Discover Keen On America
Keen On America

Keen On America
Author: Andrew Keen
Subscribed: 10,912Played: 950,002Subscribe
Share
© 2025 Andrew Keen
Description
Nobody asks sharper or more impertinent questions than Andrew Keen. In KEEN ON, Andrew cross-examines the world’s smartest people on politics, economics, history, the environment, and tech. If you want to make sense of our complex world, check out the daily questions and the answers on KEEN ON.
Named as one of the "100 most connected men" by GQ magazine, Andrew Keen is amongst the world's best-known technology and politics broadcasters and commentators. In addition to presenting KEEN ON, he is the host of the long-running show How To Fix Democracy and the author of four critically acclaimed books about the future, including the international bestselling CULT OF THE AMATEUR.
Keen On is free to listen to and will remain so. If you want to stay up-to-date on new episodes and support the show please subscribe to Andrew Keen’s Substack. Paid subscribers will soon be able to access exclusive content from our new series Keen On America.
keenon.substack.com
Named as one of the "100 most connected men" by GQ magazine, Andrew Keen is amongst the world's best-known technology and politics broadcasters and commentators. In addition to presenting KEEN ON, he is the host of the long-running show How To Fix Democracy and the author of four critically acclaimed books about the future, including the international bestselling CULT OF THE AMATEUR.
Keen On is free to listen to and will remain so. If you want to stay up-to-date on new episodes and support the show please subscribe to Andrew Keen’s Substack. Paid subscribers will soon be able to access exclusive content from our new series Keen On America.
keenon.substack.com
1699 Episodes
Reverse
Might 2025 turn out to be the new 1925? In other words, are we currently in the Roaring Twenties and on the brink of another Great Depression? This historical analogy, according to the Financial Times’ chief economics commentator Martin Wolf, isn’t entirely fanciful. Economic history doesn’t exactly repeat itself, Wolf acknowledges, but it has a rhythmic quality. We are living, he suggests, in a “slow-motion” interwar moment. And while FDR is Donald Trump’s mirror image, perhaps the most similar President to Trump was Warren Harding whose administration was deeply tarnished by the Teapot Dome scandal. Crypto, Wolf suggests, might turn out to be Trump’s Teapot Dome. And 2026, Martin Wolf warns, might turn out to be significantly more turbulent for both the US and global economies than 2025.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
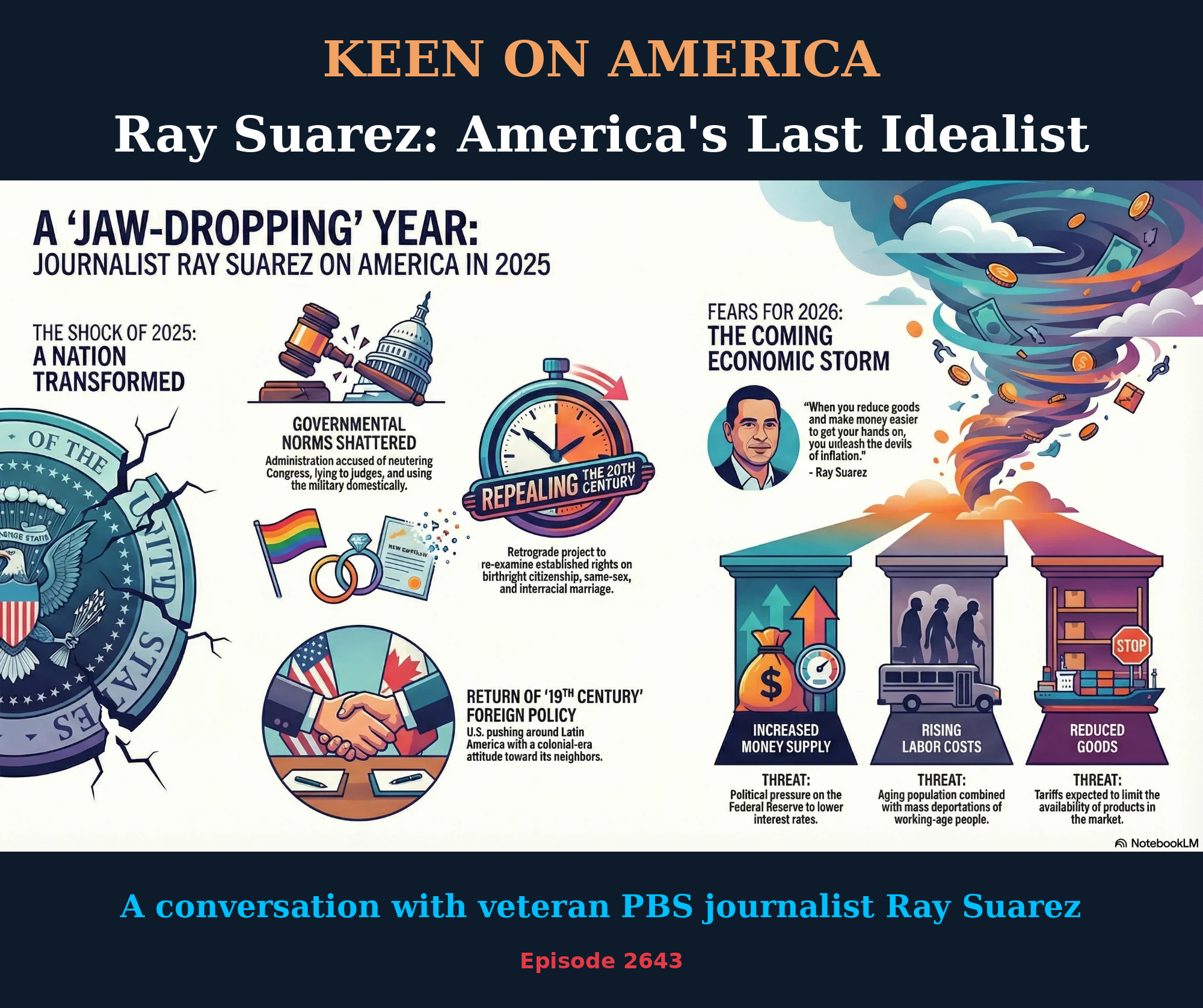
“If they want to put on my tombstone ‘The Last Idealist’, that’s fine,” the iconic (and I don’t use that word lightly) American journalist Ray Suarez tells me. But even Suarez’s idealism was tested by Trump’s America in 2025. It was a “jaw-dropping” year, he tells me, astonishing for a veteran journalist like Suarez. In some senses, he says, America has reverted to being a 19th century colonial power. So what happens when you “repeal” the 20th century? For all his idealism, Suarez is a realist, particularly in economics. So it's worth noting his warnings about the “devils of inflation” in 2026 which he sees as a likely consequence of Trump’s economic populism. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
So what does the latest Time Warner brouhaha tell us about the state of America? According to Daniel Bessner, host of the American Prestige podcast, it reflects the imminent death of Hollywood itself. Having written a recent Harper’s cover story about “The Life and Death of Hollywood”, Bessner is no stranger to the existential struggle of America’s dream machine. And for Bessner, the latest Netflix-Paramount drama is just one proof point not just of Hollywood’s last dance, but also the imminent crisis of American capitalism. It’s the canary in the coal mine, he argues, about the future of every industry. His apocalyptic take would, of course, make a great movie. The only problem is that Hollywood won’t be around to make it. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
