing which school was attackedA colleague’s embrace as the reality of the shooting becomes clearParenting under threat and the visceral fear of losing one’s children“Nothing has happened at Hawley School. Please hear me. I have opened every door and seen your children.” (Hawley School’s Principal sends this message to parents, including Carol Ann)Living inside the tension where nothing happened and everything changedWriters allowing mystery, unknowing, and time to remain unresolvedNaming “directly affected families” and later “families of loss”Ethical care for proximity without flattening grief into universalityThe moral value of being useful within an affected communityNarrowing attention as survival, parenting, and poetic disciplineChoosing writing, presence, and community over national policy debatesChildhood formation under the long shadow of gun violence“I think of the shooting as a nail driven into the tree. And I’m the tree.” (Carol Ann quotes her older son, then in 4th grade)Growth as accommodation rather than healing or resolutionIntegration without erasure as a model for living with traumaRefusing happy-ending narratives after mass violence“I don’t believe life feels like beginnings, middles, and ends.”Poetry as dwelling inside experience rather than extracting meaningResisting stories that turn suffering into takeawaysCrucifixion imagery, nails, trees, and the violence of embodiment“I’m capable of anything. I’m afraid I’m capable of anything.”Violence as elemental, human, animal, and morally unsettlingDistinguishing intellectual mastery from dwelling in lived experienceA poem’s turn toward fear: loving children and fearing harm“I tried to love and out of me came poison.”Childhood memory, danger, sweetness, and oceanic smallnessBeing comforted by smallness inside something vast and terrifyingEnding without closure, choosing remembrance over resolution#CarolAnnDavis#PoetryAndViolence#TraumaAndAttention#SandyHook#SandyHookPromise#FaithAndWriting#Poetry#ChildhoodAndMemoryProduction NotesThis podcast featured Carol Ann DavisEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Macie Bridge, Alexa Rollow, Zoë Halaban, Kacie Barrett & Emily BrookfieldA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
“Our longings are much more powerful than our logic, and our desires are stronger than our reason.” (Graham Tomlin on the thought of Blaise Pascal)The Rt. Rev. Dr. Graham Tomlin (St. Mellitus College, the Centre for Cultural Witness) joins Evan Rosa for a sweeping exploration of Blaise Pascal—the 17th-century mathematician, scientist, philosopher, and theologian whose insights into human nature remain strikingly relevant. Tomlin traces Pascal’s life of brilliance and illness, his tension between scientific acclaim and radical devotion, and his deep engagement with Descartes, Montaigne, and Augustine. The conversation moves through Pascal’s analysis of self-deception, his critique of rationalism and skepticism, the transformative Night of Fire, his compassion for the poor, and the wager’s misunderstood meaning. Tomlin presents Pascal as a thinker who speaks directly to our distracted age, revealing a humanity marked by greatness, misery, and a desperate longing only grace can satisfy.This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. Visit tyndale.foundation to learn more.Episode Highlights“Our longings are much more powerful than our logic, and our desires are stronger than our reason.”“The greatness and the refuse of the universe—that’s what we are. We’re the greatest thing and also the worst thing.”“If everybody knew what everybody else said about them, there would not be four friends left in the world.”“Only grace can begin to turn that self-oriented nature around and implant in us a desire for God.”“The reason you cannot believe is not because of your reason; it’s because of your passions.”Show NotesGraham Tomlin introduces the Night of Fire and Pascal’s meditation on “the greatness of the human soul”Evan Rosa frames Pascal as a figure of mystery, mechanics, faith, and modern technological influence.Tomlin contrasts Pascal with Descartes and Montaigne—rationalism vs. skepticism—locating Pascal between their poles.Pascal’s awareness of distraction, competition, and “all men naturally hate each other” surfaces early as a key anthropological insight.Evan notes Nietzsche’s striking admiration: “his blood runs through my veins.”Tomlin elaborates on Pascal’s lifelong tension between scientific achievement and spiritual devotion.The story of the servant discovering the hidden Night of Fire parchment in Pascal’s coat lining is recounted.Tomlin reads the core text: “Joy, joy, joy, tears of joy… Let me never be separated from him.”Pascal’s distinction: “God of Abraham, God of Isaac, God of Jacob, not of the philosophers.”Discussion of Jansenism, Augustinian anthropology, and the gravity of human fallenness.Tomlin sets the philosophical context: Pascal as a counter to both rationalist optimism and skeptical relativism.Pascal’s core tension—grandeur and misery—is presented as the interpretive key to human nature.Quote emerges: “the greatness and the refuse of the universe—that’s what we are.”Tomlin describes Pascal’s political skepticism and the idea that politics offers only “rules for a madhouse.”Pascal’s diagnosis of self-deception: “If everybody knew what everybody else said about them, there would not be four friends left in the world.”Evan raises questions about social hope; Tomlin answers with Pascal’s belief that only grace can break self-love.They explore Pascal’s critique of distraction and the famous line: “the sole cause of man’s unhappiness is that he does not know how to stay quietly in his room.”Tomlin ties this to contemporary digital distraction—“weapons of mass distraction”.The conversation turns to the wager, reframed not as coercion but exposure: unbelief is driven by passions more than reasons.Closing reflections highlight the apologetic project of the Pensées, Pascal’s brilliance, and his ongoing relevance.Helpful Links and ReferencesSpecial thanks to the Center for Christian Witness and Seen and Unseen https://www.seenandunseen.com/Blaise Pascal: The Man Who Made the Modern World, by Graham Tomlin https://www.hachette.co.uk/titles/graham-tomlin/blaise-pascal/9781399807661/Pensées, by Blaise Pascal https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/18269Provincial Letters, by Blaise Pascal https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/2407Why Being Yourself Is a Bad Idea, by Graham Tomlinhttps://www.amazon.com/Why-Being-Yourself-Bad-Idea/dp/0281087097Montaigne’s Essays https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/3600Descartes’ Meditations on First Philosophy https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/23306Augustine’s Confessions https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/3296About Graham TomlinGraham Tomlin is a British theologian, writer, and church leader. He is the former Bishop of Kensington (2015-2022) in the Church of England and now serves as Director of the Centre for Cultural Witness and President of St Mellitus College in London. He is widely known for connecting theology with cultural life and public imagination. Tomlin is the author of several books, including Looking Through the Cross, The Widening Circle, and Why Being Yourself Is a Bad Idea: And Other Countercultural Notions. His