Discover Colloquy
Colloquy

68 Episodes
Reverse
How did the Harvard PhD experience influence W.E.B. Du Bois, the man who would become one of the leading Black activists and intellectuals of the 20th century? And what connections did he make in the vibrant Black community outside of campus? Join us as we explore these questions in the first of a two-part conversation with New York University professor and National Humanities Medal recipient David Levering Lewis, winner of the Pulitzer Prize for his two-volume biography of W.E.B. Du Bois.
As states around the country face off in a contest of Gerrymandering, what is the future of voting rights in the United States? Will the Supreme Court nullify what’s left of the landmark Voting Rights Act of 1965? How will accelerating climate change effect US politics? And what might happen in the all-important election of 2028? Harvard's Frank G. Thomson Professor of Government Stephen Ansolabehere, PhD '89, an expert in public opinion and elections and a consultant for the CBS News Election Decision Desk, recently joined Dean Emma Dench of the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences to address these and other questions in a discussion of elections, energy, and the public mood.
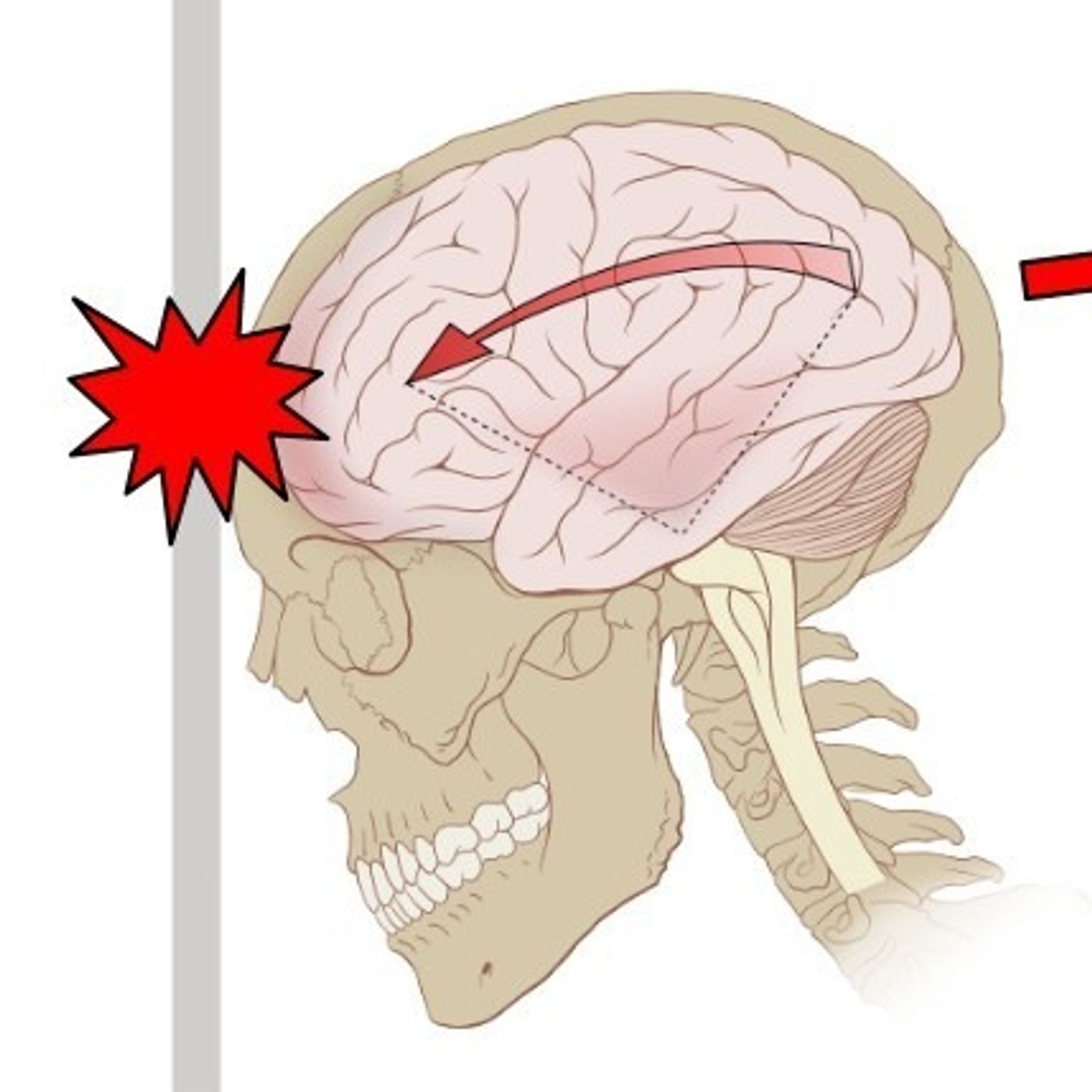
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated head injuries. It has been found in professional athletes, soldiers, and others who have experienced years of those traumas. New research from Harvard Griffin GSAS alumni Chanthia Ma and Guanlan Dong may help us better understand this condition. Their study looks at the smallest units of brain biology—individual neurons—and finds surprising clues written in the DNA itself. Using single-cell genome sequencing, they discovered that neurons in people with CTE carry distinctive patterns of genetic damage—patterns that may overlap with those seen in Alzheimer’s disease. In this episode of Colloquy, Ma discusses how her work not only sheds light on how brain trauma leads to long-term decline but also hints at possible shared mechanisms across different neurodegenerative conditions.