It’s been quite a week in tech. The Australian social media ban, the Netflix vs Paramount fight over Warner Bros & the Disney-OpenAI deal. That Was The Week’s Keith Teare and I try to explain all this in the broader context of the future of media in 2026 and beyond. Has Australia really gone Orwellian in its teen social media ban, who should own Warner and will movie theaters & serious journalism have a future in the AI age? Our answers aren’t always what you’d expect. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Mount Rushmore, with its images of four Presidents carved into the Black Hills of South Dakota, is America’s most identifiable monument. It might also be its most monumental contradiction — which is saying a lot, given the country’s gaping contradictions. According to Matthew Davis, the mountain’s biographer, the history of the Rushmore project captures both the remarkable engineering achievements of early 20th-century America and the country’s bloody colonial and racist past. So Mount Rushmore, Davis suggests, is indeed as American as cherry pie. Only that pie and those cherries aren’t quite as sweet as the MAGA crowd might like to think. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
George Packer is one of the most celebrated non-fiction writers on contemporary America. So why, in his new book The Emergency, has he turned to fiction? You’d think, after all, that MAGA America’s surrealism would be an ideal nonfictional canvas for a writer with Packer’s observational gifts. But, as Packer explains, when facts fail a society, then - like Orwell or Atwood - a writer might be obliged to turn to fiction. This emergency, then, begot The Emergency. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
The CNN anchor Carol Lin was on air on September 11, 2001 when the first plane hit the tower. So, in that now seemingly distant broadcast media age, she was the world’s first television journalist to break the news. But as Lin notes in her new memoir, When New Breaks, 9/11 broke traditional news media, both then and now. That morning was CNN’s finest hour — a network built for exactly this moment, with deep resources, high standards, and global reach. Yet it was also the beginning of the end - both for Lin’s career in journalism and for the mainstream television news industry. What followed was the rise of opinion panels, personality-driven shows, ubiquitous social media and the slow erosion of trust that leaves us asking: who do we believe anymore?Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Jessica was the good Mitford sister. The English aristocrat who fought against fascism in the Spanish Civil War, then came to America and dedicated her life to social justice. According to her biographer Carla Kaplan, Mitford had the fierce, unruly life of a great muckraker. She was a Troublemaker in the best sense of the word. Unlike prudes like Upton Sinclair or Ralph Nader, she was hysterically funny—her voice as distinctive as Jane Austen’s or Virginia Woolf’s. She understood that bullies are driven by insecurity and paranoia, and she knew exactly how to punch them in the nose with her sharp upper-class English humor. So where are you now, Jessica Mitford? When the left desperately requires a good dose of humor and the right needs to be laughed at?Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
The American economy is a numbers game and those numbers are becoming more and more unfair. “30 years ago, if you were born in the bottom 25th percentile of wealth, you had about a 25% chance of dying in the top 25th percentile.” notes the venture capitalist Seth Levine. “Today you’ve got a 5% chance.” So what to do? What Levine wants is more rather than less capitalism. As he argues in his new co-authored (with Elizabeth MacBride) book, Capital Evolution, “if we want more people to have a stake in the economy, more people have to have a stake in the economy.” Thus the case for what he calls stakeholder capitalism. Only capitalism can save capitalism, Levine argues. Whether that’s Davos-style tautology or the way to right the wrongs of American capitalism is a more complicated question. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Numbers often tell the story best. Yesterday, we discussed today’s 95/5 reality in which 5% of Americans control 95% of the wealth. Today, in our conversation with Patrick Markee, author of Placeless, the key number is 2%. That’s the number of Americans who, on any given day, are homeless. But it’s a number, Markee insists, that doesn’t have to be. Mass homelessness, America’s most shameful open secret, is a modern phenomenon, he explains, triggered by Reagan’s neo-liberal policies. There’s nothing inevitable or necessary about it. And just as economic and political policy caused the crisis, it can also solve it. What’s most chilling is how normalized it’s become. Two-thirds of Americans are too young to remember a time when large numbers of people weren’t sleeping on sidewalks. In New York City alone, 35,000 children sleep in shelters every night—numbers not seen since the Great Depression. Future generations, Markee suggests, will look back at us the way we look back at those who tolerated slavery. How could we all have just walked on by? This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Forget Pareto’s 80/20 rule. What AI is doing is producing a new rule in which 5% of society captures 95% of the value of this revolution. That Was The Week publisher Keith Teare calls this the “Great Compression”, describing it as the new math of our AI age. It’s creating a winner-take-most society of increasing inequality and outrage - the kind of situation which, historically, governments have stepped in to redistribute the rewards of a great technological leap forward. That isn’t happening today, however, thereby creating what Keith and I describe as a Code Red emergency for humanity. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Is the idea of “progress” the propaganda of the ruling class? Yes, according to Samuel Miller McDonald, author of Progress: How One Idea Built Civilization and Now Threatens to Destroy it. McDonald traces this “narrative formula” back 5,000 years to the first market empires in Mesopotamia—societies that were parasitic from the start, extracting from nature for profit and expansion. The Mesopotamian epic Epic of Gilgamesh, McDonald argues, is essentially a celebration of deforestation. Fast forward a few thousand years and modern industrialization didn’t corrupt this system; it supercharged it. His solution? Sortition, agroecology, and dissolving elite power. “I have more faith in the general public,” he tells me about a contemporary world dominated by what he sees as extractive billionaires like Bill Gates and Peter Thiel, “than in people who seek positions of power and control.” This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
They certainly are an odd couple. Silicon Valley veterans Dave McClure and Aman Verjee have been friends and business partners for 25 years — first at PayPal, then at 500 Startups, and now at Practical Venture Capital. Yet they have quite different styles, personalities and, above all, politics. What they share, however, is an unvarnished take on the world — especially on the much mythologized Silicon Valley. In this refreshingly unfiltered conversation, they assess tech’s two most dominant titans: Sam Altman and Elon Musk. McClure describes Altman as someone he’d never want to face across a poker table — “there’s probably three layers of chess going on in his head.” Verjee breaks down the competitive psychology driving Musk as OpenAI’s valuation leapfrogs SpaceX. Plus Verjee makes sense of Google’s Gemini challenge to ChatGPT domination and McClure leaves us with one of his trademark blunt takes on Trump’s crypto conflicts. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