latest book is an intellectual and spiritual biography, Blaise Pascal: The Man Who Made the Modern World.Production NotesThis episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House FoundationThis podcast featured Graham TomlinProduction Assistance by Emily Brookfield and Alexa RollowEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaA production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Loneliness seems to be part of what it means to be a relational being. Does that mean loneliness can never really be “solved”? Here’s one way to think about loneliness: As a gap between relational expectation and social reality—something that signals our essentially relational, reciprocal nature as human beings.This episode is part 6 of a series, SOLO, which explores the theological, moral, and psychological dimensions of loneliness, solitude, and being alone.In this reflective conclusion to the series, Macie Bridge and Ryan McAnnally-Linz explore loneliness not as a pathology to solve but as a universal, creaturely experience that reveals our longing for relationship. Drawing on insights from conversations throughout the series, they consider how loneliness emerges in the gap between what we desire relationally and what we actually have, and why this gap might be intrinsic to being human. They discuss solitude as a vital space for discernment, self-understanding, and listening for God; how risk is inherent to relationships; why the church holds unique potential for embodied community; and how even small interactions with neighbors and strangers can meet real needs. Together they reflect on grief, social isolation, resentment, vulnerability, and the invitation to turn loneliness into attentiveness—to God, to ourselves, and to our neighbors, human and non-human alike.Episode Highlights“Loneliness is just baked into our creaturely lives.”“There really is no solution to loneliness—and also that’s okay.”“We invite a certain level of risk because we invite another person closer to our own human limits.”“There’s no blanket solution. We are all experiencing this thing, but we are all experiencing it differently.”“I realized I could be a gift to her, and she could be a gift to me, even in that small moment.”About Macie BridgeMacie Bridge is Operations Coordinator for the Yale Center for Faith & Culture. Macie is originally from the small town of Groton, Massachusetts, where she was raised in the United Church of Christ. As an undergraduate at Trinity College in Hartford, CT, Macie studied English literature, creative writing, and religious studies. She spent a year in Chapel Hill, North Carolina with the Episcopal Service Corps after receiving her B.A. There, she served as Events & Communications Coordinator for L’Arche North Carolina—an emerging L’Arche community, and therefore an incredible “crash course” into the nonprofit world.About Ryan McAnnally-LinzRyan McAnnally-Linz is Associate Director of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture and a theologian focusing on flourishing, meaning, and the moral life. He is co-author of Public Faith in Action and The Home of God with Miroslav Volf, and Life Worth Living: A Guide to What Matters Most with Miroslav Volf and Matt Croasmun.Show NotesLoneliness as Creaturely ConditionLoneliness as “baked into our creaturely lives,” not a sign of brokenness or failureThe “gap between what we want and what we have” in relationshipsLoneliness as a universal human experience across ages and contextsSolitude and DiscernmentSolitude as a place to listen more clearly to God and oneselfTime alone clarifies intuition, vocation, and identity.Solitude shapes self-knowledge outside societal expectations.Community, Church, and EmbodimentChurches can be embodied spaces of connection yet still feel lonely.Hospitality requires more than “hi”; it requires digging deeper into personal encounter.Embodied church life resists technological comforts that reduce vulnerability.Grief, Risk, and VulnerabilityDistinguishing grief-loneliness from social-isolation lonelinessRelationships inherently involve risk, limits, and potential hurt.Opening oneself to others requires relinquishing entitlement.Everyday Encounters and Ecological AttentionSmall moments with neighbors (like taking a stranger’s photo) can be meaningful.Loneliness can signal attention toward creaturely neighbors—birds, bugs, landscapes.Turning loneliness outward can widen our capacity for care.Production NotesThis podcast featured Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow, Emily Brookfield, and Hope ChunA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Living alone may be difficult, but what about dying alone? Physicians and nurses are the new priests accompanying people as they face death. But the experience of nursing homes, assisted living, and palliative wards are often some of the loneliest spaces in human culture.“He said, ‘Someone finally saw me. I’ve been in this hospital for 20 years and I didn’t think anyone ever saw me.’”This episode is part 5 of a series, SOLO, which explores the theological, moral, and psychological dimensions of loneliness, solitude, and being alone.In this episode, Columbia physician and medical ethicist Lydia Dugdale joins Macie Bridge to reflect on loneliness, solitude, and what it means to die—and live—well. Drawing from her clinical work in New York City and the years of research and experience that went into her book The Lost Art of Dying, Dugdale exposes a crisis of unrepresented patients dying alone, the loss of communal care, and medicine’s discomfort with mortality.She recalls the medieval Ars Moriendi tradition, where dying was intentionally communal, and explores how virtue and community sustain a good death. Together they discuss solitude as restorative rather than fearful, loneliness as a modern epidemic, and the sacred responsibility of seeing one another deeply. With stories from her patients and her own reflections on family, COVID isolation, and faith, Dugdale illuminates how medicine, mortality, and moral imagination converge on one truth: to die well, we must learn to live well … together.Helpful Links and ResourcesThe Lost Art of Dying: Reviving Forgotten Wisdom by Lydia S. DugdalePew Research Center Study on Loneliness (2025)Harvard Study of Adult Development on LonelinessEpisode Highlights“If you want to die well, you have to live well.”“Community doesn’t appear out of nowhere at the bedside.”“He said, ‘Someone finally saw me. I’ve been in this hospital for 20 years and I didn’t think anyone ever saw me.’”“We are social creatures. Human beings are meant to be in relationship.”“Solitude, just like rest or Sabbath, is something all of us need.”About Lydia DugdaleLydia S. Dugdale, MD, MAR is a physician and medical ethicist at Columbia University, where she serves as Professor of Medicine and Director of the Center for Clinical Medical Ethics. She is the author of The Lost Art of Dying: Reviving Forgotten Wisdom and a leading voice on virtue ethics, mortality, and human flourishing in medicine.Show NotesLoneliness, Solitude, and the CityNew York’s “unrepresented” patients—those who have no one to make decisions for them.The phenomenon of people “surrounded but unseen” in urban life.“I have a loving family … but I never see them.”Medicine and the PandemicLoneliness intensified during COVID-19: patients dying alone under strict hospital restrictions.Dugdale’s reflections on balancing social responsibility with human connection.