Discover Machine Learning Tech Brief By HackerNoon
Machine Learning Tech Brief By HackerNoon

584 Episodes
Reverse
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/a-lobster-just-took-your-job-heres-the-only-4-things-that-still-matter.
OpenClaw proved that human value is consolidating faster than anyone expected.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #openclaw, #worldcoin, #ai-lobster, #andrej-karpathy, #clawd-clawderberg, #simon-willison, #post-labor-economy, and more.
This story was written by: @juancguerrero. Learn more about this writer by checking @juancguerrero's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
OpenClaw is a free, open-source project created by an Austrian developer that went from zero to 175,000 GitHub stars in under two weeks. Over 100,000 people now run autonomous AI agents that handle tasks traditionally performed by assistants, bookkeepers, researchers, customer service reps, project managers, junior lawyers, and marketers.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/from-clawdbot-to-moltbot-to-openclaw-the-chaotic-story-of-the-trending-jarvis-ai-assistant.
Clawdbot's viral rise to 10K GitHub stars exploded into trademark fights, crypto scams & security nightmares—renamed to Moltbot, then OpenClaw. The full story!
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #clawdbot, #moltbot, #openclaw, #real-world-jarvis, #open-source-ai-assistant, #scams-and-controversy, #viral-github-repo, and more.
This story was written by: @thomascherickal. Learn more about this writer by checking @thomascherickal's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Austrian dev Peter Steinberger's Clawdbot—your always-on AI (finally, Jarvis) that texts via WhatsApp/Slack, books flights, clears emails & codes autonomously—exploded virally (Karpathy-approved). Anthropic's action forced a "Moltbot" rebrand, but scammers snagged handles in 10s for fake $CLAWD token (peaked $16M, crashed 90%). Security alarms: 4.5K exposed panels leaking API keys + prompt injection hacks. Game-changer for pros, nightmare for newbies. Read the entire story with a deep analysis here!
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/workflow-utility-spotlight-fast-impulse-response-handling-for-spatial-audio.
Learn how workflow-utilities/impulse-response uses FFmpeg to process impulse responses for convolution reverb, spatial audio, and production workflows.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #impulse-response-processing, #ir-audio-utility, #convolution-reverb, #spatial-audio-processing, #ffmpeg-audio-filters, #impulse-response-files, #reverb-simulation, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/aorchestra-turns-ai-agents-into-on-demand-specialists-not-static-roles.
This is a Plain English Papers summary of a research paper called AOrchestra: Automating Sub-Agent Creation for Agentic Orchestration. If you like these kinds of analysis, join AIModels.fyi or follow us on Twitter.
The multi-agent illusion
Most AI agent systems today operate under a fundamental constraint: they treat agents as either rigid specialists locked into predetermined roles or as context-isolated threads that lose all accumulated knowledge each time a new agent spawns. This creates a hidden tax on complex problem solving.
Imagine a software development team where every time someone switches tasks, they lose access to what they learned before. The front-end developer writes some code, hands it off to the backend developer, but the backend developer doesn't know about the design constraints the front-end developer discovered. Then the backend developer hands off to QA, and QA starts from scratch. Each handoff loses information. Alternatively, you could assign the same person to every role, but then they're constantly context-switching and never developing real expertise.
That's the trap existing multi-agent systems face. Researchers have documented this problem across frameworks, recognizing that multi-agent systems struggle with the tension between specialization and coherence. Some attempts at orchestral frameworks for agent orchestration have explored layered approaches, while others have looked at hierarchical structures for multi-agent reasoning, but they still work within this constraint.
The first approach treats sub-agents as isolated executors. Each time the system spawns a new agent, it gets only the immediate task. Everything the orchestrator learned is forgotten. This prevents "context rot" (where an agent's context window fills with accumulated, irrelevant details from past steps), but it means every new agent starts cold. If the orchestrator discovered that a user is on macOS or prefers a particular coding style, the next sub-agent never learns it.
The second approach assigns sub-agents static, pre-defined roles. You build a "Code Writer Agent," a "Testing Agent," and a "Documentation Agent," each with its own fixed tools and instructions. This preserves continuity and keeps agents specialized, but it's inflexible by design. What happens when a task needs something your pre-engineered agents can't handle? You're stuck. You'd need to anticipate every possible combination of skills beforehand, which defeats the purpose of using AI agents.
The deeper issue both approaches share is that they answer the question "What can this agent do?" at design time, not at execution time. The system cannot reshape its team composition to match the task at hand.
Comparison of sub-agent-as-tools approaches. (a) Sub-agents as context-isolated threads mitigate context rot but lack on-demand specialization. (b) Sub-agents as static roles provide specialized capabilities but are inflexible.
Comparison of sub-agent-as-tools approaches. (a) Sub-agents as context-isolated threads mitigate context rot but lack on-demand specialization. (b) Sub-agents as static roles provide specialized capabilities but are inflexible.
A recipe, not a machine
AOrchestra begins with a conceptual shift. Instead of thinking of agents as monolithic entities, treat them as recipes. A recipe doesn't describe a machine; it describes how to combine ingredients in a specific way to get a specific result.
