Discover Upwardly Mobile - API & App Security News
Upwardly Mobile - API & App Security News

 Upwardly Mobile - API & App Security News
Upwardly Mobile - API & App Security News
Author: Approov Mobile Security
Subscribed: 2Played: 75Subscribe
Share
© Copyright 2025 Approov
Description
Think the App Store’s built-in security is enough? Think again.
Welcome to Upwardly Mobile, the podcast that exposes the gaps in iOS, Android, and HarmonyOS security. Hosts Skye and George take you into the high-stakes world of mobile defense, revealing why standard protections from Apple, Google, and Samsung often leave your sensitive data exposed. Sponsored by Approov—the gold standard in mobile app attestation—we move beyond the basics to tackle weaponized AI threats and dynamic API attacks. From runtime attestation to navigating complex compliance regulations, we equip developers and security pros with the actionable strategies needed to thwart attackers. Don’t leave your app vulnerable.
Subscribe now on Spotify and Apple Podcasts to elevate your security game.
Welcome to Upwardly Mobile, the podcast that exposes the gaps in iOS, Android, and HarmonyOS security. Hosts Skye and George take you into the high-stakes world of mobile defense, revealing why standard protections from Apple, Google, and Samsung often leave your sensitive data exposed. Sponsored by Approov—the gold standard in mobile app attestation—we move beyond the basics to tackle weaponized AI threats and dynamic API attacks. From runtime attestation to navigating complex compliance regulations, we equip developers and security pros with the actionable strategies needed to thwart attackers. Don’t leave your app vulnerable.
Subscribe now on Spotify and Apple Podcasts to elevate your security game.
111 Episodes
Reverse
The 3.5 Billion WhatsApp Scraping Flaw: Is Your Mobile API Leaking?Episode Summary: In this episode, we break down a massive vulnerability discovered by researchers at the University of Vienna and SBA Research that allowed them to scrape data from roughly 3.5 billion WhatsApp accounts globally. We explore how a lack of rate limiting on the specific GetDeviceList API endpoint turned a benign contact discovery feature into a massive "enumeration oracle," allowing a single university server to query over 100 million numbers per hour. We discuss the types of data exposed—including active status, device types, public encryption keys, and millions of profile photos—and the implications for user privacy, particularly in regions where WhatsApp is banned like China and Iran. Finally, we cover Meta’s response to the disclosure and why industry experts are calling this a "masterclass in negligence" regarding API security. Key Topics Discussed:The Vulnerability: How researchers used the GetDeviceList API to bypass safeguards and identify valid accounts across 245 countries.The Scale: How a single server sustained 7,000 requests per second to verify 3.5 billion accounts without being blocked.The Data: The exposure of profile images, "about" text, and public keys, and how this data correlates with previous Facebook leaks.The Security Lesson: Why "does this number exist?" lookup APIs are inherently dangerous without strict behavioral monitoring and rate limiting.Sponsor: This episode is supported by Approov. When mobile app security is an afterthought, user privacy becomes collateral damage. Approov ensures that only genuine mobile app instances, running on safe mobile devices, can access your backend APIs.Visit the Sponsor: https://approov.ioFeatured Sources & Further Reading:BleepingComputer: WhatsApp API flaw let researchers scrape 3.5 billion accounts – Detailing the mechanics of the GetDeviceList abuse and the global scope of the data scrape.Malwarebytes: WhatsApp closes loophole that let researchers collect data on 3.5B accounts – Analysis of the privacy implications, including the exposure of users in restrictive regimes.Privacy Guides: WhatsApp contact discovery vulnerability identifies 3.5 billion users – Discussing the patch and how alternative messengers handle contact discovery.Keywords: WhatsApp, API Security, Rate Limiting, Data Scraping, Mobile Security, Cybersecurity, Meta, Privacy, Enum, GetDeviceList, Infosec, Approov. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Apple's DMA Non-Compliance: An Open LetterIn this episode of *Upwardly Mobile*, we break down the seismic shift in the mobile app landscape following the European Commission’s decision to formally fine Apple €500 million for breaching the Digital Markets Act (DMA). We explore why regulators view Apple’s recent changes not as genuine adherence to the law, but as "malicious compliance"—a deliberate attempt to technically meet requirements while maintaining control and fees.We also discuss the December 2025 Open Letter sent by app developers to EU President Ursula von der Leyen, which argues that Apple’s new 20% commission on external transactions continues to violate the law and stifle fair competition. Finally, we contrast the situation in Europe with recent US court rulings involving Epic Games, where judges have ordered Apple to stop charging for services it doesn't provide, raising the question: Why are European developers getting a worse deal?.Key Topics Discussed:* **The €500M Fine:** The European Commission found Apple in breach of "anti-steering" obligations, restricting developers from directing users to cheaper offers outside the App Store.* **"Malicious Compliance":** An analysis of how Apple’s fee structures and "scare screens" are viewed by critics and regulators as structural impediments to the DMA’s goals.* **The Meta Connection:** A look at the parallel €200M fine imposed on Meta regarding their "pay or consent" model.* **The Developer Pushback:** Insights from the "CleanV2" Open Letter, where developers demand the removal of new commission fees that range up to 20%.* **Transatlantic Tensions:** How the US Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling regarding Epic Games highlights disparities in global enforcement.**Sponsor:**This episode is brought to you by **Approov**.Securing mobile apps is hard; Approov makes it easy. Ensure your APIs are only accessed by genuine instances of your mobile app and block scripts, bots, and modified apps.**Visit: [https://approov.io](https://approov.io)****Resources & Source Materials:*** **European Commission Press Release:** Details on the April 2025 fine regarding Apple’s anti-steering practices.* **Kluwer Competition Law Blog:** "The DMA's Teeth: Meta and Apple Fined by the European Commission" by Alba Ribera Martínez.* **Clean App Foundation Open Letter:** The December 2025 appeal to the European Commission regarding Apple's persistent non-compliance.* **Analysis of US Rulings:** Context on the Epic Games vs. Apple court case and fee limitations.Digital Markets Act, DMA, Apple Fine, App Store Fees, Anti-Steering, Malicious Compliance, European Commission, Margrethe Vestager, Sideloading, Epic Games, Mobile App Security, Tech Policy, Antitrust.🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Chinese Hackers & the React2Shell CrisisThis week, we dive deep into the critical, maximum-severity security flaw known as React2Shell (tracked as CVE-2025-55182). This vulnerability, which impacts React, the widely-used open-source JavaScript library, allows for unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) through specially crafted HTTP requests on affected servers. The episode explores the immediate aftermath of the disclosure. Exploitation attempts began quickly, with Amazon Web Services (AWS) reporting that multiple China-linked threat groups, specifically Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda, were exploiting the flaw within hours of its public availability. These actors are using both automated tools and individual exploits, and some are even actively debugging and refining their techniques against live targets. Earth Lamia has been active since at least 2023, targeting various industries in Latin America, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, while Jackpot Panda focuses on cyberespionage operations in Asia. We also discuss the significant collateral damage caused by the urgent need to patch this flaw. Internet infrastructure giant Cloudflare experienced a widespread global outage, returning "500 Internal Server Error" messages worldwide, and attributed the incident to an emergency patch deployed to mitigate the industry-wide React2Shell vulnerability. This change was related to how Cloudflare’s Web Application Firewall parsed requests. Finally, we clarify the scope of the vulnerability: React2Shell primarily impacts server-side components. Specifically, it affects React versions 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0, particularly instances using a relatively new server feature. Standard React Native mobile apps are generally safe, but any backend built using Next.js (App Router) or React 19 Server Components that communicates with the mobile app is at critical risk. Furthermore, developers need to be aware of a separate, but timely, vulnerability (CVE-2025-11953) affecting the local React Native CLI development server. Key Concepts and TakeawaysVulnerability: React2Shell, CVE-2025-55182, is a critical vulnerability allowing unauthenticated remote code execution on affected servers.Scope: Impacts the React open-source JavaScript library, particularly React version 19 and dependent React frameworks such as Next.js (App Router). Cloud security giant Wiz reported that 39% of cloud environments contain vulnerable React instances.Threat Actors: Exploitation is linked to China-linked threat groups, including Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda.Major Impact: An emergency mitigation patch designed to address React2Shell caused a widespread global outage at Cloudflare.Fix: Patches were available shortly after disclosure, reported to Meta on November 29 and patched on December 3. Users must upgrade affected dependencies like react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, and react-server-dom-turbopack to version 19.0.1 or higher.Resources and LinksSecurityWeek (Source Context): (Note: Specific articles discussed are embedded within the episode content.)Expo Changelog: For specific SDK patch instructions.Sponsor Link: Protecting mobile app integrity against security threats is vital: approov.ioKeywords (Optimized for SEO) React2Shell, , Remote Code Execution (RCE), China-linked hackers, Earth Lamia, Jackpot Panda, React Server Components (RSC), Next.js vulnerability, React 19 security, web security, patch management, cyber espionage, critical vulnerability, application security🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Sanchar Saathi: The Mandatory Cyber Safety App Triggering India's Surveillance FirestormIn this critical episode of "Upwardly Mobile," we dive into the escalating controversy surrounding India's Sanchar Saathi app, a government-mandated digital tool that is fueling a nationwide debate over state surveillance and digital privacy. Designed as a citizen-centric safety tool to combat telecom fraud and track lost or stolen devices using their unique IMEI, the app has been lauded by the government for its success in blocking millions of fraudulent connections and stolen phones. However, a recent directive mandating its pre-installation on all new smartphones sold in India has drawn fierce criticism from privacy advocates, opposition politicians, and major tech firms. What You Will Learn in This Episode: The Core Conflict: Safety vs. SnoopingThe Mandate: The Indian telecom ministry privately ordered all smartphone manufacturers to preload Sanchar Saathi on new devices within 90 days, requiring the app to be "visible, functional, and enabled" upon first setup. This directive could eventually roll out the app to more than 735 million existing phone users via software updates.Government Defense: Officials state the app is strictly for cyber security and curbing the "serious endangerment" caused by IMEI tampering, promising adequate security for personal information. They also claim the app is optional and does not read private messages.Surveillance Fears: Privacy experts and the political opposition argue the mandate is unconstitutional and creates a massive surveillance surface area. Opposition leaders have even compared the move to 'Pegasus'.Technical Deep Dive into Privacy RisksThe Sanchar Saathi app requests a range of "dangerous" or "high-risk" permissions.The app has the capability to read call logs and all incoming SMS, technically allowing it to parse bank transaction alerts, 2FA codes, and map a user's social graph.It accesses device identifiers, binding a user's identity to the hardware IMEI, which breaks standard rules for resettable identifiers and aids tracking.If pre-installed as a system-level application (the proposed state), experts warn that permissions could be auto-granted without user consent, the app could run continuous background services, and it would be virtually impossible for 99% of users to uninstall.The privacy policy is weak, lacking explicit mechanisms for data deletion, correction, or a clear opt-out feature.Industry ResistanceTech giants were given 90 days to comply with the pre-installation mandate.Apple has specifically resisted the mandate, citing concerns over privacy and system security, as iPhones require explicit user confirmation for permissions and prevent automatic background registration.The mandate is technically easier to implement on Android devices, which make up over 95% of the Indian smartphone market.Keywords Sanchar Saathi, India digital privacy, state surveillance, government mandate, telecom fraud, cyber safety app, IMEI tracking, pre-installation controversy, Android security, iOS privacy, Apple resistance, call log permissions, data deletion rights, digital rights, Indian politics.Digital Autonomy and the Sanchar Saathi AppLink 1: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-sci-tech/telecom-scindia-sanchar-saathi-optional-key-concerns-10397728/Link 2: https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/sanchar-saathi-communications-ministry-jyotiraditya-scindia-big-brother-or-cybersafety-boost-deep-dive-into-sanchar-saathi-app-9735477Link 3: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/tech-news-technology/sanchar-saathi-app-preinstalled-android-ios-privacy-security-concerns-10397922/Link 4: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cedxyvx74p4oLink 5: https://www.reuters.com/sustainability/boards-policy-regulation/what-is-indias-politically-contentious-sanchar-saathi-cyber-safety-app-2025-12-02/Sponsor This episode is brought to you by Approov Mobile Security, helping developers secure their mobile APIs and prevent reverse engineering and unauthorized data access.Sponsor Website: approov.io🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Supply Chain Security Unpacked: Combating Dependency Confusion, Poisoned PipelinesEpisode Notes: The software supply chain, the "backbone of modern software development," is under unprecedented assault, with attacks aimed at libraries and development tools soaring by an astounding 633% year-over-year. This episode explores the evolution of supply chain threats, examining everything from software vulnerabilities and malicious maintainers to hidden risks lurking in hardware and commercial binaries, and details the cutting-edge defenses developers are deploying to fight back. The Evolving Threat Landscape: Implicit Trust Exploited Modern attacks exploit the implicit trust developers place in package managers and public repositories. Key threats discussed include:Dependency Confusion: First identified by Alex Birsan, this attack exploits package managers that prioritize packages found in public repositories (especially those with a higher version number) over identically named private packages. Attackers use reconnaissance to pinpoint internal package names (often by examining manifest files like package.json), publish a malicious package with the same name and a higher version to a public repository, and wait for the target application's build process to pull and execute the malicious code. Vectors for this attack include exploiting namespaces, DNS Spoofing, and manipulating CI/CD security settings.Widespread Malware and Stolen Secrets: The npm ecosystem was recently hit by the self-replicating "Shai-Hulud" worm, which compromised over 500 packages and harvested sensitive credentials, including GitHub Personal Access Tokens (PATs) and API keys for cloud services like AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure. Stolen credentials remain a reliable attack vector, leading to incidents where attackers published malicious code on behalf of trusted entities (e.g., Nx, rspack).Poisoned Pipelines and Malicious Maintainers: Highly sophisticated attackers are compromising build and distribution systems directly, bypassing code reviews. This includes notorious attacks like SolarWinds and compromises targeting GitHub Actions pipelines (e.g., Ultralytics and reviewdog/actions-setup). Furthermore, the XZ Utils backdoor highlighted the risk of malicious maintainers who build trust over years before inserting sophisticated backdoors into critical open-source projects.Code Rot and Vulnerable Open Source: A survey of popular open-source packages found them rife with vulnerabilities, with an average of 68 vulnerabilities across 30 packages scanned, including many critical and high-severity flaws. Even actively maintained, high-traffic packages like Torchvision contained dozens of vulnerabilities, despite frequent updates.Defense and Verification: Making Trust Explicit To counter these escalating threats, the industry is focusing on making trust assumptions explicit and verifiable:Supply-chain Levels for Software Artifacts (SLSA): SLSA is a security standard that helps consumers verify the process by which an artifact was created using a signed provenance file. Achieving Level 3 compliance involves stringent build platform hardening to prevent the forgery of provenance files.Trusted Publishing and Attestations: Platforms like PyPI have implemented Trusted Publishing, which removes the need for developers to manage long-lived API tokens by utilizing short-lived OIDC tokens issued by the build platform. Building on this, digital attestations (driven by PEP 740) cryptographically bind published packages to their build provenance using Sigstore.CI/CD Security Tools: Tools like Zizmor perform static analysis for GitHub Actions to flag subtle vulnerabilities like template injection or dangerous triggers. Capslock is an experimental tool used for Go language packages that statically identifies capabilities (like network access or file system operations), allowing developers to verify what code can actually do, regardless of where it came from.Preventing Confusion: Developers can mitigate Dependency Confusion through strict naming conventions, proactively reserving namespaces (or "namesquatting" on platforms like PyPI), utilizing private package repositories with stringent access controls (RBAC/MFA), and enforcing package whitelisting and version locking using files like package-lock.json.Verifying Commercial Binaries: Risks also lurk in closed-source commercial software ("black-box" binaries). The compromise of Justice AV Solutions (JAVS) demonstrated how malware (RustDoor) can be implanted in a backdoored installer; sophisticated tools like differential analysis are necessary to detect signs of tampering and unvetted files (such as the typosquatted ffmepg.exe). Organizations must adopt a "Don't Trust, but Verify" approach to all software received from suppliers.The Future of Vulnerability Management: The cybersecurity community is moving beyond sole reliance on CVEs, especially following the NVD backlog experienced in 2024. Comprehensive security now requires visibility into threats like malware, tampering, secret leaks, and lack of hardening, rather than just known vulnerabilities. NIST SP 800-204D outlines crucial strategies for integrating SSC security measures—including generating provenance data—into DevSecOps CI/CD pipelines.Relevant Links and Resources:Learn more about Dependency Confusion Prevention and DevSecOps Orchestration: approov.comNIST SP 800-204D: Strategies for the Integration of Software Supply Chain Security in DevSecOps CI/CD Pipelines: https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-204DKeywords: Software Supply Chain Security, Dependency Confusion, Hardware Trojan, SLSA Framework, CI/CD Pipeline Security, DevSecOps, Trusted Publishing, PyPI, npm, Zizmor, Build Provenance, Side-Channel Attacks, Malware, Cryptojacking, NVD Backlog, Digital Attestations, Zero Trust. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
The Multi-Terabit Battlefield: How Aisura 'Turbo Mirai' Botnet Reshaped Mobile DDoS WarfareOn November 18, 2025, a massive Cloudflare service interruption took down major platforms worldwide, including X, ChatGPT, Shopify, and various critical transit services. Given the intense, ongoing cyber conflict, initial speculation immediately pointed toward a successful, hyper-volumetric Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack. Cloudflare has recently been at the forefront of blocking unprecedented assaults from notorious botnets, including Mirai and the newer, "TurboMirai-class" Aisuru botnet. The company successfully mitigated record-breaking Mirai-variant attacks measured at 5.6 Tbps (October 2024) and 7.3 Tbps (May 2025). Furthermore, the Aisuru botnet, which is responsible for hitting Microsoft Azure with a 15.72 Tbps DDoS attack, was also linked to a 22.2 Tbps attack mitigated by Cloudflare in September 2025. Aisuru operators were even caught attempting to manipulate Cloudflare’s public domain rankings using malicious query traffic. This track record provided a clear motive for a potential reprisal. However, Cloudflare’s official investigation quickly dispelled fears of a successful cyberattack. Cloudflare CTO Dane Knecht confirmed that the incident was not an attack, but rather an internal issue. The cause was identified as a "latent bug" in a service underpinning Cloudflare’s bot mitigation capability that started to crash following a routine configuration change. This technical flaw cascaded into a broad degradation across the network. Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince later noted that this was the worst outage the company had experienced since 2019. This incident highlights that while automated security platforms like Cloudflare can defend against 20+ Tbps DDoS attacks, they remain vulnerable to complex internal technical flaws and configuration management errors. Keywords Cloudflare outage, DDoS, Aisuru Botnet, Mirai, Configuration error, Latent bug, Dane Knecht, November 2025, IoT security, Incident Response, Cyberattack, Network Security, Cloud Security.Hashtags #ConfigurationManagement #IncidentResponse #CloudSecurity #IoT Related Links & Sources To read more about the incident and the cyber threat landscape, please refer to the following:Cloudflare Outage Not Caused by Cyberattack (SecurityWeek):Microsoft: Azure hit by 15 Tbps DDoS attack using 500,000 IP addresses:Cloudflare’s official report on the November 18, 2025 outage:Discussion on the configuration file bug:TurboMirai-Class ‘Aisuru’ Botnet Blamed for 20+ Tbps DDoS Attacks:Sponsor Message Today’s episode is brought to you by Approov. In an era where botnets like Aisuru are exploiting every vulnerability, securing your APIs and endpoints is paramount. Approov provides essential mobile app and API protection, ensuring that only trusted, legitimate clients can connect to your back-end services, providing a crucial layer of defense against sophisticated automated attacks. Learn more about protecting your mobile infrastructure at approov.com.🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Black Friday's Hidden Threat: Stopping AI-Powered Fraud and Mobile Commerce Exploits The biggest shopping days of the year—Black Friday and Cyber Monday—have also become the prime hunting grounds for cybercriminals, with global financial losses from attacks predicted to hit $10 billion in 2024. In this episode, we dive deep into the rising statistics shaping financial cybersecurity during the holiday shopping season, focusing on how sophisticated, AI-driven scams and mobile app vulnerabilities are creating a perfect storm for retailers and consumers alike. Episode Highlights: The State of Financial Cybercrime Cybercriminal activity spikes by 70% during Black Friday compared to regular shopping days. Statistics show that cyberattacks during this period were projected to rise by 20% in 2024, following a 15% increase in 2023. Key Threats and Data:The Rise of Fake Shops: Scammers are evolving at an unprecedented pace, using AI to generate persuasive copy and fully functional storefront templates that mimic legitimate communication flawlessly. A recent analysis found a 250% jump in fake Black Friday shops leading up to the sales weekend.Targeting E-commerce: E-commerce platforms experience a 65% surge in phishing attacks. Phishing scams remain the most common threat, accounting for 42% of attacks on financial transactions during the 2023 holiday shopping period.Prevalent Fraud Types: Financial institutions report detecting 30% more fraudulent transactions during Cyber Monday. Card-not-present fraud was the leading method used by cybercriminals in 2023, accounting for over 75% of online fraud cases. Credential stuffing incidents surged by 80% during Cyber Monday in 2023, affecting over 40 million accounts globally.The Cost: Financial fraud cases during holiday shopping periods account for nearly $8.5 billion annually. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are highly vulnerable, reporting an average loss of $120,000 per cyberattack.The Mobile Frontline: While many focus on suspicious websites, the true cybersecurity frontline for e-commerce is increasingly within mobile apps. Attacks on mobile apps used for shopping increased by 50% in 2023, often involving malicious app clones. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities like Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks intercepting API traffic and extracting API keys reverse-engineered from app binaries. Standard defenses like TLS encryption and certificate pinning offer necessary but incomplete protection. Industry Response: Financial institutions are bolstering security by integrating biometric authentication into 50% of mobile banking apps, adopting real-time transaction monitoring (reducing fraud by 40%), and using tokenization technology in 65% of online transactions. Furthermore, Zero Trust architecture is gaining traction, with 55% of organizations adopting it to secure financial systems. Sponsor Spotlight This episode is brought to you by Approov, the mobile security platform addressing vulnerabilities where they start: the mobile API. Approov provides a pragmatic defense-in-depth approach by ensuring that only genuine, unmodified apps connect to your backend. Approov neutralizes Black Friday exploits by using dynamic attestation to verify app integrity, and protects against API key theft by delivering short-lived, attested tokens at runtime, preventing API keys from residing within the app binary. Protect your mobile commerce from sophisticated fraud. Learn more about Approov's Mobile API Protection:approov.comRelevant Source Links For more information and detailed statistics referenced in this summary:Financial Cybersecurity Statistics for Black Friday and Cyber Monday 2025 (via CoinLaw): [Link to CoinLaw Article]Online scams skyrocket before Black Friday – NordVPN warns what shoppers should watch out for (via TechRadar): [Link to TechRadar Article]Black Friday Fraud: The Hidden Threat in Mobile Commerce Keywords & Hashtags (SEO Optimized) Keywords: Black Friday, Cyber Monday, cybersecurity statistics, financial fraud, e-commerce security, mobile commerce, API protection, card-not-present fraud, phishing scams, ransomware, credential stuffing, AI-powered scams, fake shops, Approov, NordVPN, retail cybercrime, tokenization, Zero Trust. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
In this pivotal episode of Upwardly Mobile, we dive into the significance of X (formerly known as Twitter) joining the Coalition for App Fairness (CAF). This move signals growing momentum in the global effort to reform the mobile app ecosystem, currently dominated by Apple and Google, whose practices are alleged to harm consumers and developers alike. We examine X's commitment to dismantling monopolistic practices and fostering a digital future where competition thrives and innovation is rewarded. Furthermore, we discuss the context of this fight, including the recent U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) antitrust complaint filed against Apple. CAF asserts that Apple’s alleged illegal conduct—including abusing App Store guidelines to increase prices and choke off competition—must be addressed, urging Congress to pass legislation like the Open App Markets Act. Tune in to understand how companies are pushing back against the "shackles on developers" to create a level playing field for the more than 80 members of this independent nonprofit organization. Discussion PointsDismantling Monopolies: X’s Head of Global Government Affairs stated that joining CAF is a testament to their commitment to dismantling monopolistic practices and building a mobile ecosystem that truly serves its users and fosters growth.The Problem with Gatekeepers: The current mobile app ecosystem is dominated by Apple and Google, who use their power to harm developers and users