“We are social creatures. Human beings are meant to be in relationship.”Technology, Fear, and the Online Shadow CommunityPost-pandemic isolation worsened by online echo chambers.One in five adults reports loneliness—back to pre-pandemic levels.The Lost Art of DyingMedieval Ars Moriendi: learning to die well by living well.Virtue and community as the foundation for a good death.“If you don’t want to die an impatient, bitter, despairing old fool, then you need to practice hope and patience and joy.”Modern Medicine’s Fear of DeathPhysicians unpracticed—and afraid—to talk about mortality.“Doctors themselves are afraid to talk about death.”How palliative care both helps and distances doctors from mortality.Community and MortalityThe man who reconnected with his estranged children after reading The Lost Art of Dying.“He said, ‘I want my kids there when I die.’”Living well so that dying isn’t lonely.Programs of Connection and the Body of ChristVolunteer models, day programs, and mutual care as small restorations of community.“The more we commit to others, the more others commit back to us.”Solitude and the Human SpiritDistinguishing solitude, loneliness, and social isolation.Solitude as restorative and necessary: “All of us need solitude. It’s a kind of rest.”The contemplative life as vital for engagement with the world.Death, Autonomy, and CommunityThe limits of “my death, my choice.”The communal role in death: “We should have folks at our deathbeds.”Medieval parish customs of accompanying the dying.Seeing and Being SeenA patient long thought impossible to care for says, “Someone finally saw me.”Seeing others deeply as moral and spiritual work.“How can we see each other and connect in a meaningful way?”Production NotesThis podcast featured Lydia DugdaleInterview by Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow, Emily Brookfield, and Hope ChunA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
What is the role of solitude in Christian history? Medievalist Hetta Howes comments on the allure of enclosure, how seeking solitude supports community, and what these ancient lives reveal about our modern search for connection.“Even those moments of solitude that she’s carving for herself are surprisingly sociable.”This episode is part 1 of a 5-part series, SOLO, which explores the theological, moral, and psychological dimensions of loneliness, solitude, and being alone.Medieval Anchoresses and Women Mystics sought a life of solitude with and for God—what about their vocation might illuminate our perspectives on loneliness, isolation, and solitude today?In this episode, Hetta Howes joins Macie Bridge to explore the extraordinary lives of medieval women mystics, including Julian of Norwich and Marjorie Kempee. Drawing from her book Poet Mystic Widow Wife: The Extraordinary Lives of Medieval Women, Howes illuminates how these women lived in literal and spiritual solitude—sometimes sealed in stone anchorages, sometimes carving sacred space in the midst of family and community. Together they consider the physical and spiritual demands of enclosure, the sociable windows of anchorages, and the simultaneous human longing for both solitude and companionship. Across the centuries, these women invite us to think anew about loneliness, vocation, and the need for community—even in devotion to God.Helpful Links and ResourcesPoet Mystic Widow Wife: The Extraordinary Lives of Medieval Women – Hetta HowesJulian of Norwich, Revelations of Divine Love (Penguin Classics)The Book of Margery Kempe (Oxford World’s Classics)Episode Highlights“An anchorage is a small cell, usually joined to a church… and the idea was that you would never leave that place alive again.”“Sometimes you do come across these things and you’re like, oh, maybe the cultural consciousness was so different that they had a different language for loneliness.”“Marjorie frames herself as a figure who is constantly looking for connection—sometimes finding it, but often being rejected in really painful ways.”“Even those moments of solitude that she’s carving for herself are surprisingly sociable.”“What I’ve learned from them is the importance of community—that even solitary professions absolutely rely on other people.”About Hetta HowesHetta Howes is a Lecturer in Medieval and Early Modern Literature at City St. George’s, University of London. She specializes in the literature of the Middle Ages, with particular focus on medieval women writers, mysticism, and representations of gender and devotion. Her most recent book is Poet Mystic Widow Wife: The Extraordinary Lives of Medieval Women (2024).Show NotesSolitude and SanctityHowes introduces her research on medieval women mystics and writers (Julian of Norwich, Margery Kempe, Christine de Pizan, Marie de France).Exploration of the anchoritic life—cells built into church walls where women lived sealed from the world.The paradox of solitude: enclosure for God that still required connection for survival.The Anchorite’s WorldAnchorages included small windows—to the church, the street, and for food—balancing isolation with limited engagement.Guidebooks warned women against gossip and temptation, revealing anxiety about sociability and holiness.“Why have a window to the world if you’re not ever going to converse with it?”Loneliness and BoredomLoneliness rarely appears in medieval texts; boredom and idleness were greater concerns.“Boredom comes up as a concept much more often than loneliness.”Modern readers project our loneliness onto them; their silence might reveal difference, not absence.Julian and MarjorieJulian’s quiet solitude contrasts with Marjorie’s noisy, emotional piety.Marjorie Kempe’s “roarings” and unconventional piety challenged norms; she lived in the world but sought holiness.“I wish you were enclosed in a house of stone”—a critique of her refusal to conform.Solitude and CommunityEven in seclusion, anchorites served others—praying, advising, maintaining windows to the world.Julian’s writings reveal care for all Christians; her solitude was intercessory, not selfish.Howes connects medieval community to our modern digital and emotional isolation.Modern ReflectionsHowes parallels her own experience of digital overload and motherhood with the medieval longing for quiet focus.“As amazing as the digital can be, it’s eroding so much.”She cautions against idolizing solitude but affirms its value for clarity and grounding.Production NotesThis podcast featured Hetta HowesInterview by Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow, Emily Brookfield, and Hope ChunA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Is technology the source or salve of social isolation? Given the realities of increasing division, the epidemic of loneliness, and unwanted isolation today, how should we think about the theological, ethical, and spiritual dimensions of the human experience of aloneness?