If you think the American Dream is dead, then you probably don’t know the story of Lu Zhang. Born in Mongolia and educated in China, Zhang came to Stanford as a graduate student, struck it rich as a young tech entrepreneur and is now managing partner of her own early-stage venture fund. In our conversation, Zhang makes a compelling case for why Silicon Valley remains the world’s most important innovation ecosystem—even as she warns that restrictive immigration policies threaten to strangle the very talent pipeline that made her remarkable success possible. She’s bullish on AI, bearish on energy infrastructure, and refreshingly candid about the capital market bubble that everyone in tech pretends doesn’t exist. So does Zhang really exist or is she a bot designed to promote the American Dream? She says she’s real. I believe her. Do you? This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
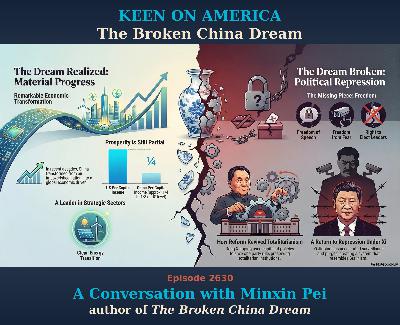
We all know about the broken American Dream. But according to the American-based China scholar Minxin Pei, China’s dream is equally broken. In his new book, The Broken China Dream, Pie argues that the party-centric reforms of both Deng Xiaoping and Xi Jinping have, by definition, revived totalitarianism. So while he does acknowledge some material achievements of the communist revolution, Pei is ultimately skeptical of its long-term benefit to the Chinese people. The party is the problem, Pei suggests. It has broken the Chinese dream. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
For Peter Wehner, American politics is a tale of two Kellys. On the one hand, there’s the moral resistance of Arizona Senator Mark Kelly to what appears to be the gratuitous violence of American forces overseas. On the other hand, there’s the conservative podcaster Megyn Kelly who has openly fantasized about this bloodthirsty behavior. For Wehner, Megyn Kelly’s immorality is an excellent example of both the moral and intellectual decline of the right. Once a serious journalist who challenged (and upset) Trump in the 2015 debates, Kelly has devolved into what Wehner calls “darkly deranged” territory - a trajectory that mirrors the broader conservative movement’s abandonment of Burkean and Madisonian principles for Kelly-style shock jocks and neo-Nazi clowns like Nick Fuentes. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Dick Cheney died four weeks ago, but his dark legacy lives on—quite literally—at Guantanamo Bay. The human rights lawyer Joshua Colangelo-Bryan was among the first attorneys to enter the notorious prison in 2004, and what he found there shattered every official justification for its existence. The “worst of the worst”? Most detainees were never even accused of acting against America. Many were simply sold to the Americans for bounties. The sophisticated interrogation program? Techniques copied from Chinese and Soviet methods designed to extract false confessions, not intelligence. In his new book Through the Gates of Hell, Colangelo-Bryan tells the story of his unlikely friendship with Jaber Mohammed, a Bahraini detainee who spent years in captivity for the crime of being an Arab man in the wrong place (Afghanistan) at the wrong time (post 9/11). Released without apology or compensation—just a form asking him not to “rejoin” organizations he’d never belonged to—Jaber now lives in Saudi Arabia with four children, focusing less on bitterness and more on those rare moments when American guards showed him unexpected kindness. As the Trump administration revives the “worst of the worst” rhetoric against immigrants and once again sends people to Guantanamo, Colangelo-Bryan’s account is a warning from recent history: demonize a racial or religious group, and you will inevitably destroy innocent lives. The gates of hell have once again been opened. Will they ever be closed? This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
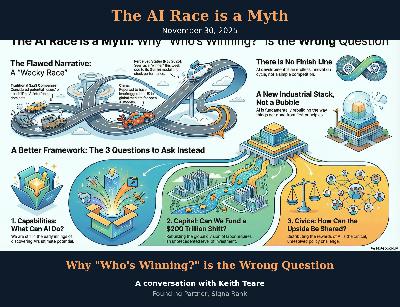
Who’s winning and losing in AI plays like a wacky race in that every week there seems to be a new leader. But that’s actually the wrong way of thinking about today’s AI revolution. The right questions are about the three Cs: Capability, Capital and Civics. That’s the lesson of Keith Teare’s latest That Was The Week tech newsletter which focuses on what he calls “the Year in Intelligence”. Nobody is winning the AI race, Teare argues, because it isn’t a race. Instead, it’s an endless innovation cycle without either a start or finish line. The three key questions are whether AI capabilities are solving real social and economic problems, whether we can fund a $200 trillion industrial rebuild, and whether the rewards can be equitably shared. Those are the questions we should be asking. Not who is winning or losing.Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
