Discover Keen On America
Keen On America

Keen On America
Author: Andrew Keen
Subscribed: 10,911Played: 954,308Subscribe
Share
© 2026 Andrew Keen
Description
Nobody asks sharper or more impertinent questions than Andrew Keen. In KEEN ON, Andrew cross-examines the world’s smartest people on politics, economics, history, the environment, and tech. If you want to make sense of our complex world, check out the daily questions and the answers on KEEN ON.
Named as one of the "100 most connected men" by GQ magazine, Andrew Keen is amongst the world's best-known technology and politics broadcasters and commentators. In addition to presenting KEEN ON, he is the host of the long-running show How To Fix Democracy and the author of four critically acclaimed books about the future, including the international bestselling CULT OF THE AMATEUR.
Keen On is free to listen to and will remain so. If you want to stay up-to-date on new episodes and support the show, please subscribe to Andrew Keen’s Substack. Paid subscribers will soon be able to access exclusive content from our new series Keen On America – keenon.substack.com
Named as one of the "100 most connected men" by GQ magazine, Andrew Keen is amongst the world's best-known technology and politics broadcasters and commentators. In addition to presenting KEEN ON, he is the host of the long-running show How To Fix Democracy and the author of four critically acclaimed books about the future, including the international bestselling CULT OF THE AMATEUR.
Keen On is free to listen to and will remain so. If you want to stay up-to-date on new episodes and support the show, please subscribe to Andrew Keen’s Substack. Paid subscribers will soon be able to access exclusive content from our new series Keen On America – keenon.substack.com
1028 Episodes
Reverse
An anti-fascist spy handed American officials evidence of murderous intent from a Nazi planning server — and they declined to act.About the GuestChristopher Mathias is a journalist covering the far right, formerly a senior reporter at HuffPost, with work appearing in The Guardian, The Nation, MSNBC, Zeteo, and WNYC. His reporting has helped unmask white supremacist cops, soldiers, teachers, and politicians, and he was a Deadline Awards finalist for feature writing. He is originally from Gettysburg, Pennsylvania and lives in New York. His new book, To Catch a Fascist: The Fight to Expose the Radical Right (Atria Books), is out now.About the EpisodeDays after Jonathan Rauch’s influential Atlantic essay announced he’d moved from fascism skeptic to fascism believer, Christopher Mathias joins the show to discuss his new book — a deeply reported investigation into the decentralized network of anti-fascist activists who infiltrate, monitor, and expose neo-Nazis and white supremacists operating in positions of power across America.The conversation quickly moves beyond whether Trump is a fascist to the harder questions his book raises: Who gets to decide who is exposed? What rights to privacy do members of extremist groups retain? Is unmasking community self-defense or vigilantism? And does the same logic that justifies exposing a neo-Nazi EMT extend to the tens of thousands of ICE agents now conducting raids on American streets?Timeline00:00 Introduction Jonathan Rauch’s Atlantic essay and the renewed fascism debate01:10 Meet Christopher Mathias Introducing the book and the journalist behind it01:45 The Greenville Moment When Mathias first used “fascist” in a headline after watching Trump whip a crowd into chanting “Send her back”02:40 Defining the F-Word Fascism as a right-wing politics of domination; Langston Hughes recognizing it in the 1930s before the word arrived04:15 The Hard Question If MAGA is a fascist movement, are the 70-plus million who voted for Trump fascists too?05:55 The Worst of the