“AI technologies aren’t capable of creating conditions in which grace can happen—it’s endemic to personhood.”This episode is part 3 of a 5-part series, SOLO, which explores the theological, moral, and psychological dimensions of loneliness, solitude, and being alone.In this episode, sociologist Felicia Wu Song joins Macie Bridge to discuss the sociology of solitude, loneliness, and isolation, framed by today’s most pressing technological challenges.Drawing from her work on digital culture and AI, Song distinguishes between isolation, loneliness, and generative solitude—what she calls “positive aloneness.” She explores how technology both connects and disconnects us, what’s lost when care becomes automated, and why the human face-to-face encounter remains vital for grace and dignity. Together they consider the allure of AI companionship, the “better-than-nothing” argument, and the church’s local, embodied role in a digitized age. Song invites listeners to rediscover curiosity, self-reflection, and the spiritual discipline of solitude as essential practices for recovering our humanity amid the noise of the crowd.Helpful Links and ResourcesFelicia Wu Song, Restless Devices: Recovering Personhood, Presence, and Place in the Digital Age — https://www.ivpress.com/restless-devicesAllison Pugh, The Last Human Job: The Work of Connecting in a Disconnected World — https://press.princeton.edu/books/hardcover/9780691240817/the-last-human-jobDavid Whyte, “Solace: The Art of Asking the Beautiful Question” — https://www.amazon.com/Solace-Art-Asking-Beautiful-Question/dp/1932887377Sherry Turkle, Alone Together: Why We Expect More from Technology and Less from Each Other — https://www.sherryturkle.com/alone-togetherEpisode Highlights“Even though I study technology, I’m really interested in what it means to be human.”“What happens when we have technologies that always bring the crowd? The crowd is always with us all the time.”“Loneliness is the gap between what I think I should have and what I actually have.”“AI technologies aren’t capable of creating conditions in which grace can happen—it’s endemic to personhood.”“We should cut ourselves a lot of slack. Feeling lonely is very human. It doesn’t mean something’s wrong with me.”About Felicia Wu SongFelicia Wu Song is a sociologist, writer, and speaker, and was Professor of Sociology at Westmont College for many years. She is author of Restless Devices: Recovering Personhood, Presence, and Place in the Digital Age. Her research examines digital technology, culture, and Christian formation, exploring how contemporary media ecosystems shape our social and spiritual lives. Learn more about her work at https://feliciawusong.com/Show NotesTechnology, Humanity, and SolitudeSong describes her sociological work at the intersection of culture, technology, and spirituality.She reflects on how technology reshapes our sense of identity, community, and human meaning.“Even though I study technology, I’m really interested in what it means to be human.”The question of loneliness emerges from the expectation of constant accessibility and permanent connection.The Crowd Is Always With Us“What happens when we have technologies that always bring the crowd?”Song critiques how digital connectivity erases silence and solitude, making stillness feel uncomfortable.Explores the challenge of practicing ancient spiritual disciplines like silence in the digital age.Connection and DisconnectionSong traces the historical celebration of communication technology’s power to transcend time and space.Notes the danger of normalizing constant connectivity: “If you can do it, you should do it.”Examines how connection can become a cultural norm that stigmatizes solitude.Defining Loneliness, Isolation, and Solitude“Social isolation is objective; loneliness is subjective; solitude is generative.”Distinguishes “positive aloneness” as a space for self-conversation and divine encounter.References David Whyte and the Desert Fathers and Mothers as guides to solitude.Youth, Boredom, and the Portal of LonelinessDiscusses the value of “episodic loneliness” as a portal to self-discovery and spiritual growth.Connects solitude to creativity and reflection through the “boredom literature.”AI, Care, and the Better-Than-Nothing ArgumentExamines the emergence of AI chatbots and companionship tools.Engages Allison Pugh’s critique of “the better-than-nothing argument.”“It sounds altruistic, but it actually leads to deeper and deeper inequality.”Raises justice and resource questions around replacing human teachers and therapists with chatbots.The Limits of Machine Grace“AI technologies aren’t capable of creating conditions in which grace can happen—it’s endemic to personhood.”Explores embodiment, dignity, and the irreplaceable value of human presence.Critiques the assumption that “being seen” by a machine equates to being known by a person.AI, Divinity, and ProjectionNotes human tendency to attribute divine or human qualities to machines.References Sherry Turkle’s early studies on human-computer relationships.“We are so relational that we’ll even take a clunky computer program and give it human-like qualities.”Faith, Solitude, and Social ConditionsSong emphasizes the sociological dimension: environments shape human flourishing.“Let’s not make it so hard for people to experience solitude.”Advocates for embodied, place-based communities as antidotes to digital disembodiment.Loneliness, Curiosity, and GraceEncourages gentleness toward oneself in moments of loneliness.“Feeling lonely is very human. It doesn’t mean something’s wrong with me.”Promotes curiosity and acceptance as pathways to spiritual and personal growth.Production NotesThis podcast featured Felicia Wu SongEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Hope Chun, Alexa Rollow and Emily BrookfieldA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Consider human ecological loneliness and our longing for reconnection with all creation. What healing is available in an era defined by environmental loss and exploitation? Can we strengthen the fragile connection between modern society and the space we inhabit?“Loneliness is the symptom that desires its cure.”In this episode Macie Bridge welcomes writer, translator, and poet Laura Marris to reflect on her essay collection The Age of Loneliness, a meditation on solitude, grief, and the ecology of attention. Marris considers what it means to live through an era defined by environmental loss and human disconnection, yet still filled with wonder. She shares stories of tardigrades that endure extreme conditions, how airports reveal our attitudes toward birds, and the personal loss of her father that awakened her to “noticing absence.” Together, they explore how ecological loneliness might transform into longing for reconnection—not only among humans, but with the creatures and landscapes that share our world. Marris suggests that paying attention, naming, and noticing are acts of restoration. “Loneliness,” she writes, “is the symptom that desires its cure.”Episode Highlights“Loneliness is the symptom that desires its cure.”“There are ways, even very simple ones, that individuals can do to make the landscape around them more hospitable.”“I don’t believe that humans are hardwired to exploit. There have been many societies with long traditions of mutual benefit and coexistence.”“It’s really hard to notice an absence sometimes. There’s something curative about noticing absences that have been around but not acknowledged.”