Us against the redcoats. That's how we often think of the American Revolution. In Ken Burns’ latest film, scheduled to drop later this month on PBS, the acclaimed documentarian takes on that simplistic notion of the nation's founding and many others. The revolution was actually a civil war, Burns says, one that pitted Americans, including indigenous and Black folk, against each other as much as the British. So, what were the divisions among the inhabitants of the British colonies and their neighbors? How did they flare into war? How did a fledgling nation with no central government or standing army defeat the world’s largest empire? And what were the contributions of indigenous and Black people and women? Philip C. Mead, PhD ’12, former chief historian and head curator of the Museum of the American Revolution in Philadelphia, weighs in.
“How long have you been in the snare of the devil?” That was the lose‑lose question asked of those—mostly women—accused of witchcraft in Essex County, where Salem Village was located, in 1692. According to the Cornell University historian Mary Beth Norton, PhD ’69, however, it was the accusers, rather than their targets, who were in the thrall of something powerful. In her 2002 Ambassador Award–winning book In the Devil’s Snare, Norton says that the Salem witchcraft crisis was driven not by a demonic force, but rather by the trauma of the nearby wars with New England’s Indigenous populations—conflicts that had been raging for many years and had left an indelible mark on many refugees who fled to towns on the North Shore of Massachusetts.
We all want to live as long and as well as possible. Diet and exercise are crucial, but how can we make sense of the flood of information, which sometimes seems to contradict itself? More importantly, how can we adapt the information in ways that work for us as individuals?Know thyself, answers Duke University Professor Herman Pontzer, PhD ’06. Every body has a story, he asserts in his new book, Adaptable. So does every part of our body. The main characters are our organs and systems. The themes and plot are a mishmash of genes and our environment. The result is an astonishing amount of diversity across humanity, united by our common ability to adapt over time and place. Pontzer says that a deeper understanding of how our bodies evolved and how that process shapes our biology can help us better take charge of our health.
2025 Harvard Horizons Scholar Sergio Alarcón Robledo explores ancient Egyptian architecture through an interdisciplinary approach that sits at the crossroads of archaeology, Egyptology, and architecture. By inquiring about the sensorial experiences of the past, the PhD student in Near Eastern languages and civilizations at the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences seeks to understand why ancient funerary structures changed and evolved into monumental buildings. Collaborating with experts from Stanford University, Alarcón Robledo employed acoustic analysis to unravel how these ancient spaces would have shaped sound and, consequently, the human interactions that took place within them.
The Inka Empire, the largest in the pre-Columbian Americas, is renowned for its impressive engineering feats, including an extensive road network and monumental architecture. Although the Inkas did not have a traditional writing system, they recorded information using a unique method: khipus. These knotted cords were essential tools for communication and record-keeping. Through meticulous structural analysis and documentation, FitzPatrick seeks to uncover the meanings encoded in khipus beyond their numerical knots. FitzPatrick’s project not only aims to advance archaeological knowledge but also seeks to reframe public understanding of the Inka Empire's complex administrative capabilities. By preserving and interpreting khipus, he hopes to reveal a more nuanced history of the Andean civilizations, illuminating the enduring legacy of their cultural innovations for contemporary audiences, as well as a powerful Indigenous perspective on Andean history—one distinct from narratives provided by Europeans.
The figure of the young, tragic male poet has long dominated cultural narratives about artistic brilliance and early death. But what if poetic genius deepens, rather than fades, with age? In this talk given at the 2025 Harvard Horizons Symposium, Slavic languages and literatures PhD candidate and Harvard Horizons Scholar Alex Braslavsky explores the creative power of poets in their advanced age in her project, "Embracing Twilight: Older Women Poets and the Unfurling of Their Voices". Focusing on three radical women writers, Braslavsky examines how aging can become a source of artistic innovation, personal transformation, and visionary insight. Drawing on archival research and a deep connection to Slavic literary traditions, her work challenges dominant cultural myths of decline and illuminates the enduring power of late-life creativity.