Any agent, under this framework, can be described as a 4-tuple: Instruction, Context, Tools, Model.
Instruction is the task-specific goal or prompt. "Parse this JSON file into Python objects" or "Debug why this test is failing." This piece changes most frequently and is the most specific to the immediate problem.
Context is the accumulated state relevant to this particular subtask. If the orchestrator learned that the user's codebase uses type hints, that matters for a code-writing subtask. If the orchestrator knows the user is working in a constrained environment with limited dependencies, that should flow to the next agent. Context connects the dots between steps; it's what prevents each new agent from starting blind.
Tools are the executable capabilities the agent can call. A code interpreter. A file reader. A database query interface. A web browser. Different subtasks need different tools. A code-writing agent might need file system access and a Python interpreter. A research agent might need only a search API. By making tools explicit, the system can grant each agent exactly what it needs, no more, no less.
Model is the language model performing the reasoning. This is where performance-cost trade-offs live. A simple verification task might run on a fast, cheap model. A complex design task might require a more capable model. The system can choose the right tool for the job.
This abstraction is powerful because it's complete and composable. These four components fully specify an agent. By making them explicit, the orchestrator can construct the right specialist for each moment on demand. You don't pre-engineer every possible combination. You assemble them at runtime based on what the task actually requires.
How orchestration actually works
The orchestrator operates in a deliberate loop. When a user gives it a task, the orchestrator doesn't immediately create one large agent to solve it. Instead, it decomposes the problem and spawns specialized agents one at a time.
Here's the decision loop:
First, the orchestrator receives the overall task. "Fix this GitHub issue" or "Answer this question using available tools."