“Ecological concerns are not a luxury. It’s actually really important to hold the line on them.”Helpful Links and ResourcesThe Age of Loneliness by Laura Marris — https://www.graywolfpress.org/books/age-lonelinessUnderland by Robert Macfarlane — https://wwnorton.com/books/9780393242140E.O. Wilson on “Beware the Age of Loneliness” — https://www.economist.com/news/2013/11/18/beware-the-age-of-lonelinessAbout Laura MarrisLaura Marris is a writer and translator whose work spans poetry, essays, and literary translation. She is the author of The Age of Loneliness and has translated Albert Camus’s The Plague for Vintage Classics. She teaches creative writing and translation at the University at Buffalo.Show NotesThe Ecology of Loneliness and LongingLaura Marris discusses The Age of Loneliness—“Eremocene”—a term coined by E.O. Wilson to describe a speculative future of environmental isolation.Fascination with poetic form and environmental prose emerging during the pandemic.Ecological loneliness arises from biodiversity loss, but also offers the chance to reimagine more hospitable human landscapes.Extreme Tolerance and the Human ConditionMarris describes tardigrades as metaphors for endurance without thriving—organisms that survive extremes by pausing metabolism.“How extremely tolerant are humans, and what are our ways of trying to be more tolerant to extreme conditions?”Air conditioning becomes an emblem of “extreme tolerance,” mirroring human adaptation to a destabilized environment.Birds, Airports, and the Language of BlameMarris explores how modern air travel enforces ecological loneliness by eradicating other species from its space.She reveals hidden networks of wildlife managers and the Smithsonian’s Feather Identification Lab.Reflects on the “Miracle on the Hudson,” where language wrongly cast geese as antagonists—“as if the birds wanted to hit the plane.”Loneliness, Solitude, and Longing“Loneliness is solitude attached to longing that feels painful.”Marris distinguishes solitude’s generativity from loneliness’s ache, suggesting longing can be a moral compass toward reconnection.Personal stories of her father’s bird lists intertwine grief and ecological noticing.Ground Truthing and Community ScienceMarris introduces “ground truthing”—people verifying ecological data firsthand.She celebrates local volunteers counting birds, horseshoe crabs, and plants as acts of hope.“Community care applies to human and more-than-human communities alike.”Toxic Landscapes and Ecological AftermathMarris recounts Buffalo’s industrial scars and ongoing restoration along the Niagara River.“Toxins don’t stop at the edge of the landfill—they keep going.”She reflects on beauty, resilience, and the return of eagles to post-industrial lands.Attention and Wonder as Advocacy“A lot of advocacy stems from paying local attention.”Small, attentive acts—like watching sparrows dust bathe—are forms of resistance against despair.Cure, Absence, and Continuing the ConversationMarris resists the idea of a final “cure” for loneliness.“Cure could be something ongoing, a process, a change in your life.”Her annual bird counts become a continuing dialogue with her late father.Wisdom for the Lonely“Take the time to notice what it is you’re lonely for.”She calls for transforming loneliness into longing for a more hospitable, interdependent world.Production NotesThis podcast featured Laura MarrisInterview by Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow, Emily Brookfield, and Hope ChunA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Theologian Miroslav Volf reflects on solitude, loneliness, and how being alone can reveal our humanity, selfhood, and relationship with God.This episode is part 1 of a 5-part series, SOLO, which explores the theological, moral, and psychological dimensions of loneliness, solitude, and being alone.“Solitude brings one back in touch with who one is—it’s how we stabilize ourselves so we know how to be ourselves with others.”Macie Bridge welcomes Miroslav for a conversation on solitude and being oneself—probing the difference between loneliness and aloneness, and the essential role of solitude in a flourishing Christian life. Reflecting on Genesis, the Incarnation, and the sensory life of faith, Volf considers how we can both embrace solitude and attend to the loneliness of others.He shares personal reflections on his mother’s daily prayer practice and how solitude grounded her in divine presence. Volf describes how solitude restores the self before God and others: “Nobody can be me instead of me.” It is possible, he suggests, that we can we rediscover the presence of God in every relationship—solitary or shared.Helpful Links and ResourcesThe Cost of Ambition: How Striving to Be Better Than Others Makes Us WorseFyodor Dostoevsky, Crime and PunishmentRainer Maria Rilke, Book of Hours (Buch der Stunden)Dietrich Bonhoeffer, Creation and FallEpisode Highlights“Nobody can be me instead of me. And since I must be me, to be me well, I need times with myself.”“It’s not good, in almost a metaphysical sense, for us to be alone. We aren’t ourselves when we are simply alone.”“Solitude brings one back in touch with who one is—it’s how we stabilize ourselves so we know how to be ourselves with others.”“Our relationship to God is mediated by our relationships to others. To honor another is to honor God.”“When we attend to the loneliness of others, in some ways we tend to our own loneliness.”Solitude, Loneliness, and FlourishingThe difference between solitude (constructive aloneness) and loneliness (diminishment of self).COVID-19 as an amplifier of solitude and loneliness.Volf’s experience of being alone at Yale—productive solitude without loneliness.Loneliness as “the absence of an affirming glance.”Aloneness as essential for self-reflection and renewal before others.Humanity, Creation, and RelationshipAdam’s solitude in Genesis as an incomplete creation—“It is not good for man to be alone.”Human beings as fundamentally social and political.A newborn cannot flourish without touch and gaze—relational presence is constitutive of personhood.Solitude and communion exist in dynamic tension; both must be rightly measured.Jesus’s Solitude and Human ResponsibilityJesus withdrawing to pray as a model of sacred solitude.Solitude allows one to “return to oneself,” guarding against being lost in the crowd.The danger of losing selfhood in relationships, “becoming echoes of the crowd.”God, Limits, and OthersEvery other person as a God-given limit—“To honor another is to honor God.”Violating others as transgressing divine boundaries.True spirituality as respecting the space, limit, and presence of the other.Touch, Senses, and the ChurchThe sensory dimension of faith—seeing, touching, being seen.Mary’s anointing of Jesus as embodied gospel.Rilke’s “ripe seeing”: vision as invitation and affirmation.The church as a site of embodied presence—touch, seeing, listening as acts of communion.The Fear of Violation and the Gift of RespectLoneliness often born from fear of being violated rather than from lack of company.Loving another includes honoring their limit and respecting their freedom.Practical Reflections on LonelinessQuestions Volf asks himself: “Do I dare to be alone? How do I draw strength when I feel lonely?”The paradox of social connection in a digital age—teenagers side by side, “completely disconnected.”Love as sheer presence—“By sheer being, having a loving attitude, I relieve another’s loneliness.”The Spiritual Discipline of SolitudeVolf’s mother’s daily hour of morning prayer—learning to hear God’s voice like Samuel.Solitude as the ground for transformation: narrating oneself before God.“Nobody can die in my place… nobody can live my life in my place.”Solitude as preparation for love and life in community.About Miroslav VolfMiroslav Volf is the Henry B. Wright Professor of Theology at Yale Divinity School and Founding Director of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture. He is the author of Exclusion and Embrace, Flourishing: Why We Need Religion in a Globalized World, and numerous works on theology, culture, and human flourishing—most recently The Cost of Ambition: How Striving to Be Better Than Others Makes Us Worse.Production NotesThis podcast featured Miroslav VolfInterview by Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow, Emily Brookfield, and Hope ChunA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
