Discover Weekly Breakthroughs
Weekly Breakthroughs

Weekly Breakthroughs
Author: Weekly Breakthroughs
Subscribed: 0Played: 0Subscribe
Share
© weekly_breakthroughs
Description
Welcome to the Weekly Breakthroughs newsletter/podcast, your go-to source for the latest breakthroughs in medicine, health innovation, biotech, and cutting-edge research. Twice a week, I sift through the flood of medical news to bring you the most fascinating discoveries, from game-changing treatments and AI-powered diagnostics to mind-blowing advancements in genetics and neuroscience.
Each episode is a fast-paced, insightful roundup of the most compelling studies and developments, breaking them down into clear, engaging discussions that highlight why they matter and how they could shape the future of medicine. Whether you're a healthcare professional, researcher, or just someone fascinated by medical progress, you'll get concise, expert-driven analysis with a touch of curiosity and humor.
Tune in and stay ahead of the curve—because the future of medicine is happening now. 🚀
weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
Each episode is a fast-paced, insightful roundup of the most compelling studies and developments, breaking them down into clear, engaging discussions that highlight why they matter and how they could shape the future of medicine. Whether you're a healthcare professional, researcher, or just someone fascinated by medical progress, you'll get concise, expert-driven analysis with a touch of curiosity and humor.
Tune in and stay ahead of the curve—because the future of medicine is happening now. 🚀
weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
23 Episodes
Reverse
🏫 The AI Hogwarts | 💉 Drug Discovery-----------------------------------------------------------------------Alpha School: Reimagining EducationInside the Model: What Alpha Says WorksAlpha School Alpha School, co-founded by MacKenzie Price, emerged as a response to the outdated industrial-era education system, drawing inspiration from historical elite tutoring models like Socrates mentoring Plato. Price, an entrepreneur and podcaster, launched Alpha to address fundamental flaws in traditional schooling—such as the "one teacher, many students" assembly-line approach that stifles individual progress and treats school like "spinach: good for you but endured." In her Modern Wisdom podcast discussion with Chris Williamson, Price outlines Alpha's history, starting as a bold experiment to foster curiosity and resilience, evolving into multiple campuses emphasizing personalized, mastery-based learning over rote compliance. The model integrates AI for adaptive instruction, condensing core academics into two hours daily via personalized apps that map knowledge gaps and interests, incorporating learning science like spaced repetition and immediate feedback for up to 5x faster mastery. Guides (formerly teachers) shift to motivational mentors, while afternoons focus on life skills workshops—financial literacy, emotional resilience, entrepreneurship, even practical tasks like changing a tire—and passion-driven "masterpiece" projects, with no homework to promote intrinsic drive. Price shares outcomes: students achieve top 2% national benchmarks, closing gaps rapidly (e.g., from behind to 90th percentile in two years), with examples like student-led initiatives in high-poverty areas like Brownsville. She addresses challenges, noting resistance from skeptics on screen time and scalability, but counters that AI enhances, not replaces, human connection, proven in expansions to over a dozen sites including Houston, Phoenix, and NYC by 2025.Implications: Price's vision could catalyze a paradigm shift, blending AI personalization with real-world prep to equip kids for an AI-disrupted future, potentially extending healthier lifespans through reduced stress and lifelong learning joy. If scaled publicly, it might equalize opportunities in underserved areas, reallocating resources from lecturing to mentorship and slashing remediation needs. However, success demands transparency on data privacy, equitable access beyond $10K–$65K tuition, robust evidence of durable skills over test scores, and balancing tech with social development to avoid isolation—ultimately questioning if this "fix" for broken education unlocks unprecedented human potential or exacerbates divides in a polarized school-choice landscape.Alpha in Brownsville: Two-Hour Academics, All-Day MasteryAlpha in BrownsvilleAlpha’s Brownsville campus runs on an AI-first schedule: roughly two hours a day of adaptive, mastery-based academics delivered through apps; the rest of the day shifts to workshops, life skills, and passion “masterpiece” projects. The school replaces traditional lecturers with adult “guides” who handle motivation, mentoring, and accountability rather than direct instruction. Reported outcomes include faster progression through core subjects and strong performance on standardized benchmarks, which Alpha attributes to one-to-one pacing, spaced-repetition, rapid feedback, and continuous quizzing inside its software stack. Supporters frame the model as a way to meet any learner “exactly where they are,” compressing time-on-task while freeing afternoons for deep work; skeptics worry about over-reliance on screens, limited peer discourse, and whether results generalize beyond a self-selecting private-school population. Expansion plans and media attention have pushed the model into the school-choice debate—can a private, AI-heavy system translate to public settings with different constraints? Implications: If Brownsville’s results hold at scale, districts could reallocate teacher time from lecturing to mentoring, shrink remediation gaps with true mastery pacing, and return hours to projects and arts. But guardrails matter: transparency on assessment data, equity for students without ed-tech access at home, privacy protections around learning analytics, and evidence that AI tutors build durable understanding—not just short-term gains—will decide whether this becomes a viable public-education blueprint.Demis Hassabis on AI’s Role in Healthcare and Drug DiscoveryYouTube – Demis Hassabis InterviewDeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis lays out a vision for how AI can transform healthcare and accelerate drug discovery. He highlights the success of AlphaFold, which mapped nearly all known protein structures, and describes how this breakthrough is already being used by researchers worldwide to study disease mechanisms and design therapies. Hassabis emphasizes that AI’s true power is its ability to model complexity—seeing connections across biology that are invisible to human intuition and compressing years of lab work into months.The interview also addresses the broader medical ecosystem. Hassabis notes that AI isn’t meant to replace doctors or scientists but to act as a powerful assistant, freeing human experts to focus on creativity, judgment, and patient care. He acknowledges the hurdles: integrating AI safely into clinical workflows, ensuring results are reproducible, and creating regulatory frameworks that can adapt to rapidly evolving technologies. But he argues the trajectory is clear—AI is already shifting healthcare from a reactive model to a proactive one, where diseases can be predicted, detected earlier, and ultimately prevented.Implications: If this vision holds, AI will not just accelerate the pace of biomedical research—it could redefine it. Drug discovery pipelines may become faster, cheaper, and more precise, opening the door to personalized treatments and therapies for previously “undruggable” diseases. For clinicians, AI tools could mean earlier diagnoses, fewer errors, and more time spent with patients. Yet success will depend on trust: transparency in AI models, equitable access to breakthroughs, and careful safeguards around privacy and ethics. Hassabis frames AI in medicine not as a distant dream but as an unfolding reality—with the potential to reshape human health within the coming decade.Beyond the Hype: A Veteran’s Honest Assessment of AI in Drug DiscoveryDrug Target ReviewIndustry veteran Thibault Géoui argues that AI may finally be the technological shift capable of bending “Eroom’s Law,” the decades-long trend of drug discovery becoming slower and more expensive. Unlike past breakthroughs—combinatorial chemistry, high-throughput screening, or even genomics—AI isn’t just about brute force. Instead, it allows scientists to layer protein structures, gene networks, metabolic pathways, and environmental data into coherent models. The vision: “digital twins” of cells and organs where experiments can be run virtually before moving to the bench.Momentum is visible—AlphaFold has cracked protein folding with astonishing accuracy, while startups like Insilico and Recursion have shown that AI can design, screen, and analyze drug candidates end-to-end. Yet the reality is still embryonic. Only about 0.1% of global drug pipelines originate from AI, and many of the first AI-designed drugs in clinical trials have already failed. The bottlenecks are as much cultural as technical: pharma companies remain siloed and risk-averse, and there’s a shortage of “bilingual” talent fluent in both wet-lab science and advanced AI. Géoui likens today’s progress to the video game industry in the 1980s—foundational, exciting, but years away from maturity.Implications: If AI succeeds, it could redefine drug discovery by compressing development cycles from years to months, lowering costs, and unlocking cures for diseases once thought untouchable. But progress will demand cultural disruption inside pharma—building cross-disciplinary teams, tearing down silos, and embracing new workflows. Regulators will need to adapt to faster pipelines, new data types, and novel trial designs, while society grapples with equity, access, and ethical oversight. Hundreds of AI-biotech startups are racing forward, but only a handful will survive to deliver consistent Phase III wins. The promise is enormous—lifesaving treatments, healthier aging, extended lifespan—but the transformation will be gradual, requiring proof through repeated clinical success rather than hype.Thanks for reading! Stay tuned for more insights on transformative discoveries shaping health, science, and technology. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🔋 AI Battery Breakthrough | 🩸 Longevity Secrets | 💊 HIV | 🇨🇳 China's Drug Discovery Race | 🌐 DeepMind’s Genie-3 | 🤖 OpenAI Opens Up-----------------------------------------------------------------------AI Uncovers the Future of Batteries—and It's Not LithiumAI Battery DiscoveryAI-driven research has identified promising battery materials far superior to lithium, potentially revolutionizing energy storage. The newly discovered materials offer dramatically improved efficiency, lower costs, and fewer environmental impacts.Implications: This breakthrough could accelerate renewable energy adoption and reshape global battery production, though extensive testing and scaling challenges must be addressed before widespread adoption.Blood of Long-Lived Individuals Reveals Key DifferencesLongevity Blood StudyResearchers analyzing blood samples from exceptionally long-lived individuals uncovered unique biological markers associated with slower aging. The findings suggest specific metabolic and immune traits that enhance longevity and healthspan.Implications: Understanding these biological differences may lead to targeted therapies promoting healthier aging, but translating insights into effective treatments requires rigorous testing and validation in broader populations.China's AI Drug Discovery Boom Shakes Up Global PharmaChina's AI Pharma SurgeChina’s rapidly growing AI-driven drug discovery sector is transforming the pharmaceutical industry, powered by extensive data resources, strong government backing, and swift technological adoption. This growth has enabled Chinese companies to rival Western counterparts in innovation, accelerating timelines from drug concept to clinical trials and commercialization.Implications: China's advancement in AI drug discovery could significantly impact global healthcare markets and accelerate worldwide pharmaceutical innovation. However, navigating geopolitical dynamics, intellectual property challenges, and global regulatory compliance will be crucial for sustained success.The First Widespread Cure for HIV Could Be in ChildrenHIV Cure for ChildrenNew research highlights a groundbreaking strategy aiming for a functional cure for HIV, potentially starting with children. Early intervention shortly after birth appears to limit the virus's ability to form hidden reservoirs, potentially allowing the immune system to fully clear the infection. Early results from clinical studies indicate promising outcomes, suggesting that widespread curative strategies could first become feasible in pediatric populations.Implications: Achieving a functional HIV cure in children could radically shift global HIV treatment strategies, drastically improving long-term quality of life and reducing lifelong reliance on antiviral drugs. However, extensive clinical trials, ethical considerations, equitable access, and practical challenges in low-resource settings will determine real-world feasibility.DeepMind Introduces Genie-3: A Leap in World ModelsDeepMind Genie-3DeepMind’s latest AI model, Genie-3, represents a major advancement in world modeling, capable of accurately simulating complex real-world scenarios. Its sophisticated predictions promise significant improvements in autonomous systems, planning, and strategic decision-making.Implications: Genie-3's capabilities could revolutionize industries from logistics to robotics, but ensuring ethical use, transparency, and managing computational demands are critical next steps.OpenAI Launches 'Open Models' InitiativeOpenAI Open ModelsOpenAI has launched "Open Models," a groundbreaking initiative granting wider access to its state-of-the-art AI models. This move aims to democratize advanced AI research, fostering innovation, collaboration, and greater transparency within the AI community.Implications: Broader access could accelerate AI development globally, enhancing inclusivity and innovation. Still, responsible management, ethical guidelines, and regulatory frameworks will be crucial to prevent misuse.Thanks for reading! Stay tuned for more insights on transformative discoveries shaping health, science, and technology. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🦟 Mosquito-Killing Pills | ✈️ AI Flight Deals | 🧬 Stuttering Genetics | 🧠 Whole-Brain Organoids | ⚛️ Einstein Challenged | 🫖 Tea Cyberattack-----------------------------------------------------------------------Pill Turns Human Blood Deadly to MosquitoesMosquito-Killing PillResearchers developed a revolutionary pill that makes human blood lethal to mosquitoes, drastically reducing bites and the transmission of mosquito-borne diseases. Early trials demonstrated that mosquitoes feeding on treated blood died rapidly, significantly disrupting the insect's life cycle and reproduction.Implications: This approach could dramatically lower rates of diseases like malaria and dengue fever globally. Still, widespread use requires comprehensive safety assessments, understanding ecological impacts, and monitoring potential resistance development.AI Helps Travelers Find Cheapest FlightsAI-Powered Cheap FlightsDelta Air Lines is integrating advanced AI to help passengers automatically find the cheapest possible fares, dramatically simplifying ticket purchasing. The technology constantly scans routes and fares, alerting customers immediately when prices drop significantly.Implications: AI-assisted travel booking could redefine affordability and convenience in air travel, potentially reshaping consumer expectations and airline competition. However, industry-wide adoption depends on consumer privacy protection, pricing transparency, and equitable access to the technology.Genetic Discovery Offers Insights into StutteringGenetic Link to StutteringA groundbreaking study identified specific genetic variations linked to stuttering, providing crucial new insights into the biological basis of this complex speech disorder. The findings pinpoint genes involved in neurological pathways responsible for speech fluency, opening pathways for targeted treatments.Implications: Understanding stuttering's genetic underpinnings may lead to personalized therapies and early interventions. Still, further research is needed to translate these genetic insights into effective, broadly accessible clinical treatments.Scientists Develop First-Ever Whole-Brain OrganoidWhole-Brain OrganoidScientists successfully created the world's first "whole-brain organoid," a lab-grown miniature brain capable of modeling complex neural functions and structures with remarkable fidelity. This organoid mimics interconnected brain regions, enabling researchers to study brain disorders and developmental processes more accurately.Implications: Advanced brain organoids could significantly improve disease modeling and drug testing for neurological conditions, reducing reliance on animal experiments. However, ethical concerns around organoid consciousness and moral considerations require careful navigation.MIT Experiment Challenges Einstein's Quantum AssumptionsMIT Quantum BreakthroughIn a historic experiment, MIT physicists challenged Einstein's assumptions regarding quantum entanglement and locality. Their groundbreaking tests confirmed predictions that defy Einstein's traditional views, reinforcing quantum mechanics' fundamental principles and potentially reshaping future quantum research.Implications: This confirmation could accelerate developments in quantum computing, secure communications, and foundational physics research. Yet, widespread practical application depends on overcoming significant technological and conceptual hurdles.Hackers Breach Major Tea Company, Exposing Security RisksTea Company CyberattackA prominent tea manufacturer experienced a major cyberattack, exposing vulnerabilities in operational technology and data management. Attackers disrupted production and threatened supply chains, prompting industry-wide concern regarding cybersecurity preparedness in traditionally low-tech sectors.Implications: The incident underscores critical cybersecurity gaps beyond traditional tech industries, emphasizing the urgent need for robust security infrastructure and proactive strategies across all sectors. Effective response requires regulatory attention, cross-industry collaboration, and enhanced cyber-risk education.Thanks for reading! Stay tuned for more insights on transformative discoveries shaping health, science, and technology. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🧬 AI Drug Breakthroughs | 🍬 Sugar-Based Cancer Killer | 🤖 AI's Thinking Paradox | 👂 Gene Therapy for Deafness | 🩸 Stem Cell Safety Boost-----------------------------------------------------------------------ILargest Four-Day Workweek Trial Shows Happier Workers, Equal ProductivityFour-Day Workweek TrialThe most extensive trial yet on the four-day workweek revealed significant improvements in employee happiness, reduced stress levels, and maintained productivity. Thousands of participants across various industries reported better work-life balance, higher job satisfaction, and no notable drop in output despite fewer working hours.Implications: These results strengthen the case for widespread adoption of shorter workweeks, potentially transforming global labor practices. However, industries must address logistical challenges, maintain productivity standards, and consider economic impacts before broader implementation.AI-Designed Drugs Target Previously Undruggable ProteinsAI Drug DiscoveryAI-powered drug discovery platforms have successfully designed compounds targeting previously "undruggable" proteins involved in cancer and Alzheimer's disease. These AI-designed molecules effectively bind to challenging protein sites, offering promising new avenues for therapy development.Implications: This AI breakthrough could revolutionize drug development, unlocking treatments for diseases currently lacking effective therapies. Nevertheless, rigorous clinical validation, safety testing, and cost management remain critical steps.Supercharged Sugar Substitute Kills Cancer CellsSugar Substitute vs. CancerResearchers modified a common sugar substitute, dramatically boosting its anti-cancer activity. The enhanced compound selectively targets cancer cells, disrupting their metabolism and leading to cell death, all without harming healthy cells in early studies.Implications: This discovery offers potential for low-cost, targeted cancer treatments. Yet, extensive human trials must confirm effectiveness, safety, and lack of unintended metabolic consequences.The "Weird AI Problem": Why Longer Thinking Makes AI DumberAI Thinking ParadoxAnthropic researchers uncovered an intriguing paradox: allowing AI models more processing time can sometimes decrease their accuracy and decision-making quality. The phenomenon, dubbed the "Weird AI Problem," challenges assumptions that longer computational time naturally improves outcomes.Implications: Understanding and addressing this paradox is crucial for developing reliable, efficient AI systems, particularly in high-stakes fields like healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles.Gene Therapy Successfully Reverses Genetic DeafnessGene Therapy for DeafnessA groundbreaking gene therapy successfully restored hearing in patients with genetic deafness across multiple age groups. By correcting specific genetic mutations in auditory cells, the therapy led to measurable improvements in hearing function, with sustained benefits.Implications: This breakthrough could offer lasting solutions for hereditary deafness. Wider clinical adoption depends on long-term safety, ethical approval, patient selection criteria, and affordability.Stem Cell Transplant Made Safer by Removing Toxic CellsSafer Stem Cell TransplantsResearchers have developed a novel method to remove toxic cells from stem cell transplants, significantly reducing dangerous side effects like graft-versus-host disease. Early clinical applications showed improved patient outcomes, fewer complications, and enhanced overall safety.Implications: Enhanced safety protocols could expand stem cell treatment options and accessibility. Broader application will require larger trials, robust clinical validation, and cost-effective implementation.Thanks for reading! Stay tuned as we continue exploring transformative innovations reshaping technology, education, construction, and more. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
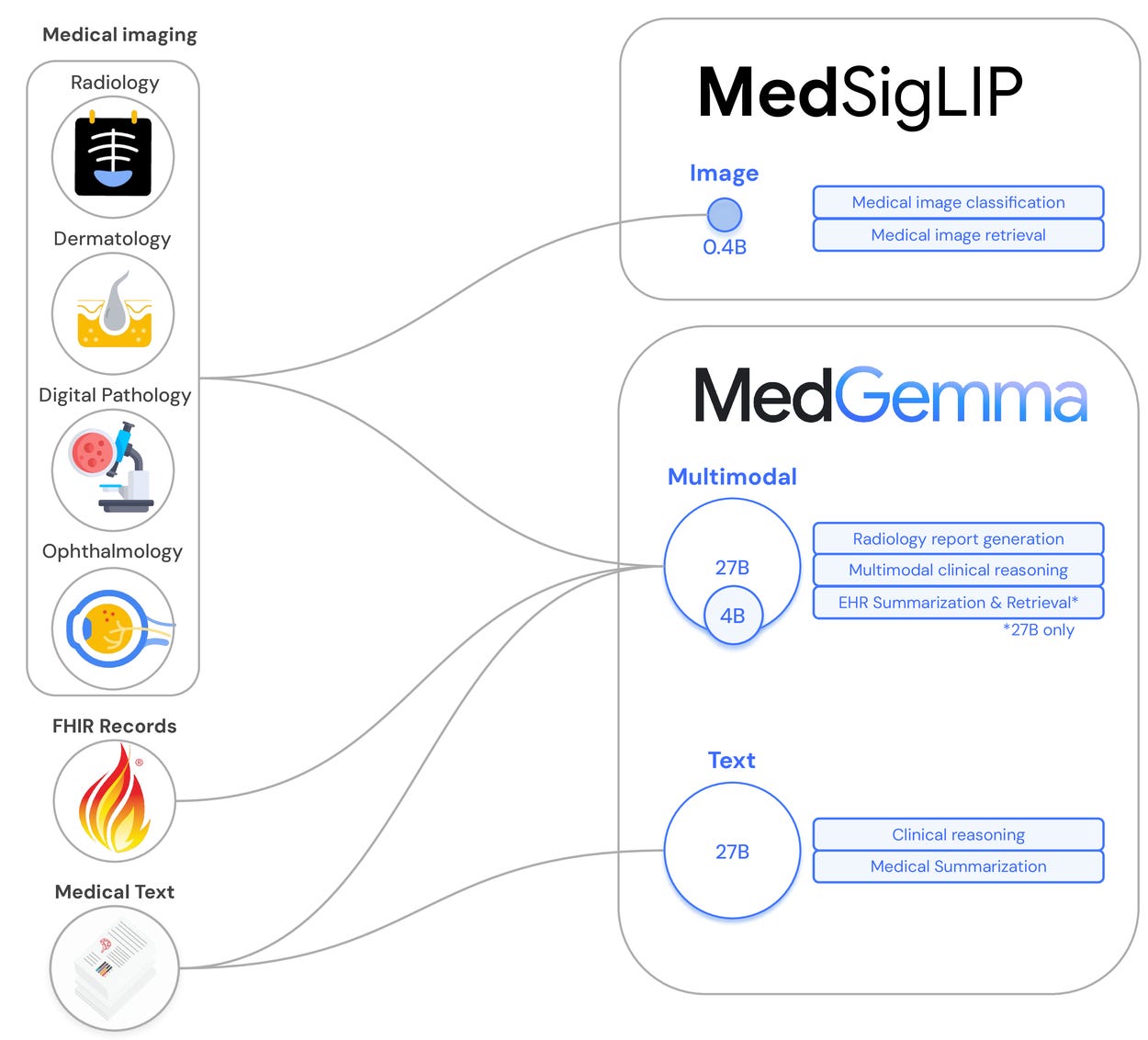
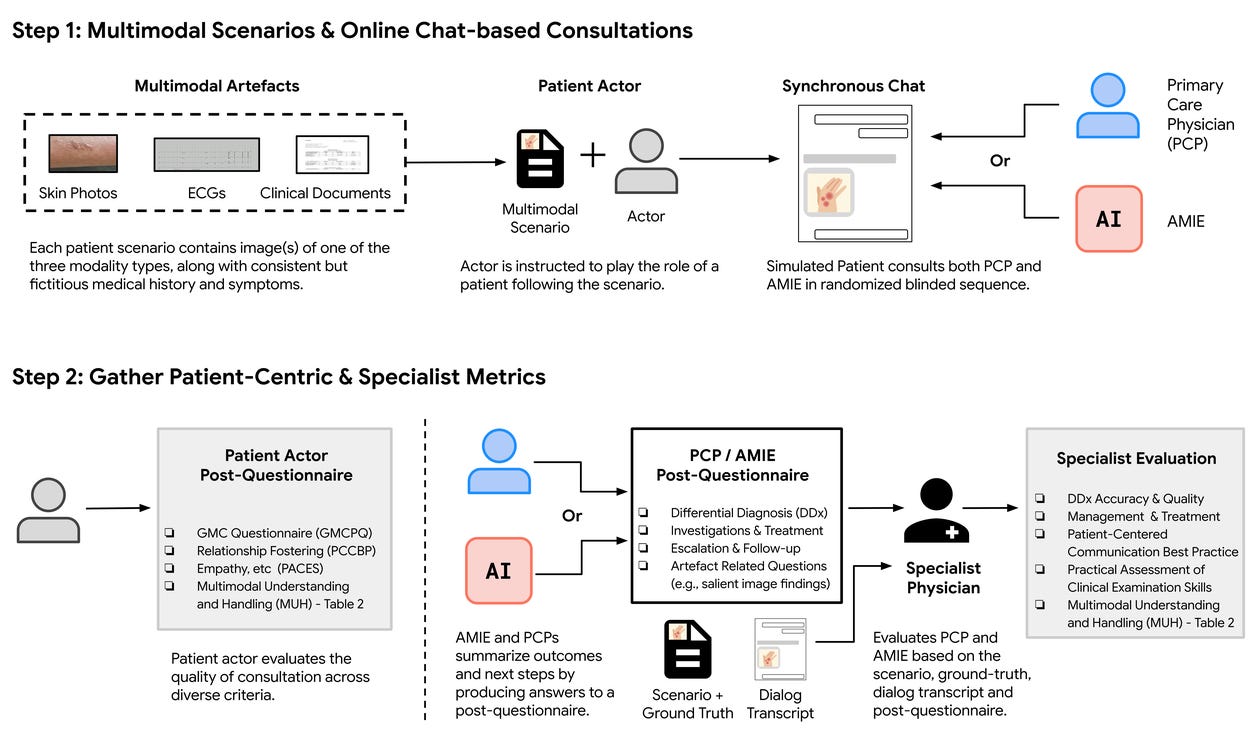
🏥 AI in Healthcare | 🎓 Classroom AI Allies | 💻 Evaluating AI Efficiency | 🔋 Battery Fire Safety | 📹 AI Videos & YouTube | 🏗️ Massive 3D-Printed Construction-----------------------------------------------------------------------Inside Google's MedGemma: AI Models Revolutionizing HealthcareGoogle's MedGemmaGoogle unveiled MedGemma, a sophisticated AI model designed specifically for healthcare applications, capable of accurately analyzing medical texts, images, and clinical data. The system promises enhanced diagnostic precision, personalized treatment insights, and streamlined patient management through advanced multimodal processing.Implications: Integration of AI like MedGemma could dramatically improve medical decision-making and patient outcomes, but real-world effectiveness will depend on robust data privacy, clinician trust, and clear regulatory oversight.AI in K-12 Education: Partners, Not ReplacementsAI in K-12 EducationResearch from the University of Connecticut emphasizes AI’s role as supportive tools rather than replacements for educators in K-12 classrooms. AI systems are providing personalized learning experiences, assisting teachers with data-driven insights, and fostering student engagement while reinforcing human-led instruction.Implications: Properly balanced, AI could significantly enhance education quality and accessibility, although careful integration is essential to avoid dependence and ensure equitable access to advanced technologies.Stanford Develops Affordable Method to Evaluate AI Language ModelsAffordable AI EvaluationStanford researchers introduced a cost-effective technique to rigorously evaluate AI language models, significantly reducing resources and computational expenses previously required. This method enables broader access to testing advanced AI capabilities, helping smaller labs and startups compete in AI research.Implications: Democratizing AI evaluation methods could accelerate innovation, increase transparency, and enable broader participation—but ensuring consistent, unbiased evaluation standards remains critical.A Specialized Fire Extinguisher for EV Battery FiresEV Battery Fire ExtinguisherScientists have developed an innovative fire extinguisher specifically targeting lithium-ion battery fires in electric vehicles. Using a unique chemical formula, the extinguisher rapidly cools and safely neutralizes battery cells, significantly improving safety and reducing firefighting risks.Implications: Specialized extinguishers could greatly enhance public safety and facilitate EV adoption. Still, widespread implementation hinges on firefighter training, cost considerations, and regulatory acceptance.YouTube vs. AI-Generated Videos: No Humans, No MonetizationYouTube Policy on AI VideosYouTube clarified its stance on AI-generated content, stating that fully AI-generated videos lacking human input or oversight will not qualify for monetization. This policy aims to maintain content authenticity and prevent platform saturation by AI-produced material.Implications: This decision highlights tensions between AI creativity and platform governance, influencing how creators and tech companies manage AI's role in content creation. The impact on future digital content strategies remains to be seen.Qatar Launches World's Largest 3D-Printed Building ProjectQatar's Massive 3D ConstructionQatar initiated the world's largest-ever 3D-printed building project, using advanced COBOD printers to create large-scale residential and commercial structures efficiently. This project aims to significantly reduce construction times, material waste, and labor costs, positioning Qatar at the forefront of innovative construction methods.Implications: Large-scale 3D printing could transform global construction practices, enhancing sustainability and affordability. However, challenges including structural integrity, regulatory approval, and industry-wide acceptance remain.Thanks for reading! Stay tuned as we continue exploring transformative innovations reshaping technology, education, construction, and more. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