Worst Why the book targets explicit neo-Nazis in positions of power, not ordinary Trump supporters08:15 Who Decides? Privacy, accountability, and whether everyone at Charlottesville deserves exposure10:45 Antifascist Amnesty Leave the movement and we leave you alone; return and we publish12:30 The Equivalence Trap Why Mathias rejects the idea that this is just radicals exposing radicals14:05 From Neo-Nazis to ICE How anti-fascist tactics are now used to identify masked federal agents17:15 Where Does It End? Drawing lines between violent enforcement and bureaucratic participation19:40 “Just Following Orders” Why some orders shouldn’t be followed, and the occupation of Minneapolis21:30 The Battle Over Shame Competing databases, surveillance, and what America should be ashamed of23:15 The Spy Who Warned Charlottesville An infiltrator uncovers plans for violence that officials ignore26:00 Minneapolis as Model “We protect us” and a blueprint for grassroots resistance28:45 The Underground War Intelligence, counterintelligence, and the personal cost of exposure30:30 Closing Fascism as a snake eating its own tail and the urgent task of limiting the damageLinks & ReferencesMentioned in this episode:Jonathan Rauch, “Yes, It’s Fascism” — The Atlantic (January 2026)To Catch a Fascist: The Fight to Expose the Radical Right by Christopher Mathias (Atria Books, February 2026)Christopher Mathias reporting archiveFollow Christopher Mathias: BlueSky | XAbout Keen On AmericaKeen On America is a daily podcast hosted by Andrew Keen, the Anglo-American writer and Silicon Valley insider named by GQ magazine as one of the world’s “100 Most Connected Men.” Every day, Andrew brings his sharp Transatlantic wit to the forces reshaping the United States — interviewing leading thinkers and writers about American history, politics, technology, culture, and business. With nearly 2,800 episodes since the show’s founding on TechCrunch in 2010, Keen On America is the most prolific intellectual interview show in the history of podcasting.Website | Substack | YouTube
Can meat save the planet? That’s the paradoxical promise of the longtime vegan activist Bruce Friedrich, founder of the Good Food Institute. In his new book, Meat, Friedrich argues that plant-based and cultivated meat can satisfy the craving of the most hardline carnivore while simultaneously fixing the apocalyptic environmental consequences of industrial farming. So new tech, particularly the latest technology that magically mimics meat, will enable the regeneration of the (real) natural world. For this vegan advocate of meat, this next agricultural revolution will not only transform humanity’s favorite food but also our planet’s environmental future. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
There’s something absurdly Strangelovian about the American quest for a perfect weapon. As Jeffrey Stern warns in The Warhead, his new history of The Paveway, the first “smart” bomb, weapons are always, like their human engineers, imperfect. “It’s always exploding somewhere,” Stern dryly notes, and those explosions in the Texas Instruments developed Paveway were not only unexpected, but often tragically imperfect. So for example, the Second Gulf War was the most precise air war in history and yet within a year, more civilians died than in Hiroshima and Nagasaki combined. The conceit of “perfection”, Stern warns, might be as quintessentially American as the fatally flawed Walt Disney corporation or the Kennedy dynasty (both part of the Paveway story). Which is why this history of smart weapons makes such chilling reading in an AI age when Americans are once again being promised perfect military technology. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Why did Nixon trigger a remarkable cultural American renaissance while Trump has generated an avalanche of social media bluster, but few great movies, songs or novels? For Silicon Valley critic Jon Taplin, the problem isn’t just technological. Yes, he argues in Rolling Stone, social media has sucked a lot of the cultural vitality out of America and created a self-interested new class of influencers. But Sixties veteran Taplin sees this cultural crisis in generational terms arguing that young American artists need a “cojones transplant”. Perhaps. Although one wonders if Taplin is part of an American gerontocracy which is hoarding not just power and wealth, but also virtue. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Is AI going through an adolescent crisis, even it’s still just a toddler? There certainly seems to be a lot of adolescent angst amongst our new AI overlords like Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei. In his latest essay, appropriately entitled “The Adolescence of Technology”, Amodei lays out all the existential dangers of AI while simultaneously rejecting the doomsday pessimism of many tech sceptics. Amodei, That Was The Week’s Keith Teare quips, “reminds me of a teenager raised by religious parents to believe you should only have sex after marriage, but he wants to have sex now and feels guilty about it." Teare is right. Amodei - not unlike fellow adolescents Sam Altman and Elon Musk - certainly wants to have his cake and eat it too. So when will they all grow up? Some, like the perpetually infantile Musk, never will. But perhaps like Keith Teare’s conflicted teenager, maybe Dario Amodei will eventually grow out of his guilty adolescence and become a responsibly accountable adult. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
When asked what his parents did, Atlantic CEO and competitive marathoner Nicholas Thompson had a stock response. "My mother's an art historian at Babson," he would answer, "my father runs a male brothel in Bali." Thompson's new best-selling autobiography, The Running Ground, is an extended version of his extraordinary family history, focusing on the dramatic fall from grace of his Rhodes Scholar father, W. Scott Thompson. The confessional is partly a discourse on running — a discipline that the father passed down to the son. But it's also a meditation on parenting. So was his father a good dad? "If the standard is whether you go bankrupt, lean upon your children, ask them to perform bigamist weddings, threaten to kill yourself, blackmail them, then no," Nick Thompson reflects. "If the standard is does he love you every day, then yes."Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
According to our favorite literary reviewer, Bethanne Patrick, these are the seven books that “will really matter” in 2026:* Land by Maggie O’Farrell — The Hamnet author returns with a luminous novel set in 1865 Ireland, two decades after the Great Famine. A father and son survey their region for the British—mapping the land in English when their hearts speak Gaelic. O’Farrell explores post-famine trauma, colonialism, and the mysterious pull of place, weaving in neolithic history and Irish wolfhounds that feel almost magical. As some characters emigrate to the New World, the novel asks what it means when land becomes identity, when a nation is defined not by commerce but by the places that feed our souls.* The Fire Agent by David Baerwald — A stunning debut from the Grammy-winning songwriter behind Sheryl Crow’s Tuesday Night Music Club. This 600-page thriller is based on Baerwald’s own family history: his grandfather Ernst was sent to Tokyo as the purported sales director for IG Farben, the company complicit in the Holocaust. The novel spans continents and decades, from a 1920s throuple to Wild Bill Donovan’s OSS becoming the CIA, complete with family photographs. Patrick calls it “a knockout”—not a potboiler, but a wild, scary ride where almost everything actually happened.