From bipartisan cooperation to prayerful gratitude, Senator Kirsten Gillibrand joins Drew Collins to reflect on joy, wisdom, and love of enemy in a divided nation—offering a vision of public service grounded in the way of Jesus.“Jesus defied expectations—he welcomed the stranger, he fed the hungry, he loved his enemies.”Together they discuss the role of faith in public life amid deep division. Reflecting on Jesus’s call to love our enemies and the Apostle Paul’s exhortation to “rejoice always,” she describes how Scripture, prayer, and gratitude sustain her work in the U.S. Senate.From bipartisan collaboration to the challenges of resisting an authoritarian executive branch, Gillibrand speaks candidly about the challenges of embodying gentleness and compassion in politics, consistently seeking spiritual solidarity with colleagues across the aisle. Drawing on Philippians 4, she testifies to the peace of God that transcends understanding, revealing a vision of political life animated by faith, courage, and joy—all in the spirit of hope, humility, and the enduring call to love in public service.Episode Highlights“Faith is the greatest gift you could have. It grounds me; it reminds me why I’m here and what my life is supposed to be about.”“We can disagree about public policy, but we don’t have to be in disagreement as people.”“Jesus defied expectations—he welcomed the stranger, he fed the hungry, he loved his enemies.”“Rejoice in the Lord always. I will say it again, rejoice… let your gentleness be evident to all.”“I pray for wisdom every day. Scripture tells us if you ask for it, you will receive it—and boy do I need it.”About Kirsten GillibrandKirsten Gillibrand is the U.S. Senator from New York, serving since 2009. A graduate of Dartmouth College and UCLA Law School, she has focused her legislative career on ethics reform, national security, and family policy. Grounded in her Christian faith, she seeks to model bipartisan leadership and compassionate public service. For more information, visit gillibrand.senate.gov.Helpful Links and ResourcesPhilippians 4:4–9 (Bible Gateway)Redeemer Presbyterian Church (Tim Keller)Gospel in Life Podcast (Tim Keller)Chaplain Barry C. Black – U.S. Senate ChaplainKirsten Gillibrand, Official Senate PageFaith and DivisionGillibrand describes America’s current political and social moment as deeply divided, weakened by retreat into ideological corners.“We’re stronger when we work together—when people love their neighbors and care as if they were their own family.”Faith offers grounding amid chaos; social media and tribalism breed extremism and hate.Following Jesus in Public LifeFaith clarifies her purpose and sustains her in political life.“It makes everything make sense to me.”Living “out of step with what’s cool, trendy, or powerful” defines Christian vocation in public office.Bipartisanship and Common GroundWorks with Senators Cynthia Lummis (R-WY) on crypto regulation, Ted Cruz (R-TX) on first responder support, and Josh Hawley (R-MO) on stock trading bans.“If I can restore some healthcare or Meals on Wheels, I’ll go that extra mile to do that good thing.”Collaboration as moral practice—faith expressed through policy partnership.Loving Enemies and Welcoming StrangersDraws parallels between Jesus’s ministry and bipartisan cooperation.“He would sooner convert a Roman soldier than go to war with him.”“If I went to a Democratic rally and said, ‘love your enemy,’ I don’t know how that would go over.”Testifying to FaithWeekly Bible study with Senate Chaplain Barry C. Black.“He told us: Testify to your blessings. Share what God is doing in your life.”Posts daily blessings on social media, mixing joy and public witness.The Faith of DemocratsCounters perception that Democrats lack faith: “There are more ordained ministers and theology degrees on our side than people realize.”Mentions Senators Tim Kaine, Chris Coons, Raphael Warnock, Amy Klobuchar, and Lisa Blunt Rochester, all of whom regularly meet and discuss their faith and its impact on public office.Faith and Policy DifferencesOn reproductive rights and LGBTQ equality: “It’s not the government’s job to discriminate.”Frames Matthew 25 as central to Democratic faith—feeding, caring, welcoming.Compares differing theological interpretations of government’s role in justice.Joy and GratitudePhilippians 4 as daily anchor: “Rejoice in the Lord always… let your gentleness be evident to all.”Keeps a five-year daily gratitude journal: “You rewire your brain to look for what is praiseworthy.”Rejoicing doesn’t deny suffering; it transforms it into solidarity.Prayer and WisdomPrays constantly for family, colleagues, nation, and reconciliation.“Wisdom’s usually the one thing I ask for myself.”Prayer as discernment: deciding “where to put my voice, effort, and relationships.”Production NotesThis podcast featured Senator Kirsten Gillibrand.Edited and Produced by Evan Rosa.Hosted by Evan Rosa.Production Assistance by Alexa Rollow and Emily Brookfield.A Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School (faith.yale.edu/about)Support For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: faith.yale.edu/give
“The gifts and the calling of God are irrevocable.” Theologian R. Kendall Soulen joins Drew Collins to discuss supersessionism, the name of God (tetragrammaton), the irrevocable covenant between God and the Jews, and the enduring significance of Judaism for Christian theology.Together they explore religious and ethnic heritage, cultural identity, community, covenant, interfaith dialogue, and the ongoing implications for Christian theology and practice.They also reflect on how the Holocaust forced Christians to confront theological assumptions, how Vatican II and subsequent church statements reshaped doctrine, and why the gifts and calling of God remain irrevocable. Soulen challenges traditional readings of Scripture that erase Israel, insisting instead on a post-supersessionist framework where Jews and Gentiles bear distinct but inseparable witness to God’s faithfulness.Image Credit: Marc Chagall, ”Moses with the Burning Bush”, 1966This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. Visit tyndale.foundation to learn more.Episode Highlights“The gifts and the calling of God are irrevocable.”“Supersessionism is the Christian belief that the Jews are no longer God’s people.”“The Lord is God—those words preserve God’s identity and resist erasure.”“Israel sinned. They are still Israel. That identity is irrevocable.”