Second, it identifies the immediate subtask. What's the next step? Does the system need to understand the problem context? Read some files? Write code? Run a test? Each of these is a discrete piece of work.
Third, it curates the context dynamically. The orchestrator extracts only the information relevant to this specific subtask from everything it knows. If you mentioned you're using Python 3.11 but the current task is writing JavaScript, that context doesn't travel forward. Keeping context lean means agents spend their tokens on the actual task, not on irrelevant background.
Fourth, it selects the right tools. Based on the subtask, the orchestrator grants the agent access to specific capabilities. Need to execute Python? Grant a code interpreter. Need to search the web? Grant a search API. Need to modify files? Grant file system access. To...
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/turn-text-into-narration-fast-with-minimax-speech-28-hd.
Need natural-sounding TTS? MiniMax Speech-2.8 HD on fal.ai generates high-quality speech from text with voice selection.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #minimax, #fal-ai-on-fal, #minimax-speech-2.8-hd, #fal.ai-text-to-speech, #multi-voice-tts, #voiceover-generator, #multilingual-tts, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Need natural-sounding TTS? MiniMax Speech-2.8 HD on fal.ai generates high-quality speech from text with voice selection—plus tips for testing tones and A/B variants.
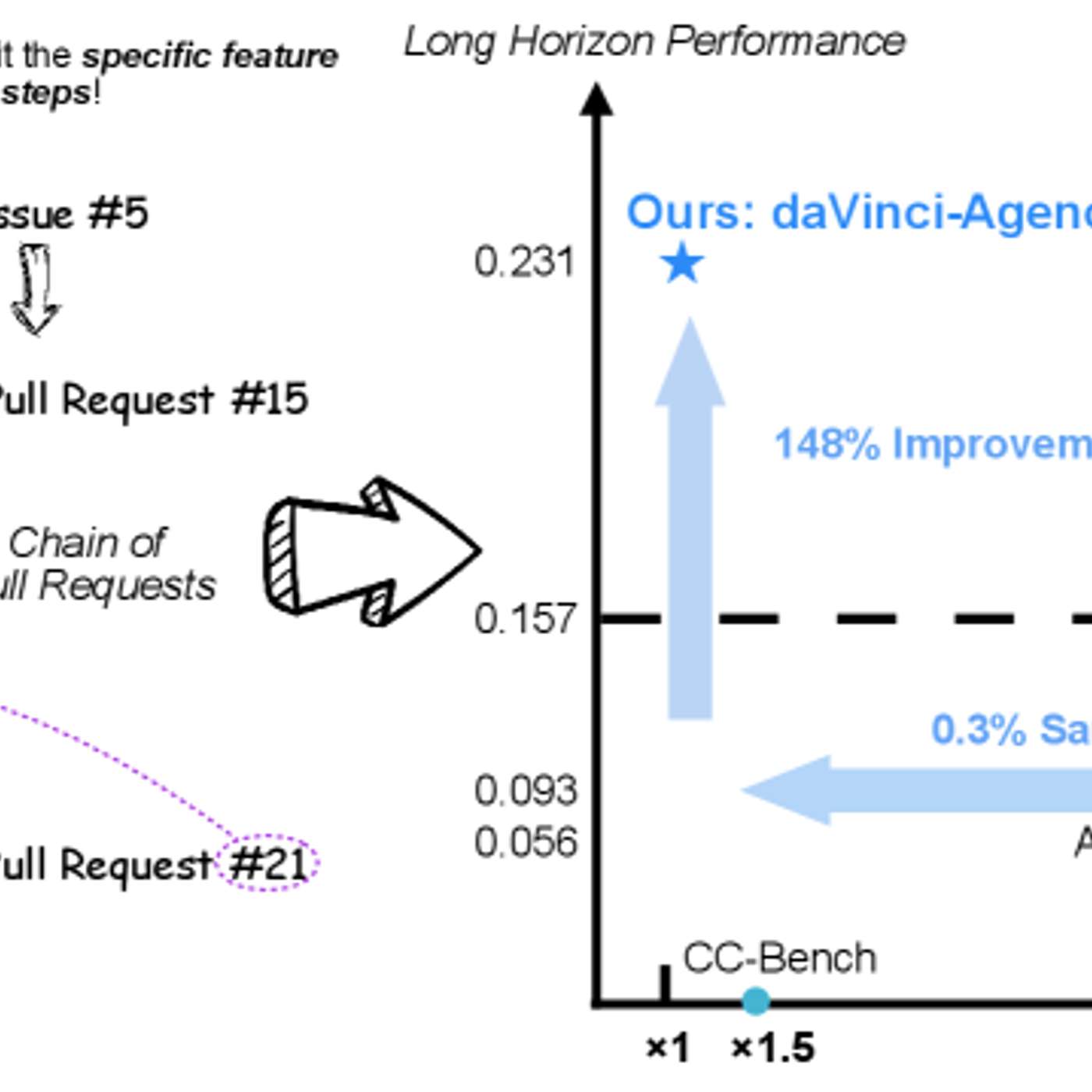
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/davinci-agency-a-shortcut-to-long-horizon-ai-agents.
DaVinci-Agency uses existing language models to generate diverse synthetic trajectories.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #davinci-agency, #long-horizon-agency, #synthetic-training-data, #data-efficient-training, #ai-agents, #error-propagation, #agentic-language-models, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
DaVinci-Agency uses existing language models to generate diverse synthetic trajectories, training long-horizon agents that plan and execute multi-step tasks with far less human data.
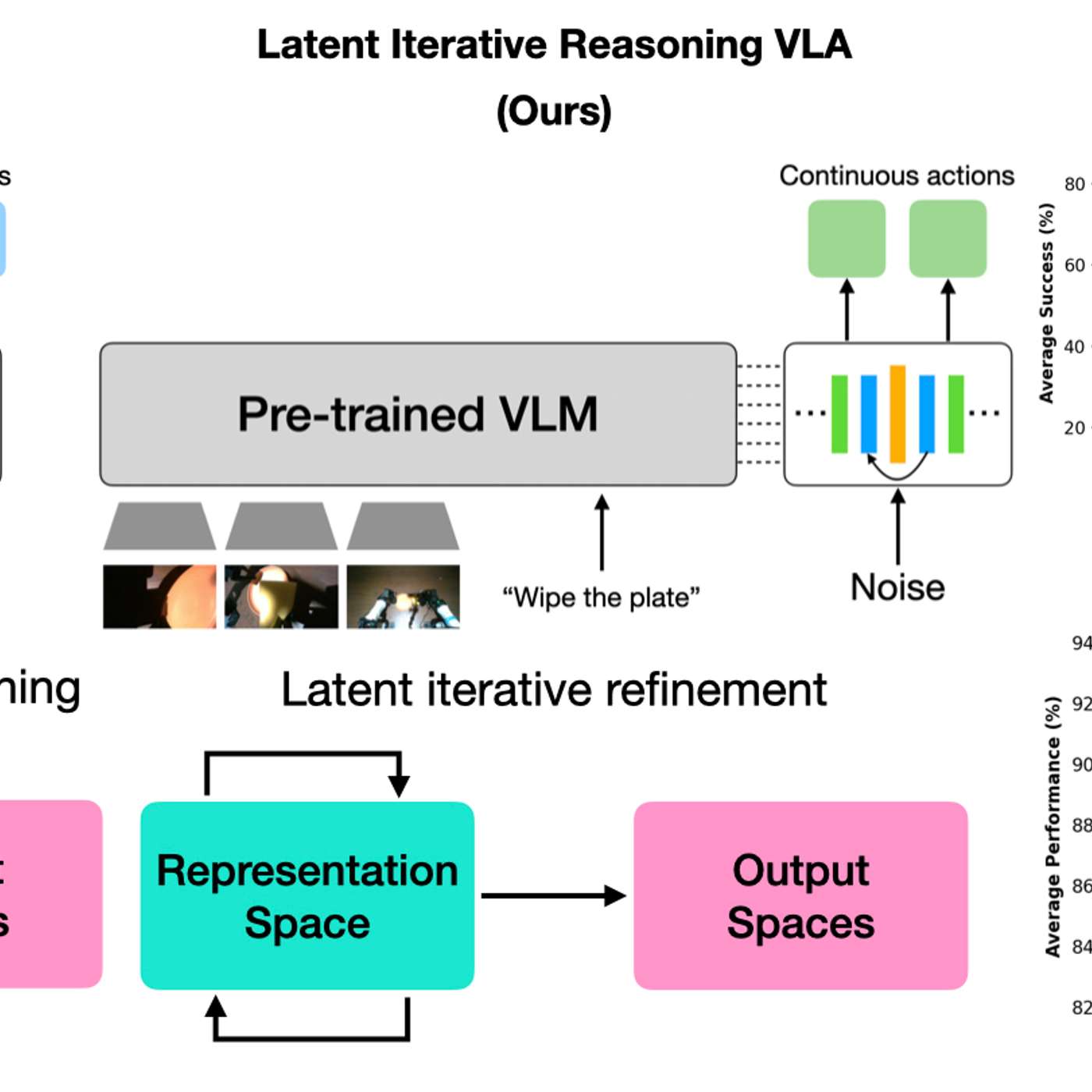
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/test-time-compute-scaling-of-vla-models-via-latent-iterative-reasoning-an-overview.