through excessive costs and restrictions on innovation. Global Policy Counsel for CAF noted that businesses on platforms like X are harmed by these anticompetitive app store practices.The Antitrust Fight: The DOJ, along with 16 attorneys general, filed an antitrust complaint against Apple, accusing the company of illegally monopolizing smartphone markets. CAF supports this strong stand against Apple’s "stranglehold over the mobile app ecosystem".The Path Forward: CAF advocates for legislation, like the Open App Markets Act, to create a free and open mobile app marketplace and put an end to the anticompetitive practices of all mobile app gatekeepers.About CAF: The Coalition for App Fairness is an independent nonprofit organization focused on protecting consumer choice, fostering competition, and creating a level playing field for app and game developers globally.Approov Sponsored Segment: The increasing regulatory and commercial pressures are weakening app store monopolies. As the mobile ecosystem decentralizes, the need for robust, independent security is crucial. Our sponsor, Approov, provides strong, app-centric security solutions that operate independently of basic app store protections. Approov helps mobile app developers reduce security dependencies on app stores by delivering runtime protection and attestation for mobile apps and their APIs, shielding against tampering and unauthorized access. Approov’s approach decentralizes security, ensuring developers are not limited by the basic security checks provided by Apple, Google, or any third-party app store (especially relevant as regulations like the EU DMA take effect). Key security features include:Dynamic Certificate Pinning: Secures connections against man-in-the-middle attacks and allows instant over-the-air (OTA) updates without requiring republishing through app stores.Just-in-Time Secrets Management: API keys and secrets are removed from the app and delivered only to verified app instances, protecting against reverse engineering and credential scraping attempts.Run-time Application Self-Protection (RASP): Provides real-time shielding against threats like OS manipulation or hostile frameworks, regardless of how or where the app is distributed, including alternative app stores.This ability to deliver critical updates and security policies directly from Approov’s cloud platform ensures the quickest possible response to threats, bypassing store-mediated app updates.Keywords X, Twitter, Coalition for App Fairness (CAF), Mobile App Ecosystem, App Store Monopolies, Antitrust, Apple Antitrust, Google Play Store, Developer Freedom, App Competition, Open App Markets Act, Approov, App Security, API Protection, Runtime Protection, App Attestation, EU DMA. Relevant LinksX Joins CAF Announcement: [Link to source (though the specific URL is not provided in the excerpts, we reference the content that would link to this news)]CAF Mission & Membership: appfairness.orgDOJ Antitrust Complaint Context: [Link to source (though the specific URL is not provided in the excerpts, we reference the content)]Sponsor Approov: Secure your mobile apps independently of app stores at approov.comApproov Security Details:How Approov Works: [Link to source]Approov vs. Mobile App Hardening: [Link to source]Approov's Role in a Post-DMA Landscape: [Link to source and]🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
Standing Up to Extortion: Lessons from the Checkout.com Breach and the Rise of Vishing Attacks DescriptionThis week on Upwardly Mobile, we dive deep into the tactics of the prolific criminal group ShinyHunters and explore how global enterprises are responding to sophisticated cyber extortion attempts in 2025. We analyze two major security incidents that highlight critical vulnerabilities in legacy systems and modern OAuth ecosystems. The Extortion Dilemma: Checkout.com Stands FirmWe detail the incident where Checkout.com was contacted by ShinyHunters, who demanded a ransom after gaining unauthorized access to a legacy, third-party cloud file storage system. This system was used in 2020 and prior years for internal operational documents and merchant onboarding materials, affecting less than 25% of their current merchant base. Critically, the threat actors did not access merchant funds or card numbers, and the live payment processing platform was not impacted. Checkout.com publicly stated they would not be extorted and refused to pay the ransom. Instead, they are turning this attack into an investment for the entire security industry by donating the ransom amount to Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Oxford Cyber Security Center to fund cybercrime research. The company accepted full responsibility for the legacy system not being properly decommissioned. The 2025 OAuth and Vishing Wave The episode also examines ShinyHunters' 2025 campaign targeting mobile and web-based enterprise applications, particularly those connected to Salesforce and integrated platforms like Salesloft and Drift. These attacks were characterized by sophisticated social engineering and voice phishing ("vishing"), where attackers impersonated IT staff (sometimes using AI-generated voices) to persuade employees to authorize malicious versions of Salesforce tools via mobile or web apps. By exploiting OAuth tokens, ShinyHunters compromised sensitive internal APIs and data from high-profile victims, including Google, Cloudflare, Qantas, Allianz Life, and Adidas. Analysts noted that these techniques bypassed technical controls by abusing human trust, enabling the theft of over 1.5 billion Salesforce records from approximately 760 organizations. These incidents underscore that modern mobile application security is deeply dependent on robust cloud and OAuth ecosystem safeguards. Sponsor This episode of Upwardly Mobile is brought to you by approov.io, helping protect your mobile API access and application endpoints from sophisticated attacks like those utilizing stolen OAuth tokens.Sponsor Link: approov.ioKeywords: ShinyHunters, Cyber Extortion, Ransomware, Legacy System Vulnerability, OAuth Exploitation, Vishing, Voice Phishing, Salesforce Security, Checkout.com, Cybercrime Research, Cloud Security, Supply Chain Attack, Mobile Application Security, Digital Economy Security, Data Breach.Relevant Source Materials and LinksCheckout.com’s official statement on the incident concerning a legacy system and their decision not to pay the ransom, authored by Mariano Albera.ShinyHunters Salesforce Cyberattacks via Vishing and OAuth ExploitationThe Hackernews: Why the ShinyHunters Data Breach vs. SaaS highlights vulnerabilitiesTrueSec: Cyber extortion group ShinyHunters targets Salesforce customersCM Alliance: Reports on major cyberattacks and data breaches in September 2025EclecticIQ: Analysis of ShinyHunters' financially motivated data extortion group targeting enterprise cloud applicationsReSecurity: Examining the alliance of threat actors and their global cybercrime spreeObsidian Security: The merger of chaos between ShinyHunters and Scattered Spider in the 2025 Salesforce attacksCysecurity News: Coverage of ShinyHunters’ voice phishing attacksReliaQuest: Threat spotlight on ShinyHunters targeting Salesforce amid collaboration with Scattered SpiderCloudProtection: Reporting on Salesforce attacks in 2025PKWARE: Recent Data Breaches🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | PodcastThis episode includes AI-generated content.
