Discover The Rx Bricks Podcast
The Rx Bricks Podcast

The Rx Bricks Podcast
Author: USMLE-Rx
Subscribed: 278Played: 6,350Subscribe
Share
© 2024 USMLE-Rx
Description
The Rx Bricks podcast from USMLE-Rx is designed to help you master medical school. Each episode is an audio version of one of our revolutionary Rx Bricks, which are short, high-yield, interactive learning modules. Each week, we present a new audiobrick based on an important basic science topic (e.g., pressure-volume loops) or clinical concept (e.g., ischemic heart disease). Learn more at www.usmle-rx.com
111 Episodes
Reverse
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Shock brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Tackle High-Yield Concepts for USMLE Step 2 CK Cardiology
This interactive session, led by Dr. Abraham Titus (Hematology/Oncology Fellow, University of South Alabama) and ScholarRx’s Jeff Downing, focuses on challenging USMLE Step 2 CK cardiology questions that will sharpen your clinical decision-making skills and deepen your understanding of cardiovascular medicine.
WHAT YOU’LL LEARN: In this episode, we work through four board-style questions using our proven systematic approach that helps you think like a clinician first, then a test-taker second. You’ll learn how to apply clinical guidelines and make evidence-based management decisions through detailed explanations that go beyond just identifying the correct answer.
Topics Covered:
Cardiovascular risk management and pharmacotherapy
Acute coronary syndrome management strategies
Peripheral vascular disease evaluation and treatment
Secondary hypertension workup and management
Perfect for:
Medical students preparing for USMLE Step 2 CK
Clinical year medical students on cardiology rotations
IMGs studying for board exams
Anyone looking to strengthen their cardiology clinical reasoning
Review the full test: https://usmle-rx.scholarrx.com/share/1do75erd2wnmg0y
Free Resources:
Biochemistry Course: https://usmle-rx.com/biochemistry-course/
More Rx Bricks Podcasts: https://usmle-rx.com/podcast
Study Planner: https://go.usmle-rx.com/study-schedule/
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Physiology of the Renal Tubular System brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Thrombotic Disorders: Foundations and Frameworks brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Physiology of Diuretics brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Join us for this special edition of the Rx Bricks Podcast, featuring a complete Rx Question Lab session designed to help medical students master high-yield neurological concepts for USMLE Step 1.
In this interactive session, we work through four challenging board-style questions that cover essential neurology topics, including speech disorders, genetic syndromes affecting the nervous system, stroke recognition, and neurological pain conditions. Learn systematic approaches to neuroanatomy questions and develop the clinical reasoning skills needed to tackle even the most complex neurology scenarios on Step 1.
Dr. Titus, a hematology/oncology fellow at the University of South Alabama, provides expert explanations that connect basic neuroanatomical concepts with clinical presentations, helping you understand not just the correct answers but the underlying pathophysiology.
Whether you’re struggling with neuroanatomy or looking to refine your knowledge of neurological disorders, this Question Lab offers practical strategies and insights that will boost your confidence on exam day.
Perfect for medical students and IMGs preparing for USMLE Step 1. For more USMLE-Rx resources, visit www.usmle-rx.com and use the code RXPOD for 30% off any new subscription.
This special edition was recorded live during our regular Rx Question Lab series. Learn more at https://go.usmle-rx.com/question-lab
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Emergent Hypertension brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Glucose is the main source of energy for all forms of life, but it isn’t usually stored as individual C6H12O6 molecules. Animals use glycogen to do that job. Glycogen is a large branched polymer of glucose molecules, linked together by α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds. The liver and muscles break down the stored glycogen whenever the body needs an extra boost of glucose.
Glycogen storage diseases are genetic defects in glycogen metabolism resulting in accumulation of glycogen. What happens when macromolecules accumulate in cells? Cell damage and dysfunction.
Because the liver and muscles are the two main organs that use glycogen, they are also the two most affected by glycogen storage diseases. In the liver, glycogen accumulation leads to hypoglycemia since the glycogen can’t be broken down to glucose. Damage to the liver from extra glycogen can also lead to liver failure or even liver cancers. In the muscles, glycogen accumulation causes weakness, exercise intolerance, and potentially heart failure.