💊 Tylenol | 🦎 Limb Regeneration | 💻 AI Health Advances | 🩺 Kidney Repair | 🧬 Airborne DNA Detector | 🧠 Alzheimer's Breakthrough-----------------------------------------------------------------------Tylenol Stops Pain at the Source, Not Just in the BrainTylenol's New Pain MechanismA groundbreaking discovery from researchers at Hebrew University reveals acetaminophen (Tylenol) doesn't just dull pain in the brain—it also blocks pain signals at their source. Scientists identified that a metabolite called AM404 directly inhibits sodium channels in pain-sensing nerves, stopping pain signals before they even reach the brain. This overturns long-held beliefs that acetaminophen works exclusively in the central nervous system.Implications: This insight could lead to developing safer, more targeted pain medications that effectively reduce pain without common side effects like numbness or muscle weakness. However, extensive clinical research is needed to translate these findings into practical treatments.Chemical Cocktail Enables Limb Regeneration in MammalsLimb Regeneration BreakthroughResearchers successfully stimulated limb regeneration in mammals using a chemical cocktail inspired by axolotl biology. The combination reactivates dormant regenerative pathways, resulting in partial limb regrowth in mouse models—an unprecedented feat in regenerative medicine.Implications: If replicated in humans, this approach could revolutionize treatment for amputees or severe injuries. However, translating these findings to clinical practice faces challenges, including managing cell proliferation risks and ensuring functional limb regeneration.Google's AI Healthcare Initiatives at ASCOGoogle's AI Health InnovationsAt the ASCO conference, Google detailed new AI-driven initiatives aimed at transforming cancer diagnosis, treatment personalization, and healthcare data management. These tools enable faster analysis of medical data, enhancing physician decision-making and patient outcomes.Implications: Google's efforts could significantly improve oncology care efficiency and accuracy. Ensuring robust data privacy, regulatory compliance, and equitable healthcare access will be critical to the successful deployment of these AI technologies.Gene Editing Shows Promise in Kidney Disease RepairKidney Repair with Gene EditingA groundbreaking gene-editing technique successfully repaired kidney damage previously deemed irreversible, significantly restoring kidney function in animal models. The CRISPR-based method targets and repairs fibrosis-related genetic pathways, promoting healthy tissue regeneration.Implications: Such advancements offer hope for chronic kidney disease patients who currently rely on dialysis or transplants. Extensive clinical trials, ethical reviews, and careful monitoring will be required to safely translate this therapy into human applications.Handheld Device Rapidly Profiles Airborne DNAAirborne DNA DetectionA newly developed handheld device quickly identifies and profiles genetic material from airborne particles, drastically accelerating pathogen detection and environmental monitoring. This portable technology provides accurate genetic profiles within minutes.Implications: Real-time airborne DNA analysis could transform disease outbreak responses, environmental assessments, and biosecurity measures. Broader adoption will depend on cost-effective production, data security, and regulatory frameworks.Lipid-Lowering Drug Linked to Alzheimer's Cognitive ImprovementAlzheimer's Drug BreakthroughNewAmsterdam Pharma reported promising trial results linking their lipid-lowering medication to improved cognitive function and reduced Alzheimer's biomarkers. Patients showed measurable cognitive improvements alongside reduced pathological markers associated with Alzheimer's progression.Implications: This finding could revolutionize Alzheimer’s treatment by repurposing cardiovascular medications, potentially streamlining regulatory approval. Further extensive trials must confirm these benefits and evaluate long-term safety and patient-specific effectiveness.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🧬 Cancer Vaccines | 🚀 CAR-T Success | 💉 Multi-Disease Gene Therapy | 🏃 Huge Cancer/Glioblastoma 🧠 Hope-----------------------------------------------------------------------OSE Therapeutics Vaccine Boosts Cancer Survival RatesCancer Vaccine BreakthroughOSE Therapeutics unveiled impressive Phase 2 results at ASCO, showing their therapeutic cancer vaccine achieved a 65% overall survival rate in advanced cancer patients. The vaccine, designed to stimulate patients' immune systems against cancer-specific targets, significantly prolonged patient survival compared to historical benchmarks.Implications: This advancement highlights therapeutic vaccines' potential as a major addition to cancer treatment, offering personalized and less toxic options. However, larger trials are needed to confirm lasting benefits and establish widespread clinical integration.Kite's CAR-T Therapy Clears Major Safety Hurdle in LymphomaCAR-T Safety MilestoneKite Pharma's CAR-T therapy demonstrated excellent safety and effectiveness in recent lymphoma trials, significantly reducing severe side effects often associated with cellular treatments. Early data presented at ASCO shows the modified T-cells successfully targeted and eliminated cancer cells without the typical high rates of toxicity.Implications: Safer CAR-T treatments could dramatically expand patient eligibility and improve outcomes in blood cancers. Nonetheless, the complexity, cost, and manufacturing logistics still pose significant challenges to broad adoption.Gene Therapy Reverses Three Diseases with Single Bloodstream InjectionGene Therapy AdvancesScientists developed a groundbreaking gene therapy capable of simultaneously reversing three separate genetic disorders through a single intravenous injection. This innovative method delivers gene-editing tools directly into the bloodstream, correcting mutations at multiple sites with unprecedented efficiency and precision in animal models.Implications: If confirmed in human trials, multi-disease gene therapies could revolutionize treatment strategies, significantly reducing cost and complexity. But careful evaluation of long-term safety, regulatory approval, and ethical guidelines remains crucial.Exercise Shown to Improve Colorectal Cancer OutcomesExercise & Colorectal CancerA comprehensive study confirmed regular physical activity substantially improves survival and reduces recurrence in colorectal cancer patients. Researchers found exercise boosts immune function, lowers inflammation, and enhances overall recovery, directly contributing to better cancer outcomes.Implications: Integrating structured exercise programs into cancer care protocols could become standard practice, though accessibility, adherence, and personalized guidelines are necessary for broad patient benefit.UK Cancer Deaths Drop by 22% Despite Rising CasesUK Cancer Death DeclineNew UK statistics show a remarkable 22% decline in cancer deaths over the past 50 years, despite rising cancer incidence. Advances in early detection, improved treatments, and targeted therapies significantly boosted survival rates across multiple cancer types.Implications: These findings underscore the impact of continuous research and public health initiatives. Nonetheless, addressing disparities in cancer care access and outcomes remains vital for sustaining and extending these gains.CAR-T Therapy Offers New Hope for GlioblastomaCAR-T Glioblastoma BreakthroughPromising early results from Kite’s CAR-T therapy trial against glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer, indicate significant tumor shrinkage and improved patient survival. This marks a rare but critical advance in treating one of the most resistant forms of cancer, previously unresponsive to conventional therapies.Implications: CAR-T’s effectiveness in glioblastoma could open doors to treating other solid tumors. However, ensuring consistent efficacy, overcoming immune responses, and refining targeted delivery methods are essential next steps.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🔬 Real-Time Biosensors | ⚡ Gene Delivery Boost | 🧠 Migraine Breakthrough | 🐶 Cancer Connections | 👁️ Superhuman Vision | ☀️ Anti-Aging Vitamin D-----------------------------------------------------------------------Nanoscale Biosensor Tracks Molecules in Real-TimeReal-Time Molecular BiosensorScientists developed an ultra-sensitive nanoscale biosensor capable of tracking single molecules in living cells in real-time. This breakthrough technology allows unprecedented observation of cellular interactions and disease processes as they occur, dramatically enhancing biological research and drug testing.Implications: Real-time monitoring at the molecular level could revolutionize drug discovery, disease diagnostics, and personalized medicine. However, practical implementation will require substantial technological integration and validation in clinical settings.Nanostraws and Electrical Pulses Enhance Gene DeliveryNanostraw Gene DeliveryA new approach using tiny "nanostraws" combined with brief electrical pulses significantly improves the delivery of genetic material directly into cells. This method boosts transfection efficiency while minimizing cellular damage, outperforming current viral and chemical-based gene transfer methods.Implications: Enhanced gene delivery efficiency could accelerate gene therapies and cellular engineering, potentially making treatments safer and more affordable. However, safety profiles, scalability, and regulatory pathways remain critical considerations.Newfound Mechanism for Drastic Weight LossCellular Energy & Weight LossScientists have uncovered a novel biological mechanism that dramatically reprograms how cells process energy, leading to substantial weight loss in preclinical models. By targeting specific metabolic pathways, the researchers significantly increased calorie burn and improved metabolic health without altering diet or exercise routines. The discovery could pave the way for revolutionary obesity treatments.Implications: If successfully translated to humans, this metabolic approach might provide a powerful new therapeutic option against obesity and metabolic syndrome. However, extensive clinical trials will be necessary to ensure long-term safety, effectiveness, and accessibility.Dog Cancer Research Yields Insights for Childhood OsteosarcomaComparative Oncology: Dogs & KidsA comparative oncology study has identified genetic and immunological similarities between canine and childhood osteosarcoma, leading to promising treatment insights applicable to both dogs and children. Early findings point toward new therapeutic targets that could benefit human pediatric patients.Implications: Leveraging canine research may speed therapeutic development and improve outcomes for children. Yet, translating comparative findings into clinically effective therapies will require extensive validation and interdisciplinary collaboration.High-Tech Contact Lenses Offer Superhuman SightSuperhuman Vision LensesNewly developed smart contact lenses offer enhanced vision capabilities, including zoom functions, night vision, and augmented-reality overlays, drastically extending natural human vision. Early trials indicate usability and safety, opening avenues for both medical and recreational applications.Implications: Such advanced lenses could greatly assist visually impaired individuals and expand human sensory experiences, though broad adoption hinges on addressing privacy, ethical implications, and long-term eye health safety.Vitamin D Supplements May Slow Biological AgingVitamin D & AgingA large-scale study found regular vitamin D supplementation significantly slowed markers of biological aging in adults. Participants showed improved cellular health and reduced inflammatory indicators associated with chronic aging diseases.Implications: Vitamin D may represent a low-cost, accessible strategy to combat aging and chronic illness. However, individualized dosing, long-term effects, and interactions with other medications need further research before widespread recommendations are made.