Raphaël Raux's 2025 Harvard Horizon project, "Human Learning about AI," conducted in collaboration with fellow PhD student Bnaya Dreyfuss, explores how people often assume AI thinks like a human, which can lead to confusion about what these systems can and can’t do. As a PhD candidate in economics at Harvard, Raux studies the complex relationship between how humans think and how artificial intelligence works. His research challenges common assumptions about AI and encourages a clearer, more realistic understanding of the technology. In his April 2025 talk at the annual Harvard Horizons Symposium, Raux shared insights from his work, which he hopes will support smarter decisions about how we use AI and help guide its development in ways that benefit both the economy and society.
As a PhD candidate in government at Harvard's Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, 2025 Harvard Horizons Scholar Andrew O'Donohue explores the complexities of democratic resilience in his project, "Law versus Democracy: Why Courts Defend or Undermine Democracy in Turkey, Israel, and Beyond." His research delves into the varying roles that courts play in either protecting or eroding democratic systems, drawing insights from compelling case studies in Turkey and Israel.
2025 Harvard Horizons Scholar Katherine Horgan explores the legacy of the ancient Greek poet Sappho in her project, "Living Sappho: Imitation, Imagination, and Revivification in Early Modern England." A PhD student in English at Harvard's Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, Horgan delves into the complex interplay between Sappho’s textual and biographical traditions, exploring how artists and writers have continuously reimagined and celebrated Sappho over millennia. Horgan’s research argues for the transformative power of Sappho’s work throughout literary history. By illuminating the rich afterlife of Sappho's poetry and persona, Horgan not only contributes to the recovery of marginalized voices but also invites contemporary readers to engage with Sappho as a site of playful exploration and enduring inspiration.
We hate each other more than we used to, at least where politics is concerned. Measures of effective polarization, the animosity that Democrats have for Republicans and vice versa, have increased dramatically since the 1990s, according to a 2021 study by political scientists James Druckman and Jeremy Levy. Moreover, the most polarized folks are the ones most likely to vote in primaries, resulting in more extreme general election candidates, which further polarize voters, and so on. Boston University professor Jacob Brown, PhD ’22 says that where we live shapes the political party we join and the candidates we vote for. The places we grow up shape our views and social pressure influences our affiliations. Moreover, when we change neighborhoods or our neighborhoods change around us, our party ID can change too. That fact—that our affiliations are not necessarily set in stone, but can shift as the people and places around us do—may offer some hope for the future of civic life in The United States . . . if we know what to do with it.
2025 Harvard Horizons Scholar Katherine Venturo-Conerly is on a mission to revolutionize access to effective mental health care—particularly for young people. Her research project, "Tackling the Global Youth Mental Health Challenge: Lessons from Psychotherapy Research in Kenya," focuses on creating and implementing effective, accessible mental health interventions for children and adolescents in multiple countries, with a particular focus on Kenya. As co-founder of Kenya’s Shamiri Institute with her Harvard College classmate Tom Osborn, Venturo-Conerly is developing a collaborative and sustainable approach to bridge the mental health care gap around the world. In this talk delivered in April 2025 at the annual Harvard Horizons Symposium, Venturo-Conerly talks about creating, testing, and implementing effective, accessible mental health interventions for children and adolescents across multiple contexts.
The US Supreme Court’s 2023 ruling in Students for Fair Admissions v. Harvard made it illegal for colleges and universities to use race as a factor in choosing their incoming classes. As a result, schools are working harder than ever to recruit and admit first-generation and lower-income applicants to preserve the diversity of their student bodies. But the Boston University sociologist Anthony Abraham Jack says American higher education wasn’t ready for the diversity they were recruiting before the Court's ruling—and they're still not ready now. His research shows how schools often fail to acknowledge the inequities of class and race that students bring to campus from home. The solution? Pop the campus bubble and begin looking at the ways that place impacts the challenges low-income and first-generation students face. Anthony Abraham Jack is the Inaugural Faculty Director of the Newbury Center at Boston University, where he is an associate professor of higher education leadership at the Wheelock College of Education and Human Development. He has earned awards from the American Educational Studies Association, the American Sociological Association, and the Association for the Study of Higher Education, among others. His first book, The Privileged Poor: How Elite Colleges Are Failing Disadvantaged Students, earned awards from the Association for the Study of Higher Education and the Eastern Sociological Association and was named one of National Public Radio’s Best Books of 2019. His second book, Class Dismissed: When Colleges Ignore Inequality, and Students Pay the Price, won the PROSE Award in Education Theory and Practice from the Association of American Publishers. Anthony Abraham Jack received his PhD in sociology from Harvard Griffin GSAS in 2016.