* A Tender Age by Chang-rae Lee — The Pulitzer finalist delivers what his publisher calls “a spellbinding exploration of American masculinity and family dynamics.” Through an unforgettable Asian-American protagonist, Lee examines what it means to grow up with “double consciousness”—always aware of how the dominant culture perceives you, your family, your chances. Patrick places him alongside Jesmyn Ward as one of America’s finest novelists.* Witness and Respair by Jesmyn Ward — The two-time National Book Award winner collects her nonfiction, including the devastating Vanity Fair essay about her husband’s death from COVID at 33. “Respair” is Ward’s resurrection of an archaic word: the repair that comes after despair. These crystalline essays on the American South, racism, and grief reveal the deep thought behind her remarkable fiction. Patrick sees it as essential reading for 2026—a creative grappling with everything America must face.* Backtalker by Kimberlé Crenshaw — A memoir from the architect of “intersectionality” and “critical race theory,” now under attack in the current administration. Structured in three parts—raising a back talker, becoming a back talker, being a back talker—it begins with young Kimberlé desperate to play Thornrose in a classroom fairy tale, passed over week after week. When she’s finally chosen on the last day and the bell rings, her mother marches back to school and demands justice. That’s where Crenshaw learned to speak truth to power.* American Struggle edited by Jon Meacham — For the 250th anniversary, the historian assembles primary documents proving that struggle is constant and non-linear in American history. Abolitionists spoke out in the nineteenth century; civil rights activists had to speak out again in the twentieth. From Abigail Adams’s “remember the ladies” letter to Fannie Lou Hamer’s testimony at the 1964 Democratic Convention, Meacham—no fan of the current administration—shows that the fight never stays won. Patrick sees it as essential for librarians, teachers, and younger readers.* John of John by Douglas Stuart — Patrick’s sneaky seventh pick (I originally only allowed her six). The Booker Prize-winning author of Shuggie Bain returns to Scotland, this time the Isle of Harris, where men weave Harris Tweed on licensed looms. John McLeod is a fire-and-brimstone church elder; his son Cal returns from Glasgow art college with dyed hair and queer identity. What looks like prodigal son territory becomes something richer—father and son have more in common than either knows. Stuart captures a community tied to sheep farming and craft practices that feel centuries old, even as modernity crashes against the shore.Enjoy!Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Pay attention to this interview. Because, you see, attention is seriously expensive — the Silicon Valley industry being worth $17 trillion, at least according to the Princeton historian D. Graham Burnett, co-editor of a new manifesto entitled Attensity. For Burnett and his friends in the Attention Liberation Movement, the attention industry is "fracking" the human out of us. Liberating ourselves from its exploitative grasp, then, is an existential challenge. "If we take our attention away," he warns, "it collapses into sand." And so will we. So paying attention involves more than simply putting down our phones. It means joining the Attensity movement and challenging the central attention economy principles of 21st century capitalism.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