The Recurrent-Depth VLA approach represents a meaningful direction for improving robotic decision-making.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai-models, #iterative-reasoning, #test-time-compute-scaling, #vision-language-action-models, #compute-scaling, #action-models, #vla, #latent-reasoning, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
The Recurrent- depth VLA model works differently. Instead of deciding immediately, it lets the model think through the problem multiple times internally. The key twist is that this thinking happens invisibly.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/paddleocr-vl-15-a-09b-vision-language-ocr-model-built-for-real-world-documents.
This is a simplified guide to an AI model called PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 maintained by PaddlePaddle. If you like these kinds of analysis, join AIModels.fyi or follow us on Twitter.
Model overview
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 represents an advancement in compact vision-language models designed for document understanding tasks. Built by PaddlePaddle, this 0.9B parameter model handles optical character recognition and document parsing across multiple languages. Unlike its predecessor PaddleOCR-VL, the 1.5 version improves robustness for real-world document scenarios. The model combines vision and language understanding in a single, lightweight architecture suitable for deployment on resource-constrained devices.
Model inputs and outputs
The model accepts document images as visual input and processes them through a vision-language framework to extract and understand text content. It returns structured text recognition results with spatial information about where text appears within documents. The architecture balances model size with performance, making it practical for production environments where computational resources remain limited.
Inputs
Document images in standard formats (JPEG, PNG) containing text or structured document layouts
Image dimensions ranging from low to high resolution, with automatic scaling
Multi-language documents with text in various writing systems and scripts
Outputs
Extracted text with character-level accuracy and word boundaries
Bounding box coordinates indicating text location within images
Confidence scores for recognition results
Layout understanding identifying document structure and text regions
Capabilities
The model excels at extracting text from documents photographed in varied lighting conditions, angles, and quality levels. It handles forms, invoices, receipts, and handwritten documents with robust recognition. Multi-language support enables processing of documents containing text in different languages simultaneously. The system recognizes both printed and stylized text, making it suitable for diverse real-world document types.
What can I use it for?
Organizations can deploy this model for document digitization pipelines, automating data extraction from paper records without manual transcription. Financial institutions use it for invoice and receipt processing at scale. Educational platforms leverage it for converting scanned textbooks and educational materials into searchable digital formats. E-commerce companies implement it for order processing and shipping label reading. The lightweight design makes it suitable for mobile applications and edge devices where server-based processing becomes impractical.
Things to try
Experiment with severely degraded documents to test robustness limits—old photocopies, faxes, or images with heavy shadows. Test on documents combining multiple languages to see how the model handles code-switching and mixed-script scenarios. Try using it on non-standard document types like menu boards, street signs, or product packaging to explore its generalization capabilities. Process documents at various angles and rotations to understand how perspective changes affect accuracy. Run batch processing on large document collections to evaluate throughput and resource consumption in your deployment environment.
Original post: Read on AIModels.fyi
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #paddleocr-vl-1.5, #paddlepaddle, #paddlepaddle-ocr, #multi-language-ocr, #invoice-ocr-automation, #ocr-confidence-scores, #layout-analysis-ocr, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 is a compact 0.9B vision-language OCR model for real-world documents—multi-language text extraction, bounding boxes, and layout parsing.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/fix-jpeg-artifacts-fast-with-flux-kontext.
kontext-fix-jpeg-compression is a FLUX Kontext fine-tune that removes JPEG blockiness and banding while preserving the original image.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #kontext-fix-jpeg-compression, #color-banding-fix, #deblocking-ai-model, #flux-kontext-lora, #product-image-enhancement, #remove-jpeg-noise, #archived-photo-restoration, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
kontext-fix-jpeg-compression is a FLUX Kontext fine-tune that removes JPEG blockiness and banding while preserving the original image.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/the-role-of-supervised-fine-tuning-in-ai.
Supervised fine-tuning explained: how it aligns pretrained AI models for task-specific behavior, production reliability, and structured outputs.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #ml, #supervised-learning, #fine-tuning, #fine-tuning-ai, #supervised-fine-tuning, #data-bottleneck, #llm-stack, and more.