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🧠 Brain Chips | 🧬 CRISPR Miracle | 🫀 AI Cardiology | 🩸 Young Blood Trials | 🧪 Blood Test Insights | ❤️ Heart Transplant Breakthrough | 🌐 Remote Surgery | ⏰ Fasting Success-----------------------------------------------------------------------Brain Chip Restores Movement and SensationBrain Chip BreakthroughA groundbreaking brain-spine interface has enabled a patient with spinal cord injury to regain both movement and sensation. By decoding neural signals and transmitting them wirelessly to implanted electrodes, this chip successfully bypasses spinal damage, allowing voluntary limb control and sensory feedback for the first time.Implications: This advancement could drastically improve quality of life for paralysis patients. However, significant challenges remain, including ensuring long-term stability, affordability, and patient-specific customization, which will determine widespread adoption.AI Monitors Blood Clots in Real-Time for Cardiac PatientsAI in CardiologyA new AI-powered system now provides cardiologists with real-time monitoring and predictive insights on blood clot formation. By accurately assessing clot dynamics during procedures, doctors can rapidly adjust treatments, reducing patient risks and improving outcomes.Implications: Real-time AI diagnostics could significantly enhance procedural safety and precision in cardiology, though clinical adoption will rely on thorough validation, training protocols, and addressing data privacy concerns."Young Blood" Transfusions Enter Clinical TrialsYoung Blood Clinical TrialsClinical trials investigating transfusions of young blood into older adults have begun, aiming to explore potential rejuvenating effects on aging-related biomarkers, cognitive function, and chronic disease risk. Early results indicate improvements in certain health indicators, sparking considerable scientific interest.Implications: This controversial treatment could offer transformative benefits for aging populations if validated, yet significant ethical, regulatory, and safety concerns remain, necessitating rigorous oversight and public dialogue.New Blood Test Predicts Disease EarlierBlood Test BreakthroughScientists have developed a highly sensitive blood test capable of detecting disease biomarkers at earlier stages than current methods. Early validation trials showed impressive accuracy in identifying cancer and cardiovascular diseases well before symptoms emerged.Implications: This non-invasive test could transform preventive medicine by enabling earlier, more effective interventions. Nevertheless, its effectiveness must be confirmed across diverse populations, and implications regarding healthcare accessibility and potential overdiagnosis must be addressed.Custom CRISPR Therapy Saves Boy with Rare Genetic DiseaseLife-Saving CRISPRIn an unprecedented case, doctors successfully used a personalized CRISPR-based therapy to correct a lethal genetic disorder in a young boy. The custom-designed gene-editing treatment reversed debilitating symptoms, significantly extending his life expectancy and quality of life.Implications: Personalized gene-editing treatments could revolutionize rare disease care. Yet the high cost, lengthy regulatory processes, and ethical considerations of gene editing present substantial hurdles for broader application.Mayo Clinic Discovery Improves Donor Heart AccessDonor Heart BreakthroughResearchers at Mayo Clinic have discovered a method to significantly extend the viability of donor hearts, potentially increasing the donor pool by preserving hearts longer and improving transplant outcomes. Early clinical applications demonstrated increased transplant success rates.Implications: Expanding the pool of viable donor organs could save countless lives, yet implementation will require revising transplant protocols, managing resource allocation, and ensuring equitable access across patient demographics.Surgeon Performs First-Ever Remote Surgery from 7,000 Miles AwayHistoric Remote SurgeryA surgeon successfully completed the world's first remote surgical operation from over 7,000 miles away using advanced robotic technology and real-time telecommunications. The procedure demonstrated comparable precision and outcomes to in-person surgery.Implications: Remote surgery could dramatically expand specialized surgical access globally, especially in underserved regions. Still, broad adoption demands advanced infrastructure, robust fail-safes, and clear guidelines on legal liabilities and patient safety.8-Hour Time-Restricted Eating Shows Long-Term Weight Loss BenefitsTime-Restricted EatingA recent long-term clinical trial found that participants who limited eating to an eight-hour window each day experienced significant and sustained weight loss, along with metabolic health improvements. The diet strategy proved effective without strict calorie counting or food-type restrictions.Implications: This accessible dietary strategy could serve as a viable public health recommendation for weight management. However, further studies should address adherence rates, nutritional adequacy, and individual variability in response.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🖨️ 3D-Printed Tissues | 🦠 Nanotech Antifungals | 🚻 Health Risks by Gender | ⏱️ Fasting Insights | 🧠 Alzheimer’s Advance-----------------------------------------------------------------------3D-Printing Tissues Inside the Body—No Surgery Required3D-Printed TissuesResearchers have developed a groundbreaking method to directly 3D-print tissue structures within living organisms without invasive surgery. Using minimally invasive tools, bio-inks can now be precisely delivered to internal injury sites, enabling real-time tissue regeneration. Animal studies demonstrate rapid healing and integration.Implications: This technology could revolutionize trauma care and regenerative medicine, drastically reducing recovery times and complications associated with traditional surgeries.Nanoparticles Deliver Effective Antifungal TreatmentsNanotech AntifungalsA new nanoparticle-based approach enhances the effectiveness of antifungal medications, significantly improving their ability to target resistant fungal infections. The nanoparticles deliver drugs directly into fungal cells, reducing side effects and drug resistance seen with conventional therapies. Lab tests show promising results against severe fungal pathogens.Implications: If validated in clinical trials, nanoparticle antifungals could offer life-saving alternatives in immunocompromised patients, potentially overcoming current antifungal resistance challenges.Major Study Reveals Health Risk Differences Between Males and FemalesGendered Health RisksA comprehensive study has highlighted significant gender-based differences in disease prevalence and health outcomes. Researchers analyzed extensive datasets revealing disparities in cardiovascular risk, autoimmune diseases, and mental health disorders between men and women. This underscores the need for gender-specific medical approaches.Implications: Improved awareness and tailored health interventions could lead to better diagnostic accuracy and treatments, narrowing long-standing gender health gaps.Three-Month Intermittent Fasting Linked to Significant Weight LossIntermittent Fasting ResultsParticipants in a new clinical trial who followed intermittent fasting protocols for three months experienced significant weight loss, reduced insulin resistance, and improved cholesterol levels. The study supports intermittent fasting as a viable strategy for metabolic health, alongside traditional diet methods.Implications: Intermittent fasting could become widely recommended as an accessible, flexible option for weight management and reducing metabolic syndrome risks.Alzheimer’s Breakthrough in Understanding Tau Protein SpreadAlzheimer’s Tau ProteinNew research sheds light on how Alzheimer’s disease progresses, revealing crucial mechanisms behind the spread of toxic tau proteins across the brain. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular studies identified specific pathways tau uses to infect healthy neurons, potentially offering new targets for therapies.Implications: Understanding tau protein pathways may accelerate the development of effective treatments and early diagnostic tools, altering Alzheimer’s management and patient outcomes.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🤖 AI Diagnostics | 🏥 Digital Healthcare | 🩹 Electronic Healing | 🦠 Universal Vaccines | 🧠 Brain Mapping | 🐍 Antivenom -----------------------------------------------------------------------Google’s AMIE Gains Vision for AI DiagnosticsAI Diagnostic AssistantGoogle’s AMIE, an AI assistant for medical diagnosis, now incorporates multi-modal capabilities, combining visual data, dialogue, and textual medical records. Early trials demonstrate accurate preliminary diagnoses, helping clinicians prioritize complex cases.Implications: Enhanced AI assistance could dramatically improve diagnostic speed and accuracy, though maintaining trust, transparency, and regulatory approval remains critical.AI Agents Join Hospital WorkforcesAI Hospital WorkersHospitals are increasingly integrating AI agents as frontline support staff, managing tasks from patient triage and scheduling to routine documentation. Initial feedback from medical staff shows reduced burnout, improved efficiency, and higher patient satisfaction scores.Implications: As AI takes over administrative and clinical support, healthcare staff may focus more on patient interactions, though privacy, reliability, and human oversight are paramount.Electronic Band-Aid Accelerates HealingElectronic Band-AidResearchers unveiled a wearable "electronic band-aid" that uses electrical stimulation to boost healing of wounds and ulcers. Lab tests showed significantly faster tissue regeneration and reduced inflammation compared to standard dressings.Implications: This tech could revolutionize wound care, particularly for chronic wounds, but further studies must ensure safety and efficacy in diverse clinical settings.NIH Launches Universal Vaccine PlatformUniversal Vaccine InitiativeThe NIH announced a major initiative for developing a universal vaccine platform targeting multiple pandemic-prone viruses simultaneously, leveraging advanced genetic and mRNA technology. Early research suggests high cross-protective immunity in animal models.Implications: Success could transform global pandemic preparedness, but implementation requires extensive safety assessments, international collaboration, and broad public trust.3D-Printed Hairlike EEG Electrodes for Better Brain Monitoring3D-Printed EEG ElectrodesA new EEG electrode, featuring ultra-thin, hairlike structures produced by 3D printing, captures brain signals more comfortably and clearly. Tests demonstrate higher accuracy in monitoring neural activity compared to traditional EEG devices.Implications: Improved, minimally invasive brain monitoring could enhance diagnostics in epilepsy and sleep disorders, but translating to widespread clinical use requires rigorous validation.Blood of Man Who Survived Snakebites Holds Antivenom CluesSnakebite AntivenomA man who survived hundreds of snakebites has blood uniquely rich in antibodies effective against multiple snake venoms. Researchers isolated these antibodies, potentially paving the way for universal, potent, and affordable antivenoms.Implications: This discovery could save thousands globally, especially in remote regions—though production scale-up, testing, and affordability remain major challenges.CRISPR-Edited Pigs Approved for Food in the U.S.CRISPR Pigs for FoodThe U.S. government has granted approval for pigs genetically edited with CRISPR technology to enter the food supply. These pigs carry edits intended to improve animal health, growth efficiency, and disease resistance. The approval marks a milestone in agricultural biotechnology, paving the way for more genetically modified livestock entering markets.Implications: CRISPR livestock could enhance food security and reduce antibiotic use, though consumer acceptance, ethical considerations, and regulatory oversight remain critical.