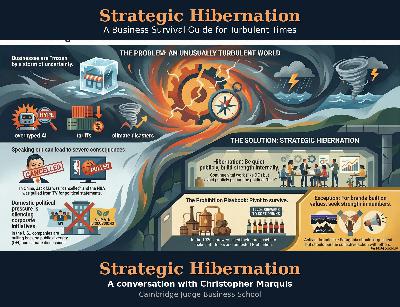
“May you live in interesting times,” is supposed to be a Chinese mantra. But according to Cambridge University China expert, Christopher Marquis, our current interesting times are actually a curse for businesses seeking stability rather than disorder. Is this, then, a moment for “strategic hibernation” Marquis asks in a provocative Harvard Business Review piece. Yes, he mostly answers. Businesses are indeed frozen by a perfect storm of uncertainty—overhyped AI, tariffs, and climate disasters. And speaking out in these turbulent times, he warns, can carry severe consequences -such as Jack Ma’s “cancellation” and the NBA’s exile from Chinese TV demonstrated after political missteps. Marquis, author of Mao and Markets, draws on his decade observing Chinese corporate survival tactics to counsel American companies navigating the stormy Trump waters: continue vital work like DEI internally, but avoid publicly poking the political bear. The Prohibition playbook offers a historical model—1920s brewers pivoted to soft drinks using their core bottling capabilities, hibernating their alcohol-making assets until the environment changed. The exception? Brands built on moral values, like Patagonia and Dr. Bronner’s, shouldn’t go silent—but even they should seek strength in collective action rather than standing alone. Rather than poking the bear, Marquis concludes about our interesting times, become the bear and hibernate. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe
Few journalists, certainly non-Italians, know Italian football as intimately as The Athletic’ James Horncastle, co-author of The Soccer 100. For Horncastle, Italian football presents a fascinating paradox: a nation celebrated for beauty, fashion, and La Grande Bellezza built its footballing identity around winning ugly. Forged in post-war austerity, the Italians embraced a minimalist, counter-attacking style—yet their greatest defenders, Paolo Maldini and Franco Baresi, were anything but ugly players, mastering their craft with elegance and brilliance. Italy, Horncastle reminds us, has also produced a remarkable lineage of world-class goalkeepers, from Dino Zoff to Gianluigi Buffon. And despite its defensive reputation, the position Italians venerate most is the creative number 10—the fantasista embodied by Roberto Baggio, the subject of an upcoming biography by Horncastle. Then there’s Maradona, the “spiritual Italian” who found his perfect home in Naples, a city with a magical realism quality that matched his unique genius. Unlike England, where football loyalties follow class lines, allegiances at Italian clubs like Roma and Lazio are drawn along political divisions—a legacy of Cold War tensions when Italy hosted Western Europe’s largest communist party. Keen On America is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.Thanks for reading Keen On America! This post is public so feel free to share it. This is a public episode. If you'd like to discuss this with other subscribers or get access to bonus episodes, visit keenon.substack.com/subscribe





















Just wanted to bring to someone's attention that the audio includes one recording on too of another (as of March 30).
oh Lord. this show is hilarious.only white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
oh Lord. this show is hilarious. white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
oh Lord. this show is hilarious. white wealthy academia and the media are pushing this narrative.
I'm new to this show and I must say it made a very good impression. The interviewee is allowed to talk most of time, which helps us understand the topic better and lends an atmosphere of calm to the whole interview. There's another show out there which is pretty good, but the host asks such lengthy questions and at such high speed that it's hard for us, let alone to the guest, I guess, to keep up (I won't name names! Lol).