This story was written by: @praveenmyakala. Learn more about this writer by checking @praveenmyakala's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Pretraining makes AI models fluent. Supervised fine-tuning makes them useful. It trains models on labeled data to enforce task-specific behavior, format control, and production reliability.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/make-flux2-yours-train-a-4b-lora-on-50-100-images.
This is a simplified guide to an AI model called flux-2-klein-4b-base-trainer [https://www.aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-klein-4b-base-trainer-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] maintained by fal-ai [https://www.aimodels.fyi/creators/fal/fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral]. If you like these kinds of analysis, join AIModels.fyi [https://www.aimodels.fyi/?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] or follow us on Twitter [https://x.com/aimodelsfyi].
MODEL OVERVIEW
flux-2-klein-4b-base-trainer enables fine-tuning of the lightweight FLUX.2 [klein] 4B model from Black Forest Labs using custom datasets. This trainer creates specialized LoRA adaptations that let you customize the model for particular styles and domains without requiring substantial computational resources. The 4B variant offers a balance between performance and efficiency, making it practical for developers working with limited hardware. For those needing more capacity, flux-2-klein-9b-base-trainer [https://aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-klein-9b-base-trainer-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] provides a larger 9B option. If you work with full-scale models, flux-2-trainer [https://aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-trainer-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] and flux-2-trainer-v2 [https://aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-trainer-v2-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] offer training capabilities for the FLUX.2 [dev] version.
CAPABILITIES
Fine-tuning produces LoRA adaptations that modify model behavior for specific use cases. You can train the model to recognize and generate images in particular artistic styles, such as oil painting or watercolor techniques. Domain-specific training adapts the model to specialized fields like medical imaging, architectural visualization, or product photography. The resulting adaptations preserve the base model's general capabilities while adding specialized knowledge from your custom dataset.
WHAT CAN I USE IT FOR?
Creative professionals can build custom models for their unique artistic style or brand aesthetic. E-commerce companies can train specialized variants for consistent product visualization across their catalog. Design agencies can create domain-specific tools that generate images matching client requirements without manual editing. Studios working on concept art can develop tools that understand their visual language and generate variations matching their established style guide. Research teams exploring specific visual domains benefit from a model tailored to their data patterns.
THINGS TO TRY
Experiment with small datasets of 50-100 images showing your target style and observe how the model adapts. Try training on images with consistent lighting conditions or color palettes to see how strongly those attributes transfer. Test the resulting LoRA on prompts that combine your specialized domain with general concepts to understand how the adaptation interacts with broader knowledge. Compare outputs from flux-2-klein-9b-base-trainer [https://aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-klein-9b-base-trainer-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] to see whether the additional parameters provide meaningful improvements for your specific use case.
----------------------------------------
Original post: Read on AIModels.fyi [https://www.aimodels.fyi/models/fal/flux-2-klein-4b-base-trainer-fal-ai?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral]
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #flux-2-klein-4b-base-trainer, #flux.2-klein-4b-trainer, #fal-ai-flux-trainer, #lora-fine-tuning-for-flux, #custom-image-style, #product-photography-lora, #small-dataset-lora, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Build LoRAs for art styles, product visuals, and specialized domains—then compare results against the 9B option.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/the-remask-and-refine-coding-model-that-beats-its-ar-twin.
Stable-DiffCoder-8B-Instruct uses diffusion-style iterative refinement for any-order code generation and editing.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #diffusion-code-generation, #block-diffusion-pretraining, #bigcodebench-accuracy, #8b-parameter-coding-model, #stable-diffcoder-8b-instruct, #low-confidence-remasking, #8k-context-length-coding-llm, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Stable-DiffCoder-8B-Instruct uses diffusion-style iterative refinement for any-order code generation and editing—plus how to tune steps, thresholds, and remasking.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/the-compact-image-editor-that-still-understands-your-intent-vibe-image-edit.
This is a simplified guide to an AI model called VIBE-Image-Edit [https://www.aimodels.fyi/models/huggingFace/vibe-image-edit-iitolstykh?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] maintained by iitolstykh [https://www.aimodels.fyi/creators/huggingFace/iitolstykh?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral]. If you like these kinds of analysis, join AIModels.fyi [https://www.aimodels.fyi/?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral] or follow us on Twitter [https://x.com/aimodelsfyi].
MODEL OVERVIEW
VIBE-Image-Edit is a text-guided image editing framework that combines efficiency with quality. It pairs the Sana1.5 diffusion model (1.6B parameters) with the Qwen3-VL vision-language encoder (2B parameters) to deliver fast, instruction-based image manipulation. The model handles images up to 2048 pixels and uses bfloat16 precision for optimal performance. Unlike heavier alternatives, this compact architecture maintains visual understanding capabilities while keeping computational requirements reasonable for consumer hardware. The framework builds on established foundations like diffusers and transformers, making it accessible to developers already familiar with the ecosystem.