“The gospel doesn’t erase the distinction between Jews and Gentiles; it reconfigures it.”About R. Kendall SoulenR. Kendall Soulen is Professor of Systematic Theology at Candler School of Theology, Emory University. A leading voice in post-supersessionist Christian theology, he has written extensively on the relationship between Christianity and Judaism, including The God of Israel and Christian Theology and Irrevocable: The Name of God and the Christian Bible.Helpful Links and ResourcesR. Kendall Soulen, Irrevocable: The Name of God and the Christian BibleR. Kendall Soulen, The God of Israel and Christian TheologyVatican II, Nostra Aetate — Vatican.vaMichael Wyschogrod, The Body of Faith: God in the People IsraelDrew Collins, The Unique and Universal ChristShow NotesR. Kendall Soulen’s formative encounters with Judaism at Yale and influence of Hans Frei and Michael WyschogrodRomans 9–11 as central to understanding Christianity’s relationship with JudaismSupersessionism defined as denying Israel’s ongoing covenant with GodImpact of the Holocaust and World War II on Christian theologyVatican II’s Nostra Aetate affirming God’s covenant with Israel remains intactOver a billion Christians now belong to churches rejecting supersessionismSoulen’s early work The God of Israel and Christian Theology diagnosing supersessionism in canonical narrativeDiscovery of the divine name’s centrality in Scripture and its neglect in Christian interpretationJesus’s reverence for God’s name shaping Christian prayer and theologyProper names as resistance to instrumentalization and fungibilityJewish and Gentile identities as distinct yet united in ChristDialogue with Judaism as essential for Christian self-understandingPost-supersessionist theology reshaping interfaith relations and Christian identityImplications for law observance, Christian Seders, and Jewish-Gentile church lifeAbrahamic faiths and typology: getting Christianity and Judaism right as foundation for interreligious dialogueProduction NotesThis episode was made possible by the generous support of the Tyndale House FoundationThis podcast featured R. Kendall SoulenEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow and Emily BrookfieldA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
Clinical psychologist Alexis Abernethy explores burnout, Sabbath rest, and resilience—reframing rest as spiritual practice for individuals and communities.“For me, it’s knowing that the Lord has made me as much to work as much to be and to be still and know that he is God.”On this episode, clinical psychologist Alexis Abernethy (Fuller Seminary) joins Macie Bridge to discuss burnout, Sabbath, worship, mental health, and resilience in the life of the church. Defining burnout through its dimensions of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced sense of accomplishment, Abernethy reflects on how church life can intensify these dynamics even as it seeks to heal them. Drawing from scripture, theology, psychology, and her own experience in the Black church and academic worlds, she reorients us to Sabbath as more than self-care: a sacred practice of being still before God. Sabbath, she argues, is not a quick fix but a preventive rhythm that sustains resilience in leaders and congregations alike. Along the way, she points to the necessity of modeling rest, the impact of daily and weekly spiritual rhythms, and the communal posture that makes Sabbath transformative.This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. Visit tyndale.foundation to learn more.Episode Highlights“For me, it’s knowing that the Lord has made me as much to work as much to be and to be still and know that he is God.”“Often people have overextended themselves in face of crises, other circumstances over a period of time, and it’s just not really sustainable, frankly, for anyone.”“We act as if working hard and excessively is dutiful and really what the Lord wants—but that’s not what He wants.”“When you are still with the Lord, you look different when you’re active.”“Sabbath rest allows you to literally catch your own breath, but also then be able to see what the congregation needs.”Helpful Links and ResourcesThat Their Work Will Be a Joy, Kurt Frederickson & Cameron LeeHoward Thurman, Meditations of the HeartEmily Dickinson, “Some Keep the Sabbath” (Poetry Foundation)About Alexis AbernethyAlexis Abernethy is a clinical psychologist and professor in the School of Psychology & Marriage and Family Therapy at Fuller Seminary. Her research explores the intersection of spirituality and health, with particular focus on Christian spirituality, church leadership, and group therapy models.Topics and ThemesBurnout in Church Leadership and Congregational LifeDefining Burnout: Emotional Exhaustion, Depersonalization, and Reduced AccomplishmentSpiritual Misconceptions of Work and DutySabbath as Sacred Rest, Not Just Self-CareSilence, Stillness, and the Presence of GodScriptural Foundations for Sabbath: Psalm 23, Psalm 46, John 15The Role of Pastors in Modeling RestPandemic Lessons for Church Rhythms and ParticipationEmily Dickinson and Creative Visions of SabbathResilience Through Sabbath: Lessons from New Orleans PastorsPractical Practices for Sabbath in Everyday LifeShow NotesExodus 20:8-11: 8 Remember the Sabbath day and keep it holy. 9 Six days you shall labor and do all your work. 10 But the seventh day is a Sabbath to the Lord your God; you shall not do any work—you, your son or your daughter, your male or female slave, your livestock, or the alien resident in your towns. 11 For in six days the Lord made heaven and earth, the sea, and all that is in them, but rested the seventh day; therefore the Lord blessed the Sabbath day and consecrated it.Opening framing on burnout, Sabbath, and confusion about self-careIntroduction of Alexis Abernethy, her background as psychologist and professorChildhood in a lineage of Methodist pastors and formative worship experiencesEarly academic path: Howard University, UC Berkeley, affirmation from her fatherDefining burnout: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, reduced accomplishment“I’m just stuck. I used to enjoy my job.”The church as both source of fulfillment and site of burnoutMisconceptions of spirituality equating overwork with dutyReference: That Their Work Will Be a Joy (Frederickson & Lee)Scriptural reflections: Psalm 23, Psalm 46, John 15Stillness, quiet, and Howard Thurman on solitude“When you are still with the Lord, you look different when you’re active.”Sabbath as sacred rest, not a quick fix or pillPastors modeling Sabbath for congregations, including personal family timeCOVID reshaping church rhythms and recalculating commitment costsEmily Dickinson’s poem “Some Keep the Sabbath”Lessons from New Orleans pastors after Hurricane KatrinaSabbath as resilience for leaders and congregationsPractical steps: scripture meditation, playlists, Lectio Divina, cultivating quietClosing invitation: Sabbath as both individual discipline and community postureProduction NotesThis podcast featured Alexis AbernethyInterview by Macie BridgeEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Alexa Rollow and Emily BrookfieldA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/give