New books are like London buses. You wait and wait and then a handful comes at the same time. Take, for example, histories of the New York City vigilante Bernie Goetz. Last week, we featured the CNN legal analyst Elliott Williams who has a new book out on Goetz. And now we have another uncannily timely book on Goetz. This one from the Pulitzer-Prize winning historian, Heather Ann Thompson. Entitled Fear and Fury, Thompson focuses on the 1984 New York City case in the genealogy of white rage in America, tracing the Goetz shootings back to the Reagan Eighties as well as white vigilantes in the Trump era like Kyle Rittenhouse. What ties Goetz and Rittenhouse together, Thompson argues, is the inversion of victim and villain in a brutal haze of violence. And, of course, we can now see this tragic narrative repeated on the streets of Minneapolis. It’s as if Bernie Goetz and Kyle Rittenhouse are now working for ICE. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
This is the final conversation from DLD. And the most optimistic - at least from a European perspective. John Thornhill, the FT’s Innovation Editor and founder of Sifted, has a quite different take on Europe’s tech scene from our other guests. Yes, he acknowledges, the regulatory environment is complex. And, yes, late-stage capital is thin. But Thornhill sees something the doomsayers miss: resilience. A new generation of founders isn’t building “European champions” — they’re building global ones. Innovation hot spots are popping up across the continent: London, Berlin, Stockholm, Tallinn, Lisbon. Paris (of all places) is enjoying a renaissance. And deep tech — biological computing, synthetic biology, materials science — may finally give Europe’s research strength a viable path to commercialization. So who needs Silicon Valley Goliaths when you have an army of European Davids?Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
For media moguls, we are living, to borrow from Dickens, in the best and worst of times. As Nicholas Thompson confessed to me at DLD, The Atlantic CEO is simultaneously “excited” and “terrified” by the power of AI to revolutionize his media industry. On the one hand, Thompson explains, AI represents the best tool journalism has ever had for locating needles in haystacks. On the other hand, AI has the potential to obliterate traditional media’s entire business model. So what’s it to be: extinction or renaissance? For Thompson, a lot depends on the fate of copyright. If our Silicon Valley leviathans pay for the original content that powers their intelligence, then media companies can prosper in the age of AI. If not, then it really will turn out to be the worst of times for high quality, curated publications like The Atlantic. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
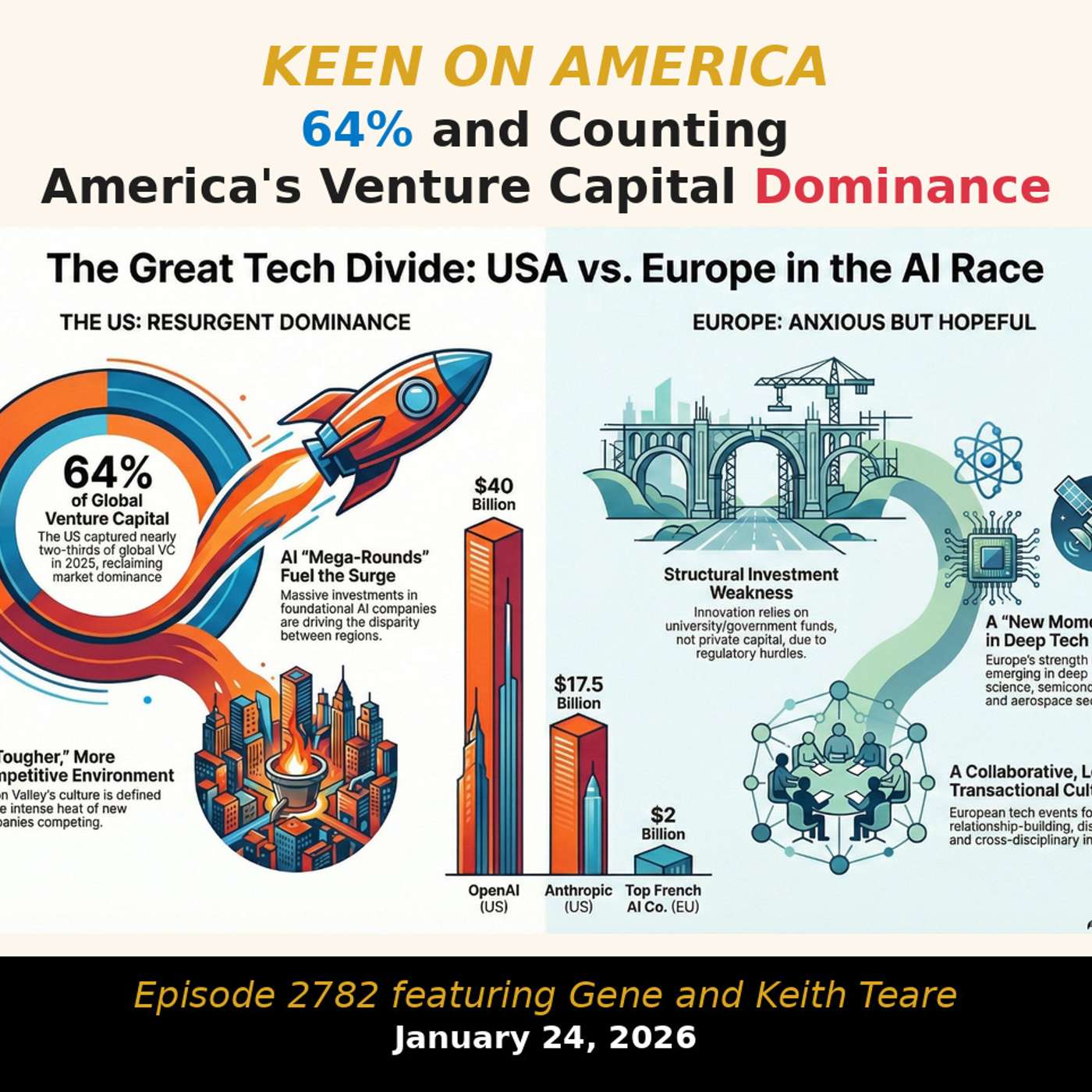
One of the most bracing presentations at DLD this year was given by Crunchbase's data queen Gene Teare. Breaking down America's VC dominance, Teare's speech might have been entitled "64% and Counting." As Teare told Keith and me in a special Teare family edition of our regular That Was The Week show, the VC gap between Europe and America is only getting wider. From 2014 to 2023, US share of global venture dipped below 50%. But in 2025, it roared back — with nearly two-thirds of all global VC flowing to America. The foundation model funding disparity tells the story: OpenAI raised $40 billion last year, Anthropic $17.5 billion. The top French AI company? $2 billion. Oh mon Dieu.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Not everything at DLD this year was on the growing US-European economic and technological divide. There were many speeches on the environment including from heavyweights like Kate Raworth. And I had the opportunity to catch up with my favorite advocate of regenerative agriculture, the managing partner at Acton Capital, Jan-Gisbert Schultze. According to Schultze, today's deepest problem is our spiritual disconnection from nature. We've lost 50% of our soil carbon, he notes, and with it the fertility that sustains us. We can save ourselves, he says, from the soil up — by embracing regenerative agricultural practices that prioritize local community activation and sustainable farming. Schultze is putting this into practice at Lake Constance, Germany's largest lake, where his Regenerate Forum is working to transform an entire county into what he calls a "climate landscape" — retraining farmers, rebuilding soil, and relocalizing the food system.