Imagine your doctor could precisely predict your personal risk of disease, diagnose the cause of illness with pinpoint accuracy when it did occur, and develop an effective treatment plan with low side effects the first time, rather than through trial and error. That's the promise of personalized medicine. And it would be a revolution in healthcare. At the heart of this vision is the notion that our genetic differences have a big impact on how each of us responds to disease and treatment. To realize a future of personalized medicine then, we need to understand and investigate just how genetic variations, including mutations, contribute to illness and respond to doctors' attempts to address it. But how can scientists do that efficiently with a human genome that spans about three billion base pairs of DNA across tens of thousands of genes? That's where the work of PhD student Dawn Chen comes in. A student in Harvard’s Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology and the Systems, Synthetic, and Quantitative Biology Program, Chen was named a recipient of the 2025 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award for Outstanding Achievement and Exceptional Research in the Biological Sciences, presented by Seattle's Fred Hutch Cancer Center. With her colleagues in the lab of Harvard professor Fei Chen, Dawn Chen is developing an innovative gene-editing tool known as helicase-assisted continuous editing, or HACE. A breakthrough in genetic engineering, supported in part by funds from the National Institutes of Health, HACE makes edits to specific genes, allowing researchers to investigate how genetic variations contribute to disease. The technique could lead to the identification of specific mutations that influence the effectiveness of drugs and therapies for illnesses like cancer.
The cost of prescription drugs is high—particularly in the US where consumers pay nearly three times more than those in 33 other nations in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. One factor in prices is fluorination, which plays a crucial role in the production of many widely-used pharmaceuticals. Driven by the high cost of reagents needed for the trifluoromethyl (CF₃) group, the process is expensive—and hard on the natural environment. If there was a way to make fluorination more accessible, sustainable, and affordable—it could reshape how we approach drug synthesis—and much else in chemistry.Chemist and Harvard Griffin GSAS PhD candidate Brandon Campbell has developed an innovative method of fluorination that could do just that. Using silver and visible light, Campbell’s pioneering approach promises a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional synthetic methods.
The history of slavery in the United States, including at the country's colleges and universities, is deeply disturbing and painful. But Professor Sara Bleich, PhD ’07, says it’s critical that our society continue to do so—and that universities have a responsibility to lead the way. Harvard’s inaugural vice provost for special projects and a former member of the Obama and Biden administrations, Bleich leads the effort to implement the seven recommendations of the 2022 report on Harvard & the Legacy of Slavery. Her goal is to help the University—and, by extension, the country — move forward into a future where Black Americans can succeed and thrive.
Technological disruption of human occupations is nothing new. In recent decades, blue-collar occupations have borne the brunt of the upheavals—think of all the factory workers now working at Wal-Mart thanks to the integration of robots on assembly lines. But all that may be changing now. Given artificial intelligence’s ability to do thought work—from crafting feature stories in seconds to writing and editing computer code—disruptive innovation is now coming to a college-educated profession near you. Feeling concerned? Take heart. Harvard's Isabelle and Scott Black Professor of Political Economy David Deming says AI is here to make us more productive, not take our jobs—at least not yet. The co-author of the recent paper, "Technological Disruption in the US Labor Market," Deming says that thanks to technology, every small businessperson or professional can now have an indefatigable digital assistant, one with a flawless memory, encyclopedic knowledge, and lightning-fast response time—and one who will never ask for a raise or even a wage.Deming, who received his PhD from the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences in 2010, spoke recently about artificial intelligence and its impact on the labor market during an event for the School’s alumni at the Harvard Club of San Francisco. He was interviewed by Harvard Griffin GSAS Dean Emma Dench, whose questions were sometimes submitted by audience members.
With filmgoers buzzing about the Bob Dylan biopic, A Complete Unknown, University of Pennsylvania Professor Jeffrey Edward Green, PhD ’07, says that the legendary singer and songwriter is more than a musician; he’s the conflicted prophet of a fallen world. In his new book, Bob Dylan, Prophet Without God, Green writes that Dylan models, "how to practice self-reliance in a world of permanent injustice and suffering, without appeal to divinity and providence, and without the self-satisfaction of believing he is also adequately fulfilling his social responsibility, or abiding by an individualism that everyone is equally free to practice if they wish." In that sense, Green contends, Dylan “has bestowed a message uniquely suited to a time such as ours."