Exploring the Multiverse: Philosophy to Science
Author: Infinite Insights SM
Subscribed: 9Played: 32Description
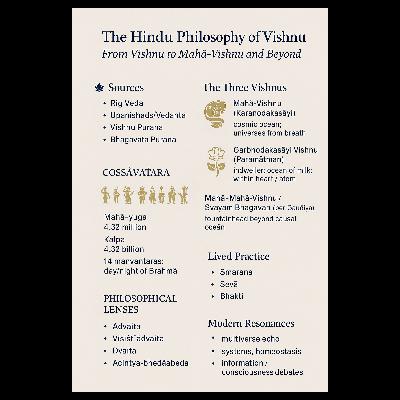
This podcast episode explores the concept of the multiverse, comparing and contrasting its presence in modern science and ancient Hindu mythology. The episode delves into the Hindu understanding of the cosmos, particularly its multilayered structure of "lokas" or realms, and how stories from the Mahabharata and Ramayana depict the interaction between these different realms. It further highlights examples from Hindu scriptures, like the story of Lord Krishna and King Muchukunda, to showcase how the idea of multiple realities is embedded in their narratives. The episode also touches upon the philosophical implications of the multiverse in the Advaita Vedanta school of thought, suggesting that the true nature of existence is an underlying oneness, beyond the illusion of individual realities. Finally, the episode concludes by emphasizing the significance of this ancient concept in fostering humility and a sense of interconnectedness in the modern world.