MODEL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
The model accepts natural language instructions paired with an image to understand both what changes should occur and where they should happen. It processes these inputs through its dual-component architecture to generate coherent edits that respect the original image composition while applying the requested modifications.
INPUTS
* Conditioning image: The image to be edited, supporting resolutions up to 2048px
* Text instruction: Natural language description of desired edits (e.g., "Add a cat on the sofa" or "let this case swim in the river")
* Guidance parameters: Image guidance scale (default 1.2) and text guidance scale (default 4.5) to control edit intensity
OUTPUTS
* Edited image: A single or multiple edited versions of the input image matching the text instruction
* Variable quality levels: Output quality controlled through inference step count (default 20 steps)
CAPABILITIES
This model transforms images based on written instructions without requiring mask inputs or additional prompts. It handles diverse editing tasks from simple object additions to complex scene modifications. The multimodal understanding from Qwen3-VL ensures instructions align properly with visual content, reducing the gap between user intent and generated results. The linear attention mechanism in Sana1.5 enables rapid inference, generating edits in seconds rather than minutes. It maintains image coherence across different scales and aspect ratios, supporting both square and rectangular compositions.
WHAT CAN I USE IT FOR?
Content creators can use this model to prototype design changes before committing to manual edits. E-commerce platforms could enable customers to visualize product modifications in context. Marketing teams can generate multiple variations of images for A/B testing without hiring designers. Social media creators could quickly iterate on visual content. The model also supports integration into commercial applications, though it operates under SANA's original license terms. Developers building image editing tools can leverage this framework as a backend engine for their applications.
THINGS TO TRY
Experiment with varying guidance scales to control how dramatically the edits change the original image. Lower image guidance produces looser interpretations while higher values preserve more of the original composition. Test complex multi-step instructions like "add snow falling and make the trees more vibrant" to see how well the model handles compound edits. Try different image aspect ratios beyond standard square formats to explore the model's flexibility. Adjust the number of inference steps to find the balance between speed and quality for your use case—fewer steps run faster but may produce cruder results. Use style keywords in instructions (similar to how prompt engineering works in image generation) to guide the aesthetic direction of edits.
----------------------------------------
Original post: Read on AIModels.fyi [https://www.aimodels.fyi/models/huggingFace/vibe-image-edit-iitolstykh?utm_source=hackernoon&utm_medium=referral]