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🤖 Robot Surgeons | 🌱 Microbiome Relief | 🍟 Food Warnings | 🧠 Psychedelic Stress Hack | 💡 AI Drug Hunters | 🛡️ Next-Gen Immunotherapy | 🗺️ Spatial Cancer Insights-----------------------------------------------------------------------Hugo Surgical Robot Heads to FDAHugo Surgical RobotMedtronic’s Hugo robotic-assisted surgery platform posted strong results in a urologic study and is now under FDA review. Early data show shorter procedure times and fewer complications versus conventional laparoscopy. If cleared, Hugo will challenge Intuitive’s da Vinci dominance while pushing hospitals toward more flexible, modular robotic systems.Implications: Increased competition could lower costs and broaden access to minimally invasive robotic surgery—though training and capital budgets remain barriers.Fecal Transplants Ease Fibromyalgia PainFecal Transplant & FibromyalgiaTransferring healthy gut microbiota reduced pain sensitivity in mice and in a small human pilot with fibromyalgia. Recipients reported better sleep and lower fatigue scores for up to three months. Researchers suspect microbial metabolites dampen systemic inflammation and modulate pain pathways.Implications: Microbiome therapy could offer a non-opioid option for chronic pain, but larger, placebo-controlled trials must confirm safety, durability, and optimal donor selection.Ultra-Processed Foods Linked to Premature DeathUltra-Processed Foods StudyA global cohort study of 600,000 adults tied high consumption of ultra-processed foods—sugary drinks, packaged snacks, reconstituted meats—to a 10–15 % increase in all-cause mortality. Even modest daily reductions yielded measurable risk drops. Critics note observational limits but applaud the scale and multiregional data.Implications: Findings bolster calls for clearer labeling, taxes, or reformulation incentives, spotlighting diet quality as a modifiable longevity lever.Psychedelics Dampen Stress Beyond the BrainPsychedelics & StressNew research shows psilocybin and LSD alter immune and endocrine signaling, not just neural circuits. In rodent models, psychedelic-induced gene expression shifts in the gut and adrenal glands lowered cortisol spikes after stress. Early human data mirror these systemic effects.Implications: Whole-body mechanisms may explain durable mood benefits and guide safer dosing or combination therapies—but regulatory and ethical hurdles persist.AI Tackles “Undruggable” TargetsAI Drug DiscoveryDeep-learning models are designing molecules for tricky protein–protein interactions once deemed undruggable. One platform generated binders for KRAS and MYC within weeks, validated in cell assays. AI accelerates hit-to-lead timelines and diversifies chemical space far beyond human intuition.Implications: Faster pipelines could revive shelved targets and expand treatment options, though experimental validation and safety profiling remain essential bottlenecks.Logic-Gated CAR-NK Cells Drive AML RemissionLogic-Gated CAR-NK TherapyAt AACR 2025, researchers unveiled a CAR-NK therapy with AND/NOT logic gates that selectively attacks acute myeloid leukemia while sparing healthy cells. In an early trial, 7 of 10 relapsed patients reached molecular remission with mild cytokine release.Implications: Smarter cell therapies could reduce off-target toxicity and broaden use beyond B-cell cancers, but larger studies are needed to confirm durability and manufacturing scalability.Spatial Biology Maps Tumor Time-TravelSpatial Biology & CancerHigh-resolution spatial transcriptomics reveals how tumor neighborhoods evolve, recording “past, present, and future” cell states in one slice. Researchers traced metastatic precursors and immune-evasion niches in breast and lung cancers.Implications: Pinpointing dangerous microenvironments could guide combination therapies and predict relapse, yet integrating multi-omic maps into routine pathology will require new workflows and AI analytics.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🤰🏽 Automated Conception | 💉 Cancer Vaccines | 🧬 Genetic Insights | 👩🏻⚕️ AI Therapies | 🏋 Weight-Loss Shakeups-----------------------------------------------------------------------Automated IVF: First “Robot-Conceived” BabyAutomated IVF BabyResearchers have announced the birth of the first baby conceived via a fully automated IVF system, where specialized devices handled fertilization steps without direct human manipulation. The technology aims to lower costs and boost success rates by minimizing human error. Early results are promising, but large-scale adoption will rely on robust clinical validation.Implications: If automated IVF proves reliable, it could expand fertility treatment access worldwide and streamline reproductive medicine.Skin Cancer Vaccine Trial on NHSSkin Cancer Vaccine TrialA pioneering trial on Britain’s NHS will test a personalized skin cancer vaccine that trains the immune system to recognize tumor-specific markers. Early data suggests a drop in relapse rates and prolonged patient remission. The vaccine is being paired with standard therapies to enhance immune response.Implications: If successful, personalized vaccines could redefine oncology, with tailored treatments driving better outcomes and fewer side effects.Large-Scale Genetic Study Reveals New Disease MarkersGenetic Disease MarkersA major international consortium has identified numerous genetic variants linked to complex diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and heart conditions. By scanning tens of thousands of genomes, scientists uncovered previously hidden markers that could improve early diagnosis. Researchers hope to translate these insights into targeted screening tools and therapeutic strategies.Implications: This expansive genetic catalog may lead to earlier interventions and more precise treatments, ultimately transforming personalized medicine.AI and Nanotech Team Up Against Oral CancerAI + Nanotech vs. Oral CancerScientists have fused AI-driven image analysis with targeted nanoparticles that deliver drugs straight to cancerous cells in the mouth. Early lab results show enhanced treatment precision, minimizing harm to healthy tissues. Real-time data feedback from the AI platform refines the therapy as it progresses, promising more dynamic and effective cancer control.Implications: This high-tech hybrid could pave the way for minimally invasive treatments with fewer side effects, revolutionizing how we tackle oral malignancies.Pfizer Drops Oral GLP-1: Blow to Obesity PipelinePfizer Axes Oral GLP-1Pfizer has discontinued development of its oral GLP-1 agonist after liver injury concerns emerged during trials. The candidate had been touted as a game-changing obesity therapy, promising convenience over injectables. This setback leaves a gap in Pfizer’s metabolic pipeline, raising questions about next steps in the booming weight-loss drug market.Implications: As competition heats up, safe and effective oral treatments remain elusive, pushing researchers toward more selective targets or alternative drug classes.Gastric Bypass in a Pill? Syntis Bio’s Ambitious Approach“Gastric Bypass” PillSyntis Bio claims to be developing a weight-loss pill that mimics the metabolic effects of gastric bypass surgery without the invasive procedure. By altering gut hormone signals and nutrient absorption, it aims to replicate the surgery’s dramatic weight-loss results. While early lab data shows promise, human trials are needed to confirm efficacy and rule out severe side effects.Implications: If a safe, pill-based alternative to bariatric surgery emerges, it could revolutionize obesity management—though scaling such technology will face stringent regulatory scrutiny.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🤰🏽 Automated Conception | 💉 Cancer Vaccines | 🧬 Genetic Insights | 👩🏻⚕️ AI Therapies | 🏋 Weight-Loss Shakeups-----------------------------------------------------------------------Automated IVF: First “Robot-Conceived” BabyAutomated IVF BabyResearchers have announced the birth of the first baby conceived via a fully automated IVF system, where specialized devices handled fertilization steps without direct human manipulation. The technology aims to lower costs and boost success rates by minimizing human error. Early results are promising, but large-scale adoption will rely on robust clinical validation.Implications: If automated IVF proves reliable, it could expand fertility treatment access worldwide and streamline reproductive medicine.Skin Cancer Vaccine Trial on NHSSkin Cancer Vaccine TrialA pioneering trial on Britain’s NHS will test a personalized skin cancer vaccine that trains the immune system to recognize tumor-specific markers. Early data suggests a drop in relapse rates and prolonged patient remission. The vaccine is being paired with standard therapies to enhance immune response.Implications: If successful, personalized vaccines could redefine oncology, with tailored treatments driving better outcomes and fewer side effects.Large-Scale Genetic Study Reveals New Disease MarkersGenetic Disease MarkersA major international consortium has identified numerous genetic variants linked to complex diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and heart conditions. By scanning tens of thousands of genomes, scientists uncovered previously hidden markers that could improve early diagnosis. Researchers hope to translate these insights into targeted screening tools and therapeutic strategies.Implications: This expansive genetic catalog may lead to earlier interventions and more precise treatments, ultimately transforming personalized medicine.AI and Nanotech Team Up Against Oral CancerAI + Nanotech vs. Oral CancerScientists have fused AI-driven image analysis with targeted nanoparticles that deliver drugs straight to cancerous cells in the mouth. Early lab results show enhanced treatment precision, minimizing harm to healthy tissues. Real-time data feedback from the AI platform refines the therapy as it progresses, promising more dynamic and effective cancer control.Implications: This high-tech hybrid could pave the way for minimally invasive treatments with fewer side effects, revolutionizing how we tackle oral malignancies.Pfizer Drops Oral GLP-1: Blow to Obesity PipelinePfizer Axes Oral GLP-1Pfizer has discontinued development of its oral GLP-1 agonist after liver injury concerns emerged during trials. The candidate had been touted as a game-changing obesity therapy, promising convenience over injectables. This setback leaves a gap in Pfizer’s metabolic pipeline, raising questions about next steps in the booming weight-loss drug market.Implications: As competition heats up, safe and effective oral treatments remain elusive, pushing researchers toward more selective targets or alternative drug classes.Gastric Bypass in a Pill? Syntis Bio’s Ambitious Approach“Gastric Bypass” PillSyntis Bio claims to be developing a weight-loss pill that mimics the metabolic effects of gastric bypass surgery without the invasive procedure. By altering gut hormone signals and nutrient absorption, it aims to replicate the surgery’s dramatic weight-loss results. While early lab data shows promise, human trials are needed to confirm efficacy and rule out severe side effects.Implications: If a safe, pill-based alternative to bariatric surgery emerges, it could revolutionize obesity management—though scaling such technology will face stringent regulatory scrutiny.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