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Few speakers at DLD this year were more sombre than The Economist's deputy executive editor Kenneth Cukier. “Civilizations aren’t killed,” Cukier says, “they commit suicide.” It's now "three minutes to midnight" in Europe, he warns, and what he called the priceless "vase" of the liberal order is about to shatter. Borrowing from Hemingway's description of personal bankruptcy, Cukier argues that civilizational suicide comes "slowly, then suddenly". So can anything avert this collapse? Cukier isn't particularly optimistic, but nor is he hopeless. The vase hasn't shattered yet. The hope, he suggests, is with new peaceful technologies that can help reinvent democracy. But if the European clock really is teetering at three minutes to midnight, it's hard to be persuaded by Kenneth Cukier’s abstract promises of ethical technology.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
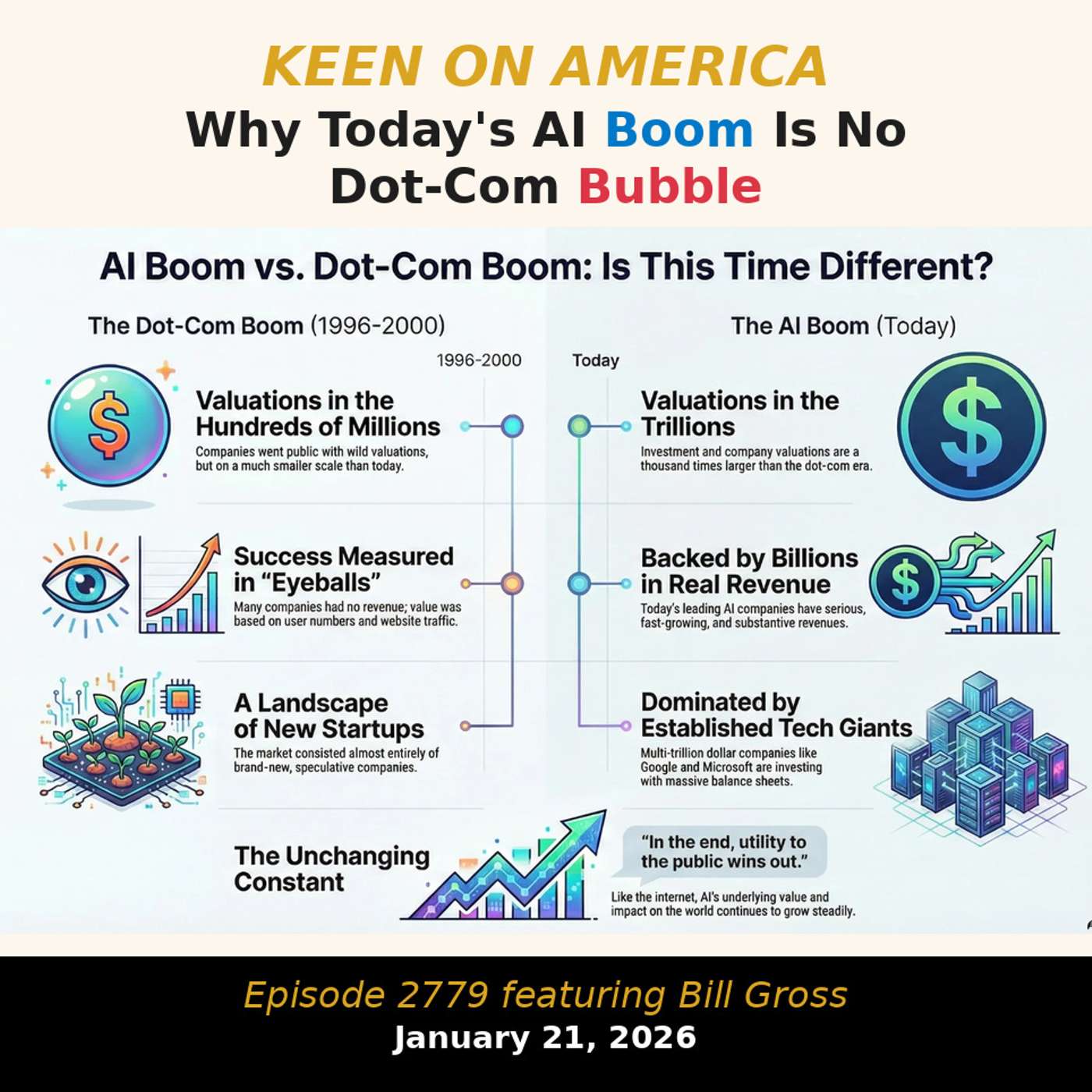
Few people experienced the Dot-Com bubble with more vertiginous intensity than Bill Gross, the Pasadena-based founder of Idealab and many many other internet startups over the last 30 years. So when I sat down with Gross at DLD, I couldn’t resist opening with the boom/bubble gambit. How, I asked him, does today’s AI hysteria compare with the Web 1.0 madness of the Nineties? While Gross - whose current ProRata.ai play is focused on protecting creativity in the age of generative AI - doesn’t believe that today’s boom is akin to the Dot-Com bubble, there are similarities. We are at what Gross calls a “Napster moment” in terms of making the big LLMs accountable for all the content they are illegally crawling (ie: stealing). And to get beyond this moment, he says, everyone from Google and OpenAI to Perplexity and Anthropic, needs to move to a “Spotify model” that fairly shares revenue with the human creators of knowledge. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Yesterday’s show from the DLD conference was about the need for Europe to relearn the language of power. Today, things get even more dire for our European friends. I asked another DLD speaker, Carl Benedikt Frey, a Swedish economic historian who teaches at Oxford, whether it’s “game over” for Europe in terms of its ability to compete with American and Chinese big tech. His answer: not yet—but close. Frey’s last book, shortlisted for the 2025 Financial Times business book of the year, is entitled How Progress Ends: Technology, Innovation and the Fate of Nations. But it’s specifically Europe’s economic progress and the fate of European nations that most concerns Frey. Unless Europeans create a true single market for services, he warns, it really could be the end of the European dream of continent-wide progress. So no more crossroads for a continent perennially at a crossroads. And that single market, Frey explains, is ultimately a matter of political rather than economic will.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