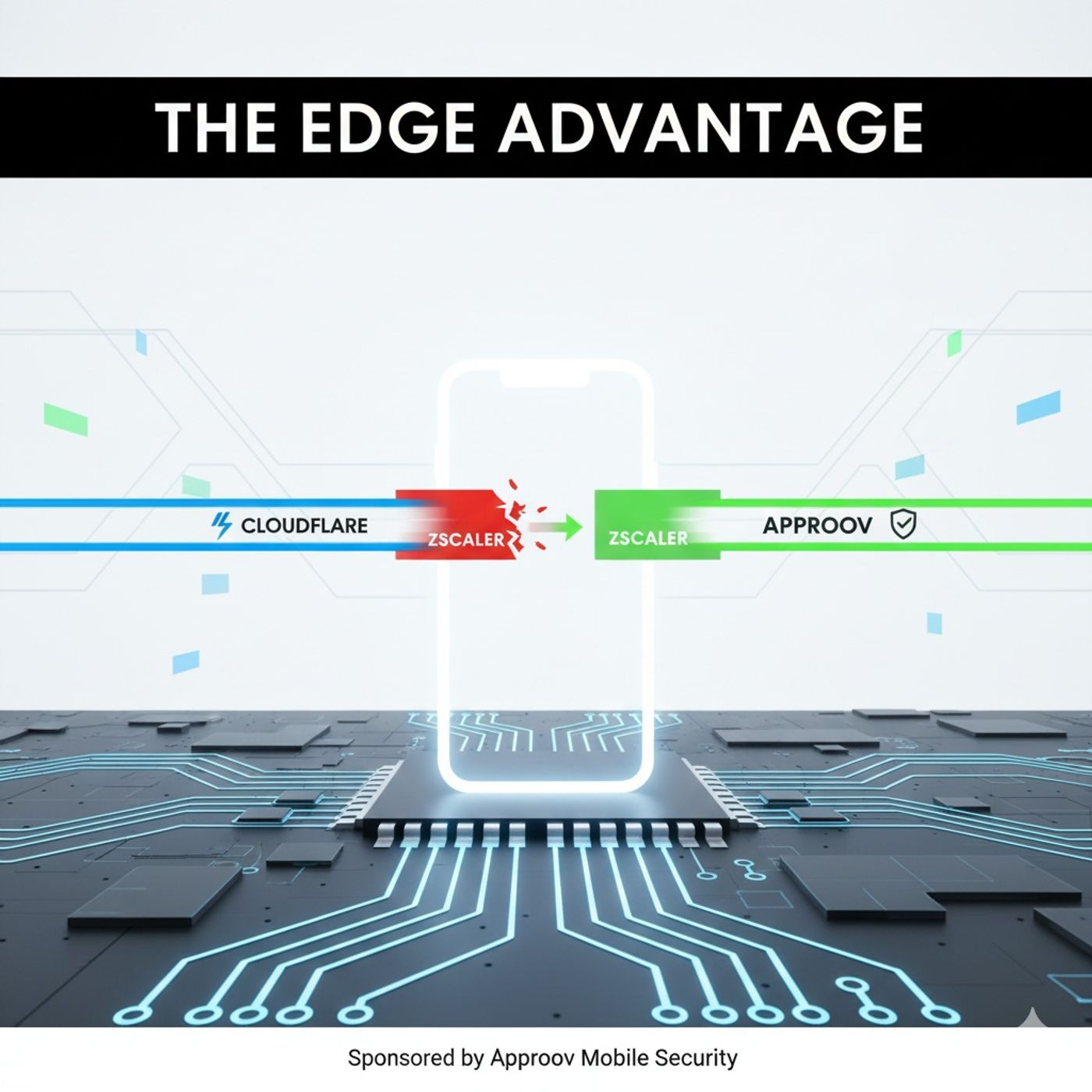
Remote Attestation vs. RASP: Securing Mobile APIs at the Edge (Zscaler vs. Approov/Cloudflare) On this episode of Upwardly Mobile, we dive deep into the most critical architectural debate in mobile API security today: Does security enforcement belong on the client device (RASP) or off-device at the network edge (Remote Attestation)? We break down the philosophical and technical differences between the integrated Zscaler ZSDK approach, which bundles Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP), and the specialized, edge-native partnership between Approov and Cloudflare. Discover why security experts argue that because the attacker ultimately controls the client environment, remote attestation is superior for defense against sophisticated, targeted attacks. Episode Highlights & Key Concepts The Philosophical Divide: RASP vs. Remote Attestation The core of the debate centers on where security decision logic is insulated.RASP (Runtime Application Self-Protection): This approach implements security logic within the application code to detect threats locally during runtime, often used for real-time overlay fraud, app tampering, and emulator abuse detection.The Risk: Any locally enforced logic provides a target for advanced adversaries. Attackers can potentially reverse-engineer RASP checks and bypass local controls to execute API requests from a tampered application instance.Remote Attestation (Approov/Cloudflare): This specialized approach verifies that only a genuine, untampered app can access APIs, protecting backend systems from unauthorized or rogue applications.Superior Resilience: Approov’s architecture minimizes local enforcement, ensuring attestation decisions are made entirely in the cloud service. This insulates the enforcement logic on the backend, offering superior resilience against sophisticated, targeted attacks.Zero Feedback Loop: A key security advantage is that the attacker receives no feedback from the client on why the token validation failed at the edge, significantly raising the cost and complexity of a successful attack bypass.Architectural and Operational Advantages The comparison between the integrated Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange (ZTNA/SSE) model and the Approov/Cloudflare Edge-First (WAAP) model highlights major differences in deployment, performance, and operational cost.Enforcement Location and TCO: The Approov/Cloudflare model focuses enforcement entirely at the Cloudflare edge using serverless functions (Workers or API Shield). This is described as a zero-operations deployment model that removes the need for customer-managed infrastructure components like Zscaler’s required App Connectors. The serverless model accelerates time-to-value and minimizes maintenance overhead.API Key Protection: Approov provides a critical security layer by leveraging attestation guarantees to securely deliver secrets, such as API keys, just-in-time to the application only when the environment is verified as genuine and unmodified. This capability directly mitigates the risks associated with reverse engineering hard-coded keys.Performance and Scale: The Cloudflare/Approov integration leverages Cloudflare’s global, high-performance network. Comparative tests show Cloudflare is significantly faster than Zscaler in various Zero Trust scenarios, a crucial factor for a smooth user experience and ensuring users don't bypass security controls. Furthermore, Approov offers a commercial attestation fabric built for scale, guaranteeing no quotas or throttling on attestation traffic for high-volume apps.API Governance: Cloudflare API Shield enhances protection with rigorous positive security via OpenAPI schema validation at the edge. This preemptively guards against modern API security risks like Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA) by ensuring that only traffic conforming to the documented API structure is accepted.Secure Your Mobile APIs with the Industry's Leading Attestation Solution This episode is proudly brought to you by Approov, the definitive solution for continuous and deterministic mobile app attestation. Approov ensures that only genuine, untampered instances of your mobile application can access your backend APIs, protecting against bot attacks, API abuse, and sophisticated tampering. Learn how to deploy mobile API security today: 🔗 https://approov.io/ Keywords: Mobile API Security, Remote Attestation, RASP, Approov, Cloudflare, Zscaler, API Integrity, Mobile App Protection, Zero Trust Architecture, Edge Security, API Abuse Prevention, Serverless Security, JWT Attestation, Mobile Bot Mitigation, Cloudflare Workers, App Attestation. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
Upwardly Mobile: Episode Notes Episode Title: App Store Revolution: Google Play Opens to Third-Party Payments (The Epic Games Aftermath) Summary: In this episode of Upwardly Mobile, we break down the monumental shift in the Android ecosystem following the Supreme Court’s refusal to hear Google's final appeal. Google has finally opened its Google Play app store to third-party payment options for U.S. developers, settling a multi-year legal battle initiated by Epic Games. We discuss what this means for developers seeking to maximize revenue, the new freedom to direct users to cheaper external payment options, and the resulting challenges in maintaining app integrity and security now that developers are operating outside Google Play Billing exclusivity. Plus, we explore crucial security solutions, like Approov, that can help developers protect their apps when relying less on Google Mobile Services (GMS) for integrity checks. Key TakeawaysPolicy Shift: Following years of legal challenges, Google is now required to allow U.S. app developers to use alternative payment methods and link users directly to external payment sources. This means developers can process payments outside of Google’s ecosystem and inform users about alternative pricing.End of Exclusivity: Previously, Google generally mandated the use of Google Play Billing and collected a commission on nearly every in-app purchase. Now, developers can provide direct links to external checkout pages and offer options like PayPal or their own payment systems.Timeline and Scope: This change became effective immediately as of October 29, 2025. However, the new rules currently apply only in the U.S. and the District Court order is set to expire on November 1, 2027.Security Challenges: While developers gain freedom and potential revenue