👀 AI Monitoring | 🧬 Genetic Fixes | 🫀Tiny Pacemakers | 🧠 Brain-Tech Frontiers | 💉 Immune Boosters-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Molecular Elevator Boosts ImmunityMolecular ElevatorChinese researchers have discovered a mechanism likened to a “molecular elevator” capable of amplifying immune responses by up to 150-fold. This involves tweaking cell signaling pathways so immune cells can more aggressively target cancer cells or dangerous viruses. Early lab work is encouraging, showing significant tumor reduction in experimental models. Further studies will be needed to confirm safety and efficacy in humans.Implications: If scalable, this breakthrough could supercharge immunotherapy, offering a potent new weapon against cancers and viral infections—though translating it from lab to clinic will be a critical challenge.Gene Editing Fixes DNAGene EditingScientists have unveiled a CRISPR-based technique that repairs mutated genes associated with severe lung and liver diseases once deemed incurable. By targeting specific errors within cells, this method allows healthy genetic sequences to be restored without causing widespread DNA damage. Preliminary trials in animal models show promising outcomes, including restored organ function. The next step involves clinical testing to confirm these effects in humans and rule out unexpected side effects.Implications: If successful, these precise gene edits could reshape how we treat genetic disorders, though regulatory hurdles and ethical debates over heritable changes remain substantial.World’s Tiniest PacemakerTiny PacemakerEngineers have created a pacemaker smaller than a grain of rice, representing a significant milestone in minimally invasive cardiac devices. Despite its tiny size, it’s designed to deliver reliable pacing while reducing surgical complications and recovery times. Early prototypes suggest lower infection risks and improved patient comfort compared to traditional implants. Researchers now need to confirm long-term durability and battery life in clinical trials.Implications: If proven safe and effective, this mini device could transform care for heart patients, cutting hospital stays and potentially expanding access in resource-limited settings.Brain-Computer InterfacesBrain-Computer InterfacesA new wave of BCIs is pushing the limits of how humans interact with computers, including neural implants that enable brain-to-text communication or mind-controlled prosthetics. These devices read electrical signals directly from the brain to drive software or external limbs, offering a lifeline for people with paralysis. Researchers also explore “closed-loop” systems that provide real-time feedback to the brain. While the potential is huge, concerns over data privacy, device invasiveness, and equitable access loom large.Implications: BCIs promise dramatic quality-of-life improvements for disabled individuals, but balancing rapid innovation with responsible deployment will be key.Onapgo for Parkinson’s DiseaseParkinson’s TreatmentA newly developed device called Onapgo delivers targeted stimulation to combat Parkinson’s-related tremors and motor deficits. Combining sensor feedback and precise drug or electrical impulses, it adapts in real time to the patient’s movement patterns. Early pilots report reduced tremors and improved daily function, but larger studies are required to validate consistency. With refined calibration, it may surpass standard deep-brain stimulation in both accuracy and patient comfort.Implications: By tailoring therapy to individual symptoms, Onapgo could offer a more patient-friendly path for managing Parkinson’s, though cost and insurance coverage remain unknown factors.Apple’s AI “Doctor”? AI Monitoring TeenagersAI Healthcare OversightRumors suggest Apple is developing AI-driven health tools that track teens’ physical and mental wellness, flagging potential problems early. The goal is to leverage wearable data—like heart rate, sleep patterns, and movement—to detect red flags such as high stress, mood shifts, or disordered eating. Privacy experts caution that continuous surveillance could lead to overdiagnosis or data misuse if not carefully regulated. Apple, meanwhile, highlights the potential for early intervention and prevention.Implications: AI-based health monitoring may revolutionize preventive care for younger populations, but ensuring robust data protections and responsible use will be paramount.Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more discoveries pushing the boundaries of healthcare, biotechnology, and beyond. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
🔮 Mind Readers | 🫁 Body Hacks | 💊 Pain Fixes | 🕷️ Robo Scouts | 🦷 Adult Teeth-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Voice from Silence: Implant Speaks for Paralyzed WomanBrain Implant Speech StudySingularity Hub reports a brain implant that turned a paralyzed woman’s thoughts into speech in near real-time. Electrodes in her brain caught neural signals as she imagined speaking, and AI decoded them into words at 78 per minute—half normal speed, but a leap from silence. Tested in 2025, it’s not perfect—errors creep in—but it’s a lifeline for those locked in by ALS or strokes. Trending chatter on X highlights its buzz as a game-changer for communication.Implications: Speech could ditch the vocal cords. If this tech scales, millions silenced by paralysis might chat again, slamming doors open for connection. Cost and glitches nag—AI’s not flawless—but it’s a mind-blowing step toward cyborg-level fixes.-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Living Spare Parts: Human Bodies as Organ FarmsOrgan Donation InnovationMIT Technology Review explores a wild idea: growing organs in living humans kept in a vegetative state. Proposed in 2025, these “organ donors” would be brain-dead but biologically alive, offering fresh livers or kidneys on demand. It sidesteps pig transplants and waitlists, but ethicists are freaking out—consent’s a minefield. Early talks hint at lab-grown bodies, not accident victims, yet the sci-fi vibe’s strong.Implications: Organ shortages could vanish. If this takes off, transplant lines shrink, but we’re dancing on a moral razor’s edge—humanity’s not ready for body farms. Tech’s years out, ethics even further.-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Cancer’s Tiny Hunter: Robot Spots Bowel Trouble EarlyBowel Cancer Robot StudyThe Financial Times unveils a penny-sized robot that could revolutionize bowel cancer detection. Developed by University of Leeds engineers in 2025, this magnetic marvel rolls through the gut, capturing 3D ultrasound scans to spot tumors early. In pig trials, it delivered high-res images, dodging invasive scopes. Human tests are slated for late 2025, aiming to catch the second-deadliest cancer—1.9 million cases yearly—when it’s most treatable. X posts buzz about its non-invasive edge.Implications: Bowel cancer might lose its stealth mode. If this bot scales, it could slash deaths with quick, painless scans—dentistry’s next rival for “open wide.” Cost and tech hiccups linger—magnets don’t come cheap—but it’s a gut-check win for early detection.-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Elder Teeth: Drug Grows New ChompersTooth Regrowth DiscoveryTimes of India reveals a drug that might grow a third set of teeth. Japanese trials in 2025 triggered dormant dental buds in adults missing teeth from birth defects, sprouting new ones in months. It’s not shark-level regeneration—yet—but it taps ancient genes we all carry. Safety’s green so far; human tests expand next year.Implications: Dentures could bite the dust. If this hits clinics, toothless grins get a redo, shaking up dentistry. Cost and quirks—like extra molars—need sorting, but it’s a jaw-dropping leap for smiles.-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Teen’s Painkiller Twist: Safer Acetaminophen AlternativePain Relief InnovationSmithsonian Magazine spotlights a 17-year-old’s acetaminophen reboot. Her 2025 science fair project tweaked the drug’s chemistry, cutting liver damage in lab tests—a fix for the overdose deaths tied to Tylenol’s dark side. It’s early, not pharmacy-ready, but pharma’s sniffing around. X buzz calls her a prodigy with grit, echoing young talent trends.Implications: Pain relief could shed its poison rep. If this scales, it’s a blockbuster—safer pills, fewer ER trips. Big Pharma’s slow grind and patents might stall it, but a teen just lit a spark.-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------That’s the roundup! From brain-talk to tooth tricks, science is rewriting the human playbook. Which one’s got you buzzing? This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
Source 1: "Breakthrough stroke drug heals the brain to restore movement" (New Atlas, March 19, 2025)Main Theme: A promising new drug, DDL-920, developed at UCLA, has shown in mice models the potential to restore movement control after a stroke by healing the brain's signaling pathways, potentially eliminating the need for extensive physical therapy.Key Ideas/Facts:First Drug for Rehabilitation: Researchers believe DDL-920 is the first drug that can comprehensively deliver rehabilitation after a stroke, unlike current approaches that rely solely on physical therapy.Quote: "There's newfound hope for stroke patients in recovery, with what researchers believe is the very first drug that can comprehensively deliver rehabilitation without the need for challenging long-term physical therapy."DDL-920 Efficacy in Mice: The drug led to the complete recovery of movement control in mice models.Quote: "Further research revealed that one of these drugs, DDL-920 – developed at UCLA, led to the complete recovery of movement control – something many stroke patients never regain."Targeting Disconnected Neurons: The drug works by reconnecting communication in an area of the brain distant from the main stroke site where neurons become isolated.Quote: "This area was distant from the brain's central stroke site, meaning disconnected neurons were isolated and unable to rebuild that link on their own."Restoring Gamma Oscillations and Parvalbumin Neuron Function: Stroke disrupts communication with parvalbumin neuron cells and the associated gamma brain rhythm. DDL-920 restored these oscillations, leading to neuronal reconnection.Quote: "The drug, tested on mice, restored these gamma oscillations, and in turn reconnected neurons to essentially heal the brain damage without arduous physical rehabilitation."Moving Rehabilitation to Molecular Medicine: The research aims to shift stroke rehabilitation from a purely physical approach to one involving molecular medicine.Quote: "“Rehabilitation is a physical medicine approach that has been around for decades; we need to move rehabilitation into an era of molecular medicine.”" - Dr S. Thomas CarmichaelPotential Impact: If successful in human trials, this drug could be "game-changing" for millions of stroke patients who currently have limited medical interventions besides physical therapy.Next Steps: DDL-920 requires extensive human trials for safety and efficacy.Publication: The study was published in the journal Nature Communications.Source 2: "Cannabis Users Under 50 Are 6 Times More Likely to Have a Heart Attack" (Healthline, March 20, 2025)Main Theme: Two new studies indicate a significantly higher risk of heart attack and other cardiovascular events in cannabis users, particularly those under 50.Key Ideas/Facts:Retrospective Study Findings: Cannabis users under 50 were found to be six times as likely to have a heart attack compared to non-users. They also had a four times higher risk of ischemic stroke, two times higher risk of heart failure, and three times higher risk of cardiovascular death, heart attack, or stroke.Quote: "A retrospective study found that cannabis users were six times as likely to have a heart attack compared to non-users."Meta-Analysis Findings: A meta-analysis of 12 previous studies showed that cannabis users had a 50% increased risk of a heart attack compared to non-users.Quote: "A meta-analysis of 12 previous studies showed that cannabis users had a 50% higher risk of a heart attack than non-users."Largest Pooled Study: The meta-analysis, including over 93,000 cannabis users and 4.5 million non-users, is the largest of its kind.Call for Clinical Assessment: Study authors suggest that clinicians should include questions about cannabis use in their assessment of patients' cardiovascular risk, similar to inquiries about smoking.Quote: "Asking about cannabis use should be part of clinicians’ workup to understand patients’ overall cardiovascular risk, similar to asking about smoking cigarettes,” - Dr. Ibrahim KamelUncertainty Regarding Inhalation vs. Ingestion: Both studies lacked sufficient data to determine if the risk differs between inhaled and ingested cannabis products.Quote: "Both studies lacked sufficient information to determine whether the risk was different for inhaled cannabis versus ingested products."Possible Mechanisms: Researchers suggest cannabis may affect heart rhythm, increase the heart muscle's oxygen needs, and contribute to arterial dysfunction.Need for More Research: Experts emphasize the need for further research to understand the long-term health risks of cannabis use, including determining safe usage levels.Quote: "But 'we don’t know for sure if that’s also true with cannabis, because those studies haven’t been done,'” - Dr. Andrew Meltzer, regarding inhalation risks.Potential Confounding Factors: The studies acknowledge that other drug use could contribute to adverse cardiovascular effects.Source 3: "Covid Vaccines Have Paved the Way for Cancer Vaccines | WIRED" (WIRED, March 13, 2025)Main Theme: The success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines has significantly accelerated the field of mRNA cancer vaccine research and development, leading to numerous ongoing trials and the potential for the first approved personalized mRNA cancer vaccine within a few years.Key Ideas/Facts:COVID Vaccine Success as a Catalyst: The rapid development and proven efficacy of mRNA technology in COVID vaccines demonstrated the feasibility and potential