The Gospel of John is a gospel of superabundance. The cosmic Christ made incarnate would of course yield an absolute superabundance of grace, love, and unity.What makes John’s Gospel so distinct from the Synoptics? Why does it continue to draw readers into inexhaustible depths of meaning? In this conversation, theologian David Ford reflects on his two-decade journey writing a commentary on John. Together with Drew Collins, he explores John’s unique blend of theology, history, and literary artistry, describing it as a “gospel of superabundance” that continually invites readers to trust, to reread, and to enter into deeper life with Christ. Together they explore themes of individuality and community; friendship and love; truth, reconciliation, and unity; the tandem vision of Jesus as both cosmic and intimate; Jesus’s climactic prayer for unity in chapter 17. And ultimately the astonishing superabundance available in the person of Christ. Along the way, Ford reflects on his interfaith reading practices, his theological friendships, and the vital role of truth and love for Christian witness today.“There’s always more in John’s gospel … these big images of light and life in all its abundance.”This episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. Visit tyndale.foundation to learn more.Episode Highlights“It is a gospel for beginners. But also it’s endlessly rich, endlessly deep.”“There’s always more in John’s gospel and he has these big images of light and, life in all its abundance.”“It all culminates in love. Father, I desire that those also you, whom you have given me, may be with me.”“On the cross, evil, suffering, sin, death happened to Jesus. But Jesus happens to evil, suffering, sin, death.”“We have to go deeper into God and Jesus, deeper into community, and deeper into the world.”Show NotesDavid Ford on writing a commentary on John over two decadesJohn’s Gospel compared to the Synoptic Gospels (Matthew, Mark, Luke)John as theological history writing (Rudolf Schnackenburg)John’s purpose statement in chapter 20: written so that you may trust“A gospel for beginners” with simple language and cosmic depthJohn as a gospel of superabundance: light, life, Spirit without measureJohn’s focus on individuals: Nicodemus, Samaritan woman, man born blind, Martha, Mary, LazarusThe Beloved Disciple and John’s communal authorshipFriendship, love, and unity in the Farewell Discourses (John 13–17)John 17 as the most profound chapter in ScriptureThe crisis of rewriting: scrapping 15 years of writing to begin anewScriptural reasoning with Jews, Muslims, and Christians on John’s GospelWrestling with John 8 and the polemics against “the Jews”Reconciliation across divisionsJohn’s vision of discipleship: learning, loving, praying, and living truthHelpful Links and ResourcesDavid Ford, The Gospel of John: A Theological CommentaryRudolf Schnackenburg, The Gospel According to St. JohnAbout David FordDavid F. Ford is Regius Professor of Divinity Emeritus at the University of Cambridge. He has written extensively on Christian theology, interfaith engagement, and scriptural reasoning. His most recent work is The Gospel of John: A Theological Commentary (Baker Academic, 2021). Ford is co-founder of the Cambridge Interfaith Programme and the Rose Castle Foundation.Production NotesThis podcast featured David FordInterview by Drew CollinsEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Macie Bridge, Alexa Rollow, and Emily BrookfieldA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/giveThis episode was made possible in part by the generous support of the Tyndale House Foundation. For more information visit Tyndale.foundation.
Miroslav Volf critiques ambition, love of status, and superiority, offering a Christ-shaped vision of agapic love and humble glory.“’And if you received it, why do you boast as if it were not a gift?’ If you received everything you have as a gift and if your existence as the recipient is also a gift, all ground for boasting is gone. Correspondingly, striving for superiority over others, seeking to make oneself better than others and glorying in that achievement, is possible only as an existential lie. It is not just a lie that all strivers and boasters tell themselves. More troublingly, that lie is part of the ideology that is the wisdom of a certain twisted and world-negating form of the world.”In Lecture 5, the final of his Gifford Lectures, Miroslav Volf offers a theological and moral vision that critiques the dominant culture of ambition, superiority, and status. Tracing the destructive consequences of Epithumic desire and the relentless “race of honors,” Volf contrasts them with agapic love—God’s self-giving, unconditional love. Drawing from Paul’s Christ hymn in Philippians 2 and philosophical insights from Rousseau, Nietzsche, and Max Scheler, Volf reveals the radical claim that striving for superiority is not merely harmful but fundamentally false. Through Christ’s self-emptying, even to the point of death, we glimpse a redefinition of glory that subverts all worldly hierarchies. The love that saves is the love that descends. In a world ravaged by competition, inequality, and devastation, Volf calls for fierce, humble, and world-affirming love—a love that mends what can be mended, and makes the world home again.Episode Highlights“Striving for superiority over others… is possible only as an existential lie.”“Jesus Christ was no less God and no less glorious at his lowest point.”“To the extent that I’m striving for superiority, I cannot love myself unless I am the GOAT.”“God cancels the standards of the kind of aspiration whose goal is superiority.”“This is neither self-denial nor denial of the world. This is love for the world at work.”Show NotesAgapic love vs. Epithemic desire and self-centered striving“Striving for superiority… is possible only as an existential lie.”Paul’s hymn in Philippians 2 and the “race of shame”Rousseau: striving for superiority gives us “a multitude of bad things”Nietzsche’s critique of Christianity and pursuit of powerMax Scheler: downward love, not upward striving“Jesus Christ was no less God and no less glorious at his lowest point.”Self-love as agapic: “I am entirely a gift to myself.”Raphael’s Transfiguration and the chaos belowDemon possession as symbolic of systemic and spiritual powerlessness“To the extent that I’m striving for superiority, I cannot love myself unless I am the GOAT.”“The world is the home of God and humans together.”God’s love affirms the dignity of even the most unlovable creatureLove as spontaneous overflow, not moral condescension“Mending what can be mended… mourning with those who mourn and dancing with those who rejoice.”Production NotesThis podcast featured Miroslav VolfEdited and Produced by Evan RosaHosted by Evan RosaProduction Assistance by Taylor Craig and Macie BridgeA Production of the Yale Center for Faith & Culture at Yale Divinity School https://faith.yale.edu/aboutSupport For the Life of the World podcast by giving to the Yale Center for Faith & Culture: https://faith.yale.edu/giveSpecial thanks to Dr. Paul Nimmo, Paula Duncan, and the media team at the University of Aberdeen. Thanks also to the Templeton Religion Trust for their support of the University of Aberdeen’s 2025 Gifford Lectures and to the McDonald Agape Foundation for supporting Miroslav’s research towards the lectureship.




![Season of Rebellion / Esau McCaulley on Lent [From the Archives] Season of Rebellion / Esau McCaulley on Lent [From the Archives]](https://s3.castbox.fm/a9/93/e6/abb68f12f13977b8088853ffc01a801f2c_scaled_v1_400.jpg)




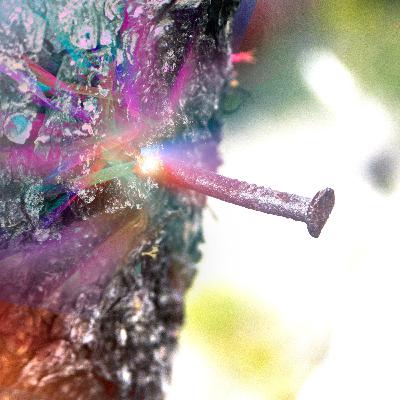













best Christian podcast in English for these Covid 19 times. imho