maximization by avoiding Play Store commissions, distributing and processing payments externally requires implementing their own robust security, update, and analytics systems, as Play services like integrity verification may not be available.App Attestation Alternative: For developers building non-GMS Android apps or those seeking customizable security outside of Google’s structure, Approov provides a solution. Approov is a runtime application self-protection (RASP) tool that offers app attestation—verifying the integrity and authenticity of an app and the device it runs on—without relying on Google PlayIntegrity or SafetyNet.Sponsored by Approov Protect your app and APIs regardless of your payment processing choices. Approov offers comprehensive runtime application self-protection (RASP) and serves as a reliable, GMS-independent alternative to Google PlayIntegrity for robust app attestation and real-time threat detection. Learn more or start a free trial today: approov.io Relevant Links & ResourcesGoogle Opens App Store to Third-Party Payment Systems (PaymentsJournal): https://www.paymentsjournal.com/google-opens-app-store-to-third-party-payment-systems/Google Play now allows Android apps to use other billing systems in the US (9to5Google): https://9to5google.com/2025/10/30/google-play-now-allows-android-apps-to-use-other-billing-systems-in-the-us/How Organizations Can Chart the Course to Agentic Commerce (Must Read): [Relevant link to PaymentsJournal content on commerce] (October 31, 2025)Keywords Google Play, third-party payments, Epic Games, app store, commission, app security, app attestation, Approov, U.S. court ruling, Google Play Billing, non-GMS apps, developer revenue, digital payments, emerging payments, API security. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
The Billion-Download Backdoor: Defending Client-Side Supply Chains Against Crypto-Draining NPM Attacks--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Episode NotesIn early September 2025, the open-source software ecosystem faced a massive supply chain attack when attackers compromised trusted maintainer accounts on npm using targeted phishing emails. This security breach led to the injection of malicious code into 18 widely used npm packages—such as chalk, debug, and ansi-styles—which together account for more than 2 billion downloads per week.This episode dives into the mechanics of the attack, the threat posed by the complex malware deployed, and the role of advanced AI-powered defenses in preventing client-side disaster.Key TakeawaysThe Threat Landscape The attackers' primary goal was crypto-stealing or wallet draining. The compromised packages contained obfuscated JavaScript, which, when included in end-user applications (including web projects and mobile apps built with frameworks like React Native or Ionic), was activated at the browser level. This malware would intercept network traffic and API requests, ultimately swapping legitimate cryptocurrency addresses (including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana) with the attackers' wallets. The attack leveraged the human factor, as maintainers were tricked by phishing emails urging them to update two-factor authentication credentials via a fake domain, npmjs[.]help.The Evolution of Malware: Shai-Hulud Beyond crypto-hijacking, researchers detected a complex self-replicating worm dubbed Shai-Hulud. This advanced payload targets development and CI/CD environments:• Autonomous Propagation: Shai-Hulud uses existing trust relationships to automatically infect additional NPM packages and projects.• Credential Theft: Using stolen GitHub access tokens, the worm lists and clones private repositories to attacker-controlled accounts.• Secret Harvesting: It downloads and utilizes the secret-scanning tool TruffleHog to harvest secrets, keys, and high-entropy strings from the compromised environment.• Malicious Workflows: Shai-Hulud establishes persistence by injecting malicious GitHub Actions workflows into repositories, enabling automated secret exfiltration.Automated Defense with AI Security Cloudflare’s client-side security offering, Page Shield, proved critical in mitigating this threat. Page Shield assesses 3.5 billion scripts per day (40,000 scripts per second) using machine learning (ML) based malicious script detection.• Page Shield utilizes a message-passing graph convolutional network (MPGCN). This graph-based model learns hacker patterns purely from the structure (e.g., function calling) and syntax of the code, making it resilient against advanced techniques like code obfuscation used in the npm compromise.• Cloudflare verified that Page Shield would have successfully detected all 18 compromised npm packages as malicious, despite the attack being novel and not present in the initial training data.• While patches were released quickly (in 2 hours or less), Page Shield was already equipped to detect and block this threat, helping users "dodge the proverbial bullet".Security RecommendationsTo protect against fast-moving supply chain attacks, organizations must maintain vigilance and implement automated defenses:1. Audit Dependencies: Review your dependency tree, checking for versions published around early–mid September 2025. Developers should pin dependencies to known-good versions.2. Rotate Credentials: Immediately revoke and reissue any exposed CI/CD tokens, cloud credentials, or service keys that might have been used in the build pipeline.3. Enforce MFA: Tighten access policies and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all developer and CI/CD access points.4. Proactive Monitoring: Monitor build logs and environments for signs of suspicious scanning activity, such as the use of TruffleHog.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------🔗 Relevant Links and Resources• Cloudflare: How Cloudflare’s client-side security made the npm supply chain attack a non-event ◦ Cloudflare Page Shield Script detection• Trend Micro Research: What We Know About the NPM Supply Chain Attack• Kaspersky Blog: Popular npm packages compromised🛡️ SponsorThis episode of Upwardly Mobile is brought to you by our friends at approov.io.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Keywords:NPM supply chain attack, Cloudflare Page Shield, Shai-Hulud worm, Cryptohijacker, crypto-stealing malware, client-side security, JavaScript obfuscation, open-source security, dependency audit, CI/CD security, phishing attack, MPGCN, machine learning security, developer accounts compromise, npm packages, software security. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