of this approach for other diseases, including cancer.Quote: "With the pandemic, however, we proved that mRNA vaccines were possible." - Lennard LeePersonalized Cancer Vaccines: Current trials focus on creating bespoke vaccines tailored to an individual patient's specific cancer by analyzing their tumor tissue.Quote: "In the current trials, we do a biopsy of the patient, sequence the tissue, send it to the pharmaceutical company, and they design a personalized vaccine that’s bespoke to that patient’s cancer."Mechanism of mRNA Cancer Vaccines: These vaccines work by instructing the body to produce harmless pieces of cancer-related proteins, training the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.Quote: "mRNA cancer vaccines work by giving the body instructions to make a harmless piece of a cancer-related protein. This trains the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells carrying that protein."UK's Role in Fast-Tracking Trials: The UK established the Cancer Vaccine Launch Pad and leveraged its existing infrastructure and genomic capabilities to rapidly initiate and enroll patients in cancer vaccine trials.Quote: "During the pandemic, we had proven we could open and deliver clinical trials fast. Also, the UK had established a genomic global lead with Genomics England and the 100,000 Genome Project."Accelerated Clinical Trial Timelines: The pandemic demonstrated that clinical trials can be conducted much faster by modernizing processes and running steps in parallel.Quote: "We showed the world that it could be done in a year if you modernize your process, run parts of the process in parallel, and use digital tools."Late-Stage Trials and Expected Approval: Several mRNA cancer vaccines are in late-stage clinical trials internationally, with the UK running 15 trials. Results from a skin cancer trial are expected by the end of 2025 or early 2026, potentially leading to the first approved personalized mRNA vaccine.Quote: "We’re hoping to have results by the end of the year or beginning of 2026. If it’s successful, we will have invented the first approved personalized mRNA vaccine, within only five years of the first licensed mRNA vaccine for Covid."Source 4: "Google shares 4 updates on generative AI in healthcare" (Google The Keyword, March 19, 2024)Main Theme: Google is making significant progress in applying generative artificial intelligence to various aspects of healthcare, from diagnostic assistance and radiology workflows to personalized health coaching.Key Ideas/Facts:Advancements in Health AI Models: Google has introduced and refined large language models (LLMs) like Med-PaLM 2 and MedLM, fine-tuned for healthcare applications.Multimodal Models: The focus is on developing models that can understand various types of medical data, including text, images (e.g., radiology), lab results, and genomics data.Quote: "Medicine is a multimodal discipline; it’s made up of different types of information stored across formats — like radiology images, lab results, genomics data, environmental context and more."MedLM for Chest X-ray: This new model has the potential to assist in classifying chest X-rays for various diagnostic use cases.Quote: "We just introduced MedLM for Chest X-ray, which has the potential to help transform radiology workflows by helping with the classification of chest X-rays for a variety of use cases."Fine-Tuning Gemini for Medical Domain: Research shows that a version of the Gemini model, specifically trained on medical data, achieves state-of-the-art performance on medical licensing exam-style questions and video datasets.Quote: "Our latest research resulted in state-of-the-art performance on the benchmark for the U.S. Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE)-style questions at 91.1%..."Personal Health LLM: Fitbit and Google Research are collaborating on a Personal Health LLM based on Gemini models to provide personalized health and wellness insights and recommendations within the Fitbit app.Quote: "Fitbit and Google Research are working together to build a Personal Health Large Language Model that can power personalized health and wellness features in the Fitbit mobile app..."AMIE for Diagnostic Reasoning: The Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer (AMIE), an AI system built on an LLM, has shown promising results in simulating patient consultations, performing comparably to or better than primary care clinicians in diagnostic accuracy, empathy, and helpful explanations.Quote: "In a randomized comparison with rea
The articles highlight innovations in non-invasive kidney stone removal, potential non-opioid pain management, gene therapy, artificial hearts, and the restoration of movement in paralyzed individuals.1. Non-Invasive Kidney Stone Removal with Acoustic Vortex Beams:Main Theme: A new technology called "Lithovortex" utilizes swirling ultrasound waves (acoustic vortex beams) to break apart kidney stones non-invasively, offering a potentially faster, easier, and safer alternative to the existing Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL).Key Ideas and Facts:Mechanism: Unlike ESWL which uses direct acoustic pulses, Lithovortex beams spin around the stones "like twister tornados," generating shear forces that cause disintegration.Improved Efficiency: The vortex beams are reportedly half as strong as ESWL pulses and take half the time to achieve the same result.Patient Benefits: This increased efficiency suggests patients may not require sedation or anesthesia, reducing pain and risks.Reduced Tissue Damage: The gentler nature of the vortex beams minimizes the risk of damage to healthy tissue surrounding the kidney stones.Portability: The Lithovortex system is being developed as a portable machine, potentially allowing for outpatient clinic procedures, unlike the large equipment required for ESWL.Development Stage: The technology is currently in prototype form, utilizing a robotic arm guided by an imaging system. Animal model validation is planned for the following year.Quote: "Instead of hitting the stones straight-on, as is the case with ESWL pulses, these beams spin around the stones like twister tornados. As they do so, they produce shear forces on the stones that cause them to disintegrate."2. Cannabis Terpenes for Chronic Pain and Fibromyalgia:Main Theme: Research indicates that terpenes, aromatic compounds found in cannabis, show promise as effective non-opioid treatments for chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia and post-surgical pain.Key Ideas and Facts:Effective Terpenes: Geraniol and linalool were identified as the most effective terpenes in preclinical mouse models for relieving fibromyalgia and post-surgical pain. Beta-caryophyllene and alpha-humulene also showed significant pain relief.Opioid Alternative: Terpenes offer a potential alternative to opioid medications without the psychoactive side effects associated with THC.Mechanism of Action: The terpenes appear to relieve pain by targeting the adenosine A2a receptor, suggesting a potential sedative mechanism.Specificity: Research suggests terpenes are more effective for chronic or pathological pain rather than acute injury pain.Impact on Untreated Conditions: The findings offer hope for fibromyalgia, a chronic condition with limited effective treatment options.Potential for Post-Surgical Pain Management: Terpenes could offer a safer alternative to opioids for post-surgical pain, potentially reducing complications like constipation.Quote: "Our research is showing that terpenes are not a good option for reducing acute pain resulting from an injury, such as stubbing your toe or touching a hot stove; however, we are seeing significant reductions in pain when terpenes are used for chronic or pathological pain."3. Gene Therapy Advance in Restoring Mutated DNA:Main Theme: Researchers have successfully corrected a disease-causing gene mutation in humans for the first time using a single infusion that precisely targeted the errant gene, offering a potential "one-and-done" therapy for certain genetic disorders.Key Ideas and Facts:Targeted Correction: The therapy directly fixes the incorrect DNA letter in the gene responsible for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD).Novel Approach: This "base editing" method differs from existing gene therapies that typically add new genes or silence existing ones.Treatment Delivery: Lipid nanoparticles, similar to those used in COVID-19 vaccines, were used to deliver the gene editor (a disabled CRISPR molecule) to the liver.Successful Outcome: Patients who received the highest dose of the gene editor produced enough normal alpha-1 antitrypsin to potentially halt liver and lung damage associated with AATD.Safety Profile: The small study reported no serious side effects.Potential for Other Genetic Diseases: This advancement holds promise for treating other genetic diseases by precisely fixing mutations.Quote: "This was the first time a mutated gene has been restored to normal."Quote: "The big pro” of the new treatment, he said, is that “it theoretically cures the liver and lung disease in one go.”4. Patient Discharged with Artificial Heart Beating Outside Hospital:Main Theme: A patient with a BiVACOR Total Artificial Heart (TAH) was discharged from the hospital for over a month while awaiting a heart transplant, marking a significant milestone in the development and use of artificial hearts as a "bridge to transplant."Key Ideas and Facts:Extended Support: The patient lived for 105 days with the artificial heart before receiving a donor heart.Out-of-Hospital Operation: This was the first instance of a maglev artificial heart operating outside of a hospital setting.Maglev Technology: The BiVACOR TAH utilizes an electro-mechanical rotary pump and magnetic levitation for the rotor, minimizing moving parts and potentially increasing durability.External Controller: The device is powered and controlled by a small external unit with a rechargeable battery.Bridge to Transplant: While not currently envisioned as a long-term replacement, the BiVACOR TAH demonstrates its potential to significantly extend the survival of patients awaiting heart transplants.Quote: "Being able to bring Australia along this journey and be part of the first clinical trials is immensely important to me and something that I set out to do from the very beginning."Quote: "Within the next decade we will see the artificial heart becoming the alternative for patients who are unable to wait for a donor heart or when a donor heart is simply not available.”5. Robotics and Spinal Stimulation to Restore Movement in Paralysis:Main Theme: A new approach combining rehabilitation robotics with precisely timed spinal cord stimulation has shown promising results in restoring movement in individuals with spinal cord injuries.Key Ideas and Facts:Integrated System: The technology seamlessly integrates an implanted spinal cord neuroprosthesis with rehabilitation robotics.Enhanced Rehabilitation: Electrical pulses are delivered to stimulate muscles in coordination with robotic movements, leading to more natural and coordinated muscle activity during therapy.Biomimetic Stimulation: The implanted stimulator delivers electrical epidural stimulation that mimics natural nerve signals, activating motor neurons more efficiently than traditional functional electrical stimulation.Real-Time Adjustment: Wireless sensors detect limb motion and automatically adjust stimulation in real time.Improved Voluntary Movement: A proof-of-concept study showed that participants not only regained muscle engagement during robotic therapy but also experienced improvements in voluntary movements even after stimulation was turned off.Real-World Application: Participants were able to use the system for activities like walking with a rollator and cycling outdoors.Potential for Standard of Care: Researchers believe this integrated therapy has the potential to become a standard of care for spinal cord injury rehabilitation.Quote: "The seamless integration of spinal cord stimulation with rehabilitation or recreational robotics will accelerate the deployment of this therapy into the standard of care and the community of people with spinal cord injury."6. The Naming Process of Prescription Drugs:Main Theme: The naming of prescription drugs is a rigorous process involving both the assignment of a generic (nonproprietary) name based on scientific principles and the development of a brand (proprietary) name for marketing and regulatory purposes.Key Ideas and Facts:Generic Names: Assigned by international organizations (USAN, FDA, WHO) based on the drug's active ingredient, chemical makeup, or therapeutic effect, ensuring clarity and consistency. Suffixes like "-statin" indicate drug classes.Brand Names: Chosen by pharmaceutical companies to be memorable, marketable, and legally distinct. They undergo thorough review by the FDA to avoid confusion with existing names, including A/B testing and consumer research.Importance of Both Names: Generic names facilitate communication among prescribers, while brand names aim to gain market share and recognition.Genericide: A phenomenon where a brand name becomes so common it becomes synonymous with the generic name, potentially causing trademark issues for the company.Quote: "If your patient is coming in and says, ‘Oh, I’m taking atorvastatin,’ you may not be familiar with that particular drug, but just from seeing the non-proprietary name that ends in -statin, you immediately can have a recognition that this is a drug to lower cholesterol."Quote: "It is in the best interest of the drug manufacturer to find a name that is highly identifiable, highly recognizable, that can be marketed in a strategic way that can resonate with the users so that it can help the drug gain demand and market share."These articles collectively showcase significant advancements in medical technology and therapeutics, offering new hope for patients with a range of conditions from kidney stones and chronic pain to genetic disorders, heart failure, and paralysis. The emphasis on non-invasive techniques, targeted therapies, and the integration of robotics and neuroprosthetics points towards a future of more effective and patient-friendly medical interventions.convert_to_textConvert to source This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