I'm just back from another stimulating Digital Life Design (DLD) conference in Munich where all the talk was about the growing technological and political gap with the United States and China. From Machiavelli and Hobbes to Napoleon and Bismarck, Europe invented the modern concept of state power. But decades of outsourcing security to NATO and the US have left the continent dangerously rusty both in the language and execution of power. According to Marta Mucznik, a senior analyst at the Brussels-based left-leaning International Crisis Group, "projecting power is the language of today's world." And unless European politicians relearn it, Mucznik warns, that growing gap between Europe and the bipolar reality of a US-China centric world will only continue to dramatically widen.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
For a country forever flirting with amnesia about its racial history, America sure struggles to forget. Take, for example, Bernie Goetz, the white subway vigilante, who shot four black teenagers on a NYC subway in December 1984. There’s not just one - but two major new books about the anything but colorblind Goetz case which we’ll be discussing over the next couple of weeks. The first is by the CNN legal analyst Elliot Williams who presents it as a Rashomon style narrative in which there is no single undisputed truth. There might not be quite five truths in Williams’ Five Bullets, but interpreting this story all depends on your political and racial perspective. “If a black man had shot four white teens,” Williams reimagines, “this would be a totally different story.”Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
In his new co-authored book It’s On You, the English behavioral scientist Nick Chater exposes how the rich and powerful - the THEM - have convinced us that we're to blame for society's deepest problems. Can't lose weight? That's because YOU lack willpower—or so THEY would have you believe. But willpower, Chater argues, is a convenient myth. And that means the behavioral economists got it wrong too. Nudge theory doesn't work because human beings are far messier than the utilitarians assume. The answer isn't self-discipline. It's systemic change—and that requires politics, not self-help or even self-discipline. It’s transferring power back from THEM to YOU. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
According to the New Yorker writer Nicholas Niarchos, Africa is rich in both raw materials and tragic paradox. We know about the continent's wealth in the rare earth minerals that enable our global transition from fossil fuels to clean energy. But it's contemporary African paradoxes that Niarchos describes in his important new book, The Elements of Power. There's the paradox of clean energy's dirty secret — the horrifying cost in African suffering of our insatiable thirst for the minerals that power our electric vehicles and solar panels. Then there's the paradox of the new scramble for Africa between what he calls the "amoral" Chinese and the "immoral" Americans. And finally there's Niarchos' own personal paradox (which he doesn’t disguise) of being the scion of two of the wealthiest and most powerful families in Europe while writing a book about some of the poorest and most exploited people on the planet.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe























Just wanted to bring to someone's attention that the audio includes one recording on too of another (as of March 30).
oh Lord. this show is hilarious.only white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
oh Lord. this show is hilarious. white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
oh Lord. this show is hilarious. white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
I'm new to this show and I must say it made a very good impression. The interviewee is allowed to talk most of time, which helps us understand the topic better and lends an atmosphere of calm to the whole interview. There's another show out there which is pretty good, but the host asks such lengthy questions and at such high speed that it's hard for us, let alone to the guest, I guess, to keep up (I won't name names! Lol).