There are at least 12 distinct glycogen storage diseases, but we’ll cover only the 4 most common ones.
After listening to this Audio Brick, you should be able to:
Identify the most common glycogen storage diseases: von Gierke disease (type 1), Pompe disease (type 2), Cori disease (type 3), and McArdle disease (type 5).
Identify the enzymes deficient in each of the most common glycogen storage diseases.
Describe the clinical manifestations of each of the most common glycogen storage diseases.
Describe management for each of the most common glycogen storage diseases.
You can also check out the original brick from our Cellular and Molecular Biology collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Acid-Base Disorders: Putting it all Together brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including over 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Looking for more information on this topic? Check out the Adrenal Insufficiency brick.
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
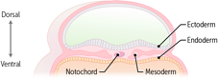
Early in fetal development, the precursors of the major systems in the body are outlined. The three germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) are formed during the third week of development. We’ll focus on the ectoderm, from which the entire nervous system (central and peripheral) forms.
But first, let’s back up to review the anatomy of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) so that we know what the end products of their development are. The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord; the PNS is composed of the 31 pairs of spinal and 12 pairs of cranial nerves and all the ganglia.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
List the derivatives of ectoderm.
Define neurulation and explain how it occurs, including closure and the dates of neuropore closure.
Describe the origin, migration, and fate of neural crest cells, particularly those that form the peripheral nervous system.
Explain how the neural tube is organized into three layers.
Describe how the spinal cord develops from the neural tube, and describe the contributions of each to these layers to the structure of the mature spinal cord, with emphasis on the alar and basal plates.
Describe the development of the brain, including the five brain vesicles, the brainstem, and the cerebral cortex.