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #artificial-intelligence, #software-architecture, #software-engineering, #backend-development, #product-management, #performance, #vibe-image-edit-model, #2048px-image-editing, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Learn VIBE-Image-Edit, a fast text-guided image editing framework using Sana1.5 diffusion and Qwen3-VL. Edit up to 2048px with guidance scales and step control.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/scientific-ai-isnt-a-scaling-problem-its-a-data-and-reasoning-problem.
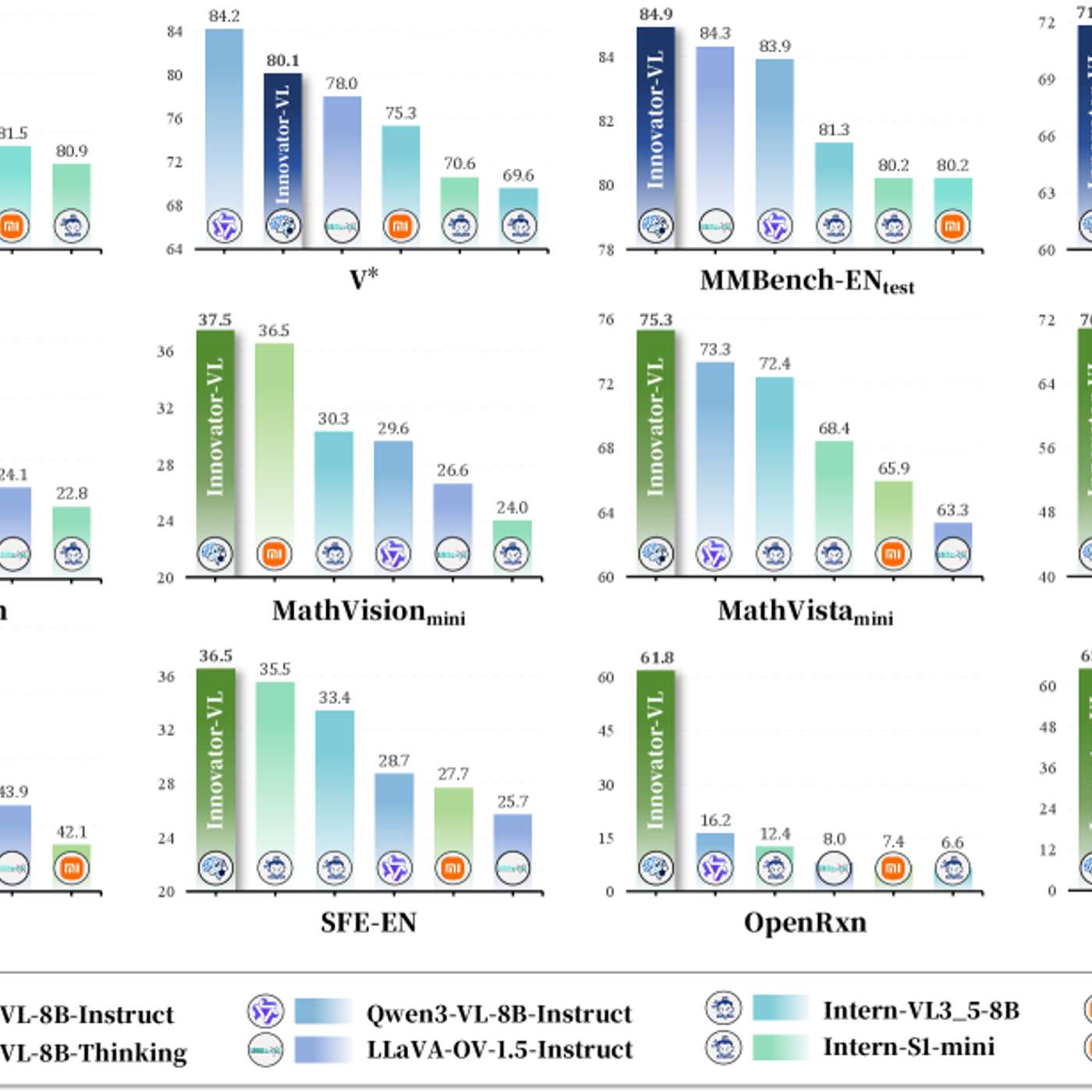
Innovator-VL argues scale isn’t destiny. With ~5M curated examples, it matches bigger models—reproducibly.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #innovator-vl, #ai-for-scientific-discovery, #multimodal-llm, #scientific-ai, #ai-data-and-reasoning, #ai-reasoning-capabilities, #ai-reasoning-problem, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Innovator-VL argues scale isn’t destiny: with ~5M curated examples, native-resolution vision tokens, and RL-for-reasoning, it matches bigger models—reproducibly.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/flux2-klein-trainer-edit-fine-tune-loras-on-a-lean-4b-base.
A simplified guide to fal-ai’s FLUX.2 klein LoRA trainer for editing.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #artificial-intelligence, #software-architecture, #product-management, #data-science, #design, #lora-fine-tuning, #parameter-efficient-tuning, #custom-image-editing, and more.
This story was written by: @aimodels44. Learn more about this writer by checking @aimodels44's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Learn how flux-2-klein-9b-base-trainer/edit helps teams train editing-focused LoRAs on the efficient FLUX.2 klein base model for custom styles, objects, and workflows.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/why-the-$70-million-aicom-domain-could-become-the-front-door-to-agi.
ai.com launches autonomous AI agents for consumers, founded by Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek, with a Super Bowl LX ad premiere on February 8, 2026.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #ai.com, #ai.com-news, #crypto.com, #blockchain, #startups, #good-company, #artificial-intelligence, and more.
This story was written by: @ishanpandey. Learn more about this writer by checking @ishanpandey's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
ai.com launches autonomous AI agents for consumers, founded by Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek, with a Super Bowl LX ad premiere on February 8, 2026.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/my-2-cents-to-improve-opus-plans.
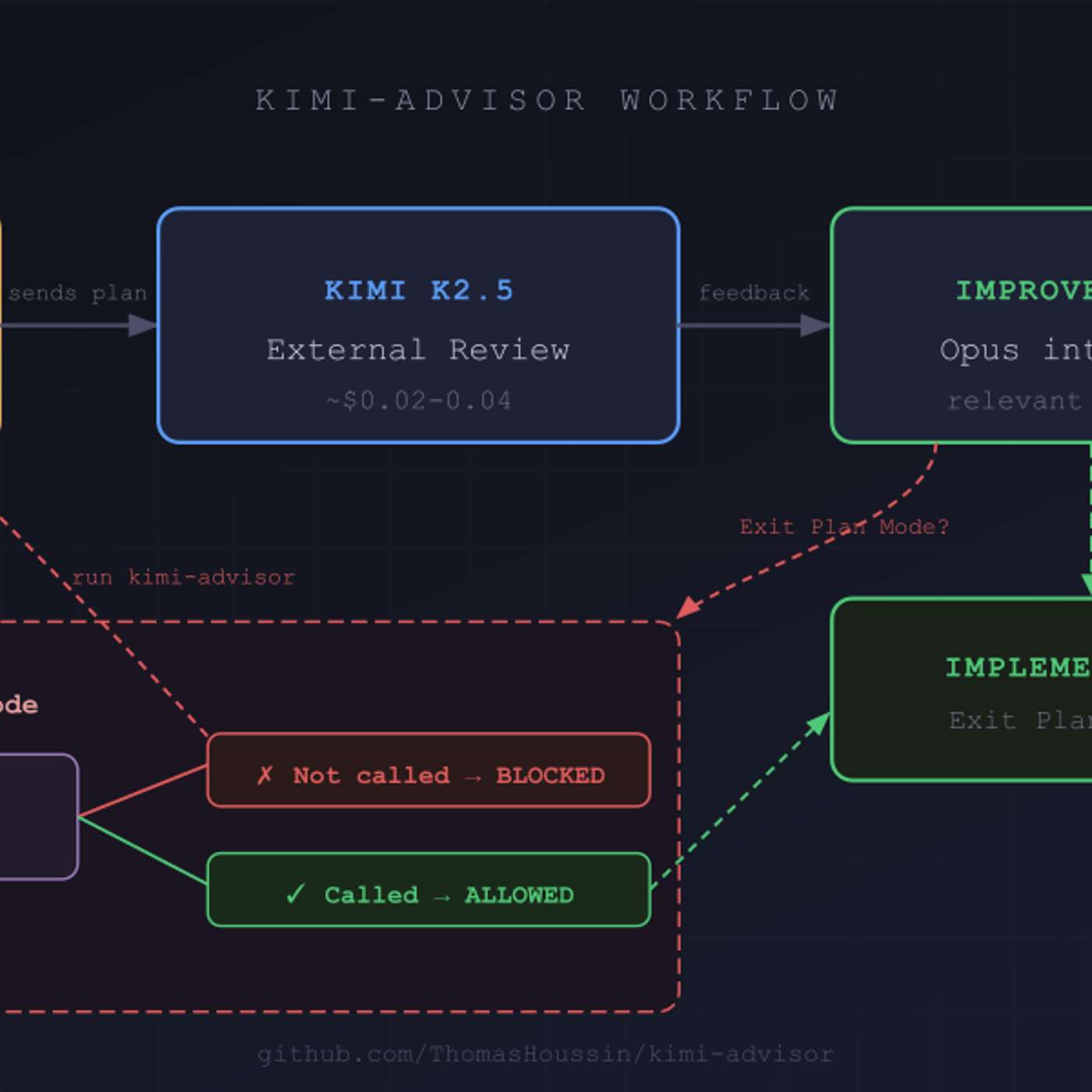
A Python CLI that adds an external Kimi K2.5 review step to Claude Code plans, with a hook to make it mandatory. Real bugs caught for a few cents per review.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai, #claude-code, #kimi-k25, #claude-opus-4.5, #code-review, #claude-code-plan-mode, #opus-plans, #improve-opus-plans, and more.
This story was written by: @thomashoussin. Learn more about this writer by checking @thomashoussin's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