Briefing Document: Key Trends in Medical Research (February 2025)This briefing summarizes recent advances in medical research across several key areas, highlighting potential breakthroughs in newborn screening, gene therapy, cancer diagnostics, diabetes treatment, and cellular aging.1. Expanded Newborn Screening via Genome Sequencing (GUARDIAN Study)Theme: Integration of genome sequencing into newborn screening (NBS) to identify a broader range of treatable genetic conditions.Key Ideas:Traditional NBS is limited to conditions detectable through specific biomarkers. Genome sequencing offers a more comprehensive approach.The GUARDIAN study demonstrated the feasibility of targeted genome sequencing in a diverse population of newborns in New York City. The study enrolled 4,000 newborns with a 72% consent rate.A screen-positive rate of 3.7% was identified for treatable conditions not included in standard NBS.The study emphasizes the importance of further research to assess generalizability and long-term health outcomes: "Ongoing research will be crucial to validate these findings and to optimize implementation strategies in various healthcare settings."Quote: "The GUARDIAN study provides promising evidence supporting the feasibility of expanded NBS through genome sequencing. This strategy could significantly improve early detection and intervention for a broader spectrum of genetic conditions, particularly in diverse populations."2. Gene Therapy for BlindnessTheme: Successful gene therapy to restore vision in children with AIPL1-associated severe retinal dystrophy.Key Ideas:MeiraGTx's investigational gene therapy, rAAV8.hRKp.AIPL1, has enabled 11 legally blind children to gain visual acuity.The therapy delivers functional copies of the AIPL1 gene directly into the eye via an adeno-associated virus.Significant improvements were observed in treated eyes, leading to life-changing benefits in various areas of development. "The effects of treatment 'extended outside the meaningful effects on vision and result in life-changing benefits in all areas of development including communication, behavior, schooling, mood, psychological benefits and social integration,' MeiraGTx's CEO Alexandria Forbes, Ph.D., said in the biotech's accompanying release."The company is pursuing accelerated approval in both the U.K. and the U.S.Quote: Evercore ISI analysts described the findings as “strong clinical data with clear evidence of efficacy in a huge unmet need pediatric population.”3. Early Pancreatic Cancer DetectionTheme: Development of a novel blood test (PAC-MANN) for early-stage pancreatic cancer detection with high accuracy.Key Ideas:Pancreatic cancer is often diagnosed late due to non-specific early symptoms, resulting in a low survival rate.PAC-MANN, a nanosensor assay, detects elevated levels of proteases, biomarkers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), in blood samples.Tests showed 85% sensitivity for stage 1 PDAC when paired with the existing biomarker CA 19-9.The test is inexpensive and requires a small blood sample, making it suitable for widespread screening, particularly in underserved areas: “The big difference with this test is the cost: It takes only 8 microliters of blood and 45 minutes to run the test at a cost of less than a penny per sample."Quote: "Our test could be used for people at high risk of pancreatic cancer, which is not targeted by current tests,” said Jose Montoya Mira, lead author of the study.4. Reversal of Type 1 Diabetes via Cell TransplantationTheme: A new cell transplantation technique using engineered blood-vessel-forming cells to reverse type 1 diabetes in preclinical studies.Key Ideas:Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the immune system's destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells.Transplanting islets along with engineered blood-vessel-forming cells (R-VECs) creates a vascularized environment that promotes islet survival and function.In diabetic mice, this co-transplantation normalized blood glucose levels for over 20 weeks.The researchers are aiming for a less invasive technique, implanting under the skin for indefinite survival of the islets.Quote: “This work lays the foundation for subcutaneous [under the skin] islet transplants as a relatively safe and durable treatment option for type 1 diabetes,” said the study’s lead author, Ge Li, PhD5. Reversing Cellular AgingTheme: Identification of the protein AP2A1 as a key regulator of cellular senescence and a potential target for anti-aging therapies.Key Ideas:Senescent cells accumulate with age and contribute to age-related diseases.AP2A1 is upregulated in the stress fibers of senescent cells.Suppressing AP2A1 in older cells promotes rejuvenation, while overexpressing it in young cells accelerates senescence.AP2A1 interacts with integrin β1, strengthening cell adhesion and contributing to the enlarged structure of aging cells.Quote: “Suppressing AP2A1 in older cells reversed senescence and promoted cellular rejuvenation, while AP2A1 overexpression in young cells advanced senescence,” explains Shinji Deguchi, senior author.Overall Implications:These advancements highlight the potential of emerging technologies such as genomics, gene therapy, nanosensors, and cell engineering to address significant unmet medical needs. While further research and clinical trials are necessary, these findings offer promising avenues for improving early disease detection, treatment efficacy, and overall healthspan.convert_to_textConvert to sourceNotebookLM can be inaccurate; please double check its responses. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com
Briefing Document: Key Trends in Medical Research (February 2025)This briefing summarizes recent advances in medical research across several key areas, highlighting potential breakthroughs in newborn screening, gene therapy, cancer diagnostics, diabetes treatment, and cellular aging.1. Expanded Newborn Screening via Genome Sequencing (GUARDIAN Study)Theme: Integration of genome sequencing into newborn screening (NBS) to identify a broader range of treatable genetic conditions.Key Ideas:Traditional NBS is limited to conditions detectable through specific biomarkers. Genome sequencing offers a more comprehensive approach.The GUARDIAN study demonstrated the feasibility of targeted genome sequencing in a diverse population of newborns in New York City. The study enrolled 4,000 newborns with a 72% consent rate.A screen-positive rate of 3.7% was identified for treatable conditions not included in standard NBS.The study emphasizes the importance of further research to assess generalizability and long-term health outcomes: "Ongoing research will be crucial to validate these findings and to optimize implementation strategies in various healthcare settings."Quote: "The GUARDIAN study provides promising evidence supporting the feasibility of expanded NBS through genome sequencing. This strategy could significantly improve early detection and intervention for a broader spectrum of genetic conditions, particularly in diverse populations."2. Gene Therapy for BlindnessTheme: Successful gene therapy to restore vision in children with AIPL1-associated severe retinal dystrophy.Key Ideas:MeiraGTx's investigational gene therapy, rAAV8.hRKp.AIPL1, has enabled 11 legally blind children to gain visual acuity.The therapy delivers functional copies of the AIPL1 gene directly into the eye via an adeno-associated virus.Significant improvements were observed in treated eyes, leading to life-changing benefits in various areas of development. "The effects of treatment 'extended outside the meaningful effects on vision and result in life-changing benefits in all areas of development including communication, behavior, schooling, mood, psychological benefits and social integration,' MeiraGTx's CEO Alexandria Forbes, Ph.D., said in the biotech's accompanying release."The company is pursuing accelerated approval in both the U.K. and the U.S.Quote: Evercore ISI analysts described the findings as “strong clinical data with clear evidence of efficacy in a huge unmet need pediatric population.”3. Early Pancreatic Cancer DetectionTheme: Development of a novel blood test (PAC-MANN) for early-stage pancreatic cancer detection with high accuracy.Key Ideas:Pancreatic cancer is often diagnosed late due to non-specific early symptoms, resulting in a low survival rate.PAC-MANN, a nanosensor assay, detects elevated levels of proteases, biomarkers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), in blood samples.Tests showed 85% sensitivity for stage 1 PDAC when paired with the existing biomarker CA 19-9.The test is inexpensive and requires a small blood sample, making it suitable for widespread screening, particularly in underserved areas: “The big difference with this test is the cost: It takes only 8 microliters of blood and 45 minutes to run the test at a cost of less than a penny per sample."Quote: "Our test could be used for people at high risk of pancreatic cancer, which is not targeted by current tests,” said Jose Montoya Mira, lead author of the study.4. Reversal of Type 1 Diabetes via Cell TransplantationTheme: A new cell transplantation technique using engineered blood-vessel-forming cells to reverse type 1 diabetes in preclinical studies.Key Ideas:Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the immune system's destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells.Transplanting islets along with engineered blood-vessel-forming cells (R-VECs) creates a vascularized environment that promotes islet survival and function.In diabetic mice, this co-transplantation normalized blood glucose levels for over 20 weeks.The researchers are aiming for a less invasive technique, implanting under the skin for indefinite survival of the islets.Quote: “This work lays the foundation for subcutaneous [under the skin] islet transplants as a relatively safe and durable treatment option for type 1 diabetes,” said the study’s lead author, Ge Li, PhD5. Reversing Cellular AgingTheme: Identification of the protein AP2A1 as a key regulator of cellular senescence and a potential target for anti-aging therapies.Key Ideas:Senescent cells accumulate with age and contribute to age-related diseases.AP2A1 is upregulated in the stress fibers of senescent cells.Suppressing AP2A1 in older cells promotes rejuvenation, while overexpressing it in young cells accelerates senescence.AP2A1 interacts with integrin β1, strengthening cell adhesion and contributing to the enlarged structure of aging cells.Quote: “Suppressing AP2A1 in older cells reversed senescence and promoted cellular rejuvenation, while AP2A1 overexpression in young cells advanced senescence,” explains Shinji Deguchi, senior author.Overall Implications:These advancements highlight the potential of emerging technologies such as genomics, gene therapy, nanosensors, and cell engineering to address significant unmet medical needs. While further research and clinical trials are necessary, these findings offer promising avenues for improving early disease detection, treatment efficacy, and overall healthspan.convert_to_textConvert to sourceNotebookLM can be inaccurate; please double check its responses. This is a public episode. If you would like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit weeklybreakthroughs.substack.com