You can also check out the original brick on the development of the nervous system from our Neurology and Special Senses collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: usmle-rx.com/blog-posts
X: @usmle_rx_
Instagram: @usmle_rx_
YouTube: youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmle-rx.com/free-bricks/
from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
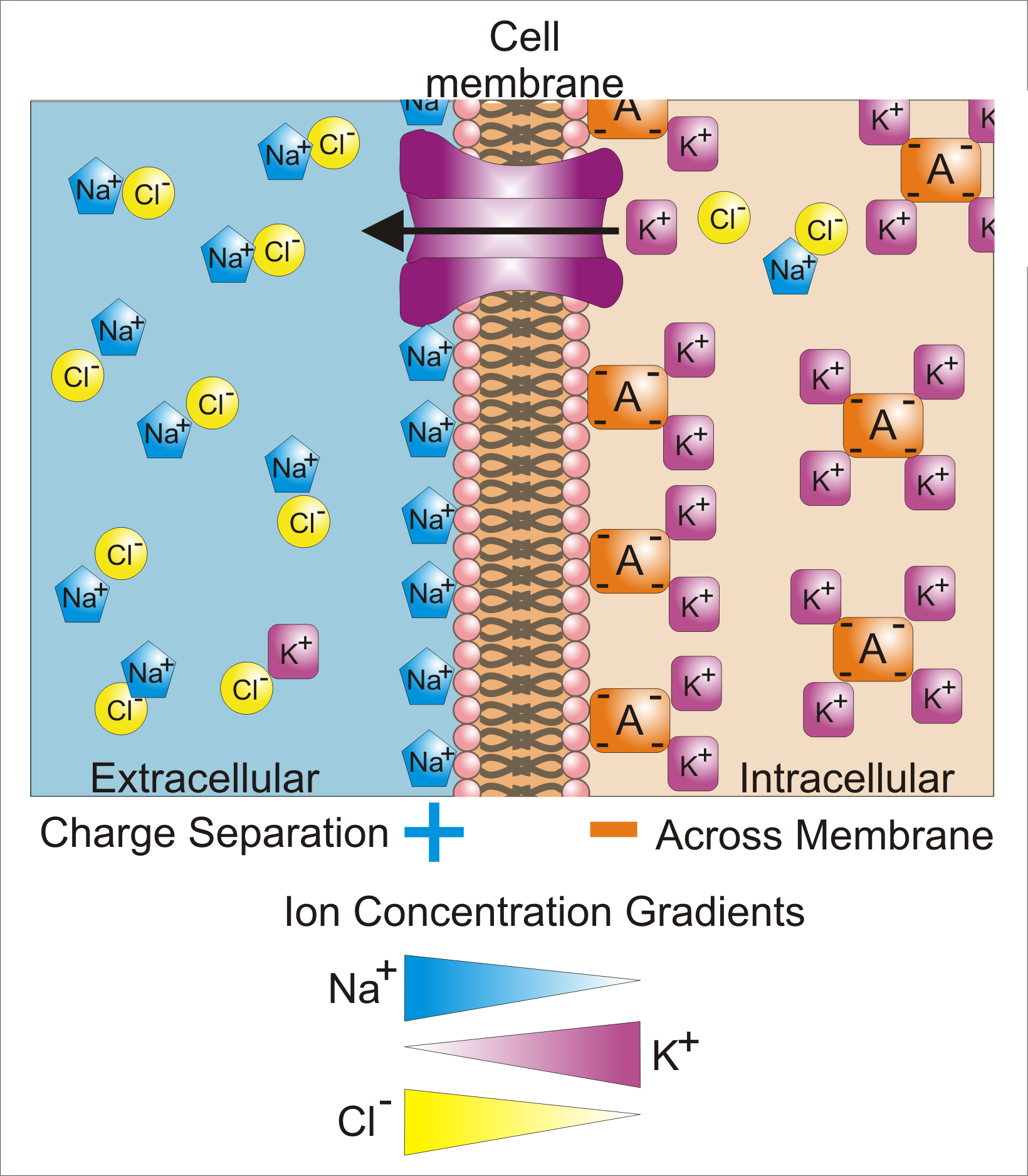
Differences in ion concentrations inside and outside a cell cause a difference in the charge of the intracellular and extracellular environments. This electrical polarization of a cell relative to its environment is referred to as cellular membrane potential. This potential serves as an energy source for a variety of cellular functions and as a way for excitable cells like muscle cells and neurons to communicate their signals. A cell controls its membrane potential by regulating the concentration of multiple ions and other charged particles. Let’s take a closer look at the biochemistry behind the cell membrane potential.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Define equilibrium and describe the forces at work on ions across a biological membrane.
Discuss the importance of the Nernst equation and equilibrium potentials.
Describe the importance of Na-K-ATPase in relation to the resting membrane potential (Vr).
Describe the nonequilibrium steady-state (NESS).
Define and discuss the chord conductance equation.
You can also check out the original brick from our Cellular Biology collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
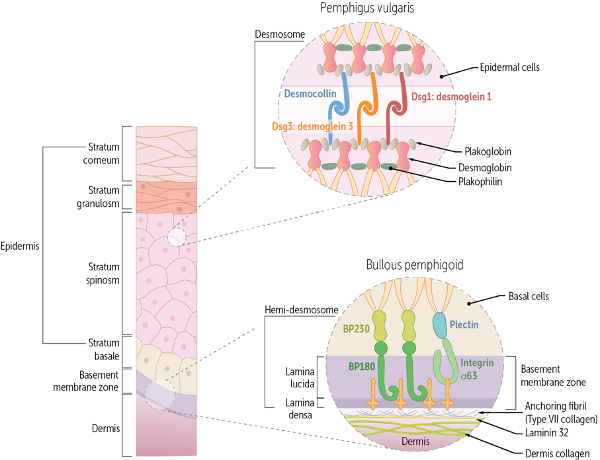
What are bullous skin disorders? Bullae are fluid-filled blisters >1 cm in diameter. They can be caused by infection, mechanical stress, or a malfunctioning immune system. In this discussion, we tackle the latter, focusing on the most common autoimmune bullous (blistering) disorders: pemphigus vulgaris, bullous pemphigoid, and dermatitis herpetiformis. Distinctly, the blisters in each of these disorders involve different layers of the skin and autoantibodies against different proteins.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Describe the typical clinical presentation, risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnostic features, and treatment of pemphigoid vulgaris.