A cheap external reviewer for Claude Code plans. A Python CLI sends your plan to Kimi K2.5 for critique before implementation, and a Claude Code hook makes the review mandatory. A few cents per review, real bugs caught.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/the-weather-report-lie-ai-isnt-fate.
AI is told like a weather report; terms are consent, accountability, limits, auditability, and the right to shut it down.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #artificial-intelligence, #ai-governance, #humanity, #surveillance, #ai-risk, #decision-making, #accountability, #hackernoon-top-story, and more.
This story was written by: @husseinhallak. Learn more about this writer by checking @husseinhallak's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
The dominant story about AI is told like a weather report: it's coming, it's inevitable, it will accelerate, take over work, reshape society and government. It puts technology at the center of gravity and pushes humans out of the frame.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/i-talked-to-claude-code-more-than-humans-in-2025-heres-what-i-learned.
AI agents are becoming the real “users.” Why MCP struggled, why skills won, and what agent-first software design looks like in 2026.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #ai-agents, #claude-code, #model-context-protocol, #ai-skills-prompts, #agent-first-design, #devops-with-ai, #future-of-ai, #ai-skills-architecture, and more.
This story was written by: @burninganna. Learn more about this writer by checking @burninganna's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
While Twitter discovers Claude Code in 2025, I was doing all this 6 months ago. MCP got hyped but couldn't scale. Skills emerged as the practical alternative. Best skill of December 2025? One line that keeps Claude working without stopping. Burn tokens, give Claude full context like you would a human colleague, and push the limits. In 2026, agents become first-class internet users.
This story was originally published on HackerNoon at: https://hackernoon.com/beyond-the-perimeter-securing-ai-for-the-quantum-era.
Former Mastercard and Equifax AI Lead Jeremy Samuelson reveals how to deploy production-grade and quantum-resilient AI without exposing sensitive data.
Check more stories related to machine-learning at: https://hackernoon.com/c/machine-learning.
You can also check exclusive content about #machine-learning, #machine-learning-research, #quantum-computing, #ai-and-quantum-computing, #founder-interview, #ai-security, #ml-security, #privacy-preserving-ai, and more.
This story was written by: @viceasytiger. Learn more about this writer by checking @viceasytiger's about page,
and for more stories, please visit hackernoon.com.
Most AI systems don’t fail because the models are bad — they fail because the systems around them are fragile, insecure, and poorly governed. In this interview, Jeremy Samuelson, EVP of AI & Innovation at Integrated Quantum Technologies, explains why the real ceiling of applied AI is set by architecture and data movement, not model accuracy. He also introduces VEIL, a new security architecture that removes sensitive data from the ML pipeline entirely, making AI systems breach-resilient and inherently quantum-safe by design.