Describe the typical clinical presentation, risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnostic features, and treatment of bullous pemphigoid.
Describe the typical clinical presentation, risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnostic features, and treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis.
You can also check out the original brick on Bullous Skin Disorders from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
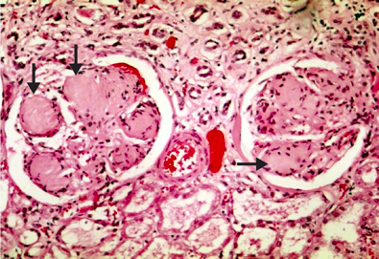
A macrovascular complication of diabetes, diabetic nephropathy is progressive, chronic kidney disease seen in patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, usually after at least 10 years of hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels). The three main lesions that are seen in the kidney in patients with diabetes are glomerular lesions, vascular lesions, and pyelonephritis. This brick will focus primarily on the first two of these three lesions; diabetic pyelonephritis is covered in a separate brick.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Define diabetic nephropathy.
Outline the timeline of progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN) by urine, serum, and histologic criteria.
Describe the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy.
Outline the prevention of diabetic nephropathy and, once it is established, how to slow its progression.
Describe the management of diabetic nephropathy.
You can also check out the original brick from our Renal collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
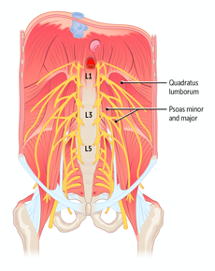
It might not be the flashiest anatomical structure, but if you want to stand upright, and keep your retroperitoneal organs (like your kidneys) in place, the posterior abdominal wall is pretty important. Located at the back of the body, bounded by the lateral abdominal walls and the posterior parietal peritoneum, the posterior abdominal wall is a complex combination of muscles, bones, nerves, and vessels that provides structural support for the body and for the organs of the retroperitoneal space.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Describe the structure and relationships of the posterior abdominal wall, including the aorta (including collateral channels), inferior vena cava (including collateral tributaries), lymphatics, muscles (psoas major, quadratus lumborum), sympathetic chain, and lumbar plexus.
Describe the relationship of the kidneys in the retroperitoneal space as it relates to posterior abdominal wall anatomy.
You can also check out the original brick from our Cardiovascular collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
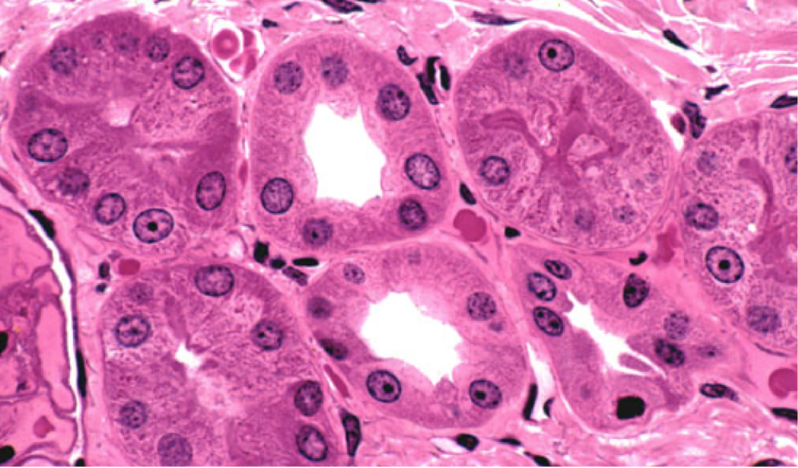
Epithelium is one of the four basic tissue types (the other three are muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue). It is found throughout the body—covering it; lining organs, vessels, and cavities; and forming glands. It absorbs nutrients, transports electrolytes, secretes hormones, and regulates body temperature by producing sweat.
We begin with some general principles of how epithelial tissue is organized, and then we describe its various components.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
List the two types of epithelium (covering/lining and glandular) and describe their functions.
Describe the structure and histologic features of epithelial tissue.
Explain how covering/lining epithelium is classified.
Describe the histologic features of glandular epithelium.
Describe the five types of epithelial intercellular junctions.
You can also check out the original brick on the Histology of Epithelial Tissue from our Musculoskeletal, Skin, and Connective Tissue collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
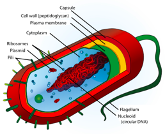
What do you know about prokaryote structure and the gram stain? Bacteria are members of a unique taxonomic kingdom consisting of prokaryotic unicellular organisms. Prokaryote is a term from ancient Greek meaning “before the kernel.” The kernel in this case is a nucleus, which prokaryotes lack. Prokaryotes also do not have any membrane-bound organelles. In fact, many of the organelles found in eukaryotes—like an endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes—are completely absent in prokaryotes.
Bacteria first began to be identified by a “defective method.” Or so its Danish inventor, a recent medical school grad named Hans Christian Gram, deemed it in 1884. Gram was working with lung tissue from cadavers who had died of infections from Streptococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae when he discovered that those organisms reacted differently to certain substances under the microscope, and—voilà—the Gram stain was born, to identify gram-positive bacteria. The defect he mentioned was overcome by German pathologist Carl Weigert, who added a final step to Gram’s procedure and gave us the method to identify gram-negative bacteria. We’re still using the same techniques more than 130 years later!
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Describe the structure of prokaryotic cells.
Discuss the physiologic niche of bacteria and their growth characteristics.
Describe the staining characteristics and classification and identification of bacteria.
To learn more about prokaryote structure and the gram stain, check out the original brick on Gastrointestinal Regulatory Substances from our Gastrointestinal collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
What Is Global Health?
In our increasingly interconnected world, health challenges transcend national boundaries and demand global solutions. Global health is an interdisciplinary field of study and practice that seeks to improve the health and well-being of populations worldwide, focusing on the health challenges that require global and national action in every country. It encompasses epidemiology, public health, medicine, environmental health, anthropology, sociology, health policy, and economics.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Explain how globalization impacts health.1
Explain how health status varies across countries, time, age, and gender.2
Identify the main threats to global health.
You can also check out the original brick from our Global Health collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/
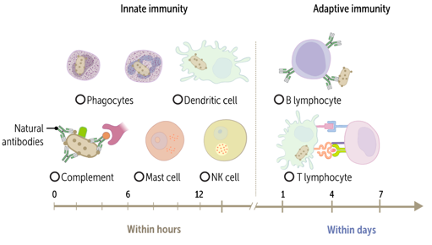
How do we survive in a complex environment filled with harmful organisms that thrive on colonizing us? Our heroic defender is the immune system, a network of organs and cell lines that exist with the mission of protecting the body from harm. While we often recognize the pathogen-fighting capabilities of the system, we can sometimes forget that the immune system is also crucial in ensuring the body is kept safe from itself, as in when our cells transform into cancer cells. On the dark side, sometimes our immune system can get overactive, reacting against our own normal body tissue. Taken together, the immune system is both critical for survival and a vital topic for new medical research.
After listening to this AudioBrick, you should be able to:
Discuss the main purposes of the immune system.
Briefly explain how the innate immune system works, and describe how antigens are transferred from the innate to the adaptive immune system (dendritic cells).
Briefly describe the main purpose of the adaptive immune system, and explain how the two arms (cellular and humoral) work.
Describe what happens after an immune response is finished.
You can also check out the original brick from our Immunology collection, which is available for free.
Learn more about Rx Bricks by signing up for a free USMLE-Rx account: www.usmle-rx.com
You will get 5 days of full access to our Rx360+ program, including nearly 800 Rx Bricks. After the 5-day period, you will still be able to access over 150 free bricks, including the entire collections for General Microbiology and Cellular and Molecular Biology.
***
If you enjoyed this episode, we’d love for you to leave a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps with our visibility, and the more med students (or future med students) listen to the podcast, the more we can provide to the future physicians of the world.
Follow USMLE-Rx at:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/usmlerx
Blog: www.firstaidteam.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/firstaidteam
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/firstaidteam/
YouTube: www.youtube.com/USMLERX
Learn how you can access over 150 of our bricks for FREE: https://usmlerx.wpengine.com/free-bricks/









5