The Unseen Storm: Securing APIs and Protecting Against Key ExposureThis week on Upwardly Mobile, we delve into the hidden dangers lurking within seemingly simple applications and the advanced solutions required to close the modern mobile security trust gap. We analyze a case study involving a basic weather application to illustrate how common development mistakes—like exposing sensitive API keys and neglecting input validation—create catastrophic security vulnerabilities, potentially leading to data breaches, financial loss, and system compromise. The Problem: Client-Side Secrets and Architectural Flaws The proliferation of web applications consuming public APIs has vastly expanded the attack surface. Developers often treat the client environment as trusted, leading to critical architectural failures. We discuss how exposed API keys embedded in client-side JavaScript are considered "low-hanging fruit" for attackers.Key Takeaways from the Security Analysis:Reconnaissance and Exploitation: Attackers can use tools like curl and grep with regular expressions to scan target URLs for hardcoded API key patterns. Once obtained, keys can be used for unauthorized calls, potentially exceeding quotas and incurring costs.Interception: Tools like Burp Suite enable attackers to intercept and modify API traffic, revealing the exact structure of API calls, including the API key and parameters.Injection Attacks: Poor input sanitization on server-side search functionalities is a primary attack vector. We examine verified command snippets used to test for command injection (e.g., appending cat /etc/passwd) and NoSQL Injection (e.g., using MongoDB operator syntax).Lateral Movement: An exposed API key is often just the beginning. If the key has excessive permissions, it can allow an attacker to enumerate IAM policies, check for sensitive S3 buckets, and even create persistent administrative users, leading to a full cloud account takeover.Defensive Fundamentals for Developers: To combat these threats, security must be shifted left—integrated into the earliest stages of development. We review critical defensive measures:Environment Variable Security: API keys must never be exposed to the client; they should reside in secure server-side environment variables. The client should request data from your secure server endpoint, which then internally fetches the data from the third-party API using the hidden key.Rate Limiting: To protect backend APIs from abuse and "Denial-of-Wage" attacks (attacks that incur cost), rate limiting middleware (like express-rate-limit) is essential. This blocks automated scripts by limiting each IP to a set number of requests within a time window.Cloud Hardening: Security extends to infrastructure. Developers must audit cloud resources, checking S3 bucket policies for leaks and ensuring EC2 security groups only allow necessary web traffic (ports 80 and 443).Closing the Mobile API Security Trust Gap with Positive Authentication While these fundamentals are crucial, mobile app security introduces unique challenges, creating a concerning "trust gap". Traditional security measures like TLS, mutual TLS, embedded API keys, and signature-based approaches are often insufficient, as they are vulnerable to reverse engineering, MitM attacks, and spoofing. We discuss Approov, a solution designed for the mobile world that uses a positive trust model to authenticate the app instance itself, rather than just the user or the connection.App Attestation: Approov uses a challenge-response cryptographic protocol to dynamically measure the integrity of the runtime app image.Tokens (JWT): Only genuine, untampered apps are granted a short-lived JSON Web Token (JWT). Requests without a valid token are immediately rejected by the backend API.Protection against Reverse Engineering: Because the system does not rely on static secrets embedded in the app, traditional reverse engineering techniques are ineffective. Approov also provides a runtime secrets protection capability, allowing developers to remove third-party API keys from the app package entirely, substituting them only just in time for the API call after the app has passed attestation.Benefits: This positive authentication model blocks sophisticated bots, automated scraping systems, and repackaged apps, ensuring that only registered, authentic versions of your application can access your valuable digital assets.Links & Resources Source Material Reference:Excerpts from "The Unseen Storm: How A Simple Weather App Exposes Critical API Security Flaws - Undercode Testing"Excerpts from "WP-How Approov Adresses the Security Trust Gap"Sponsor:Learn how Approov protects your revenue and business data by deploying Mobile Security: approov.ioKeywords API security, mobile security, API key protection, reverse engineering, input validation, client-side vulnerabilities, app attestation, JWT, zero-trust architectures, rate limiting, cloud security, Denial-of-Wage, Man-in-the-Middle (MitM), Burp Suite, Approov. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
UK CMA Declares Apple & Google Have Strategic Market Status (SMS): The Future of Mobile Competition and Security In this pivotal episode of "Upwardly Mobile," we break down the monumental decision by the UK Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) to officially designate Apple and Google with Strategic Market Status (SMS) in their respective mobile platforms. This move is set to reshape digital markets across the UK and has massive implications for app developers, businesses, and mobile security worldwide. Key Takeaways from the CMA's Decision (Published 22 October 2025): The CMA launched its investigations in January 2025 under the Digital Markets, Competition and Consumers Act 2024 (DMCCA), aiming to address the "unprecedented market power" held by a few large digital firms.SMS Designation Confirmed: Following consultation with over 150 stakeholders, the CMA confirmed that both Apple and Google meet the legal tests for having Substantial and Entrenched Market Power (SEMP) and a Position of Strategic Significance (POSS) in their mobile platforms.Scope of Mobile Platforms: The designation applies to the holistic Mobile Platform provided by each company, grouping together highly interconnected digital activities:Apple: Smartphone Operating System (iOS), Tablet Operating System (iPadOS), Native App Distribution (App Store), and Mobile Browser and Browser Engine (Safari and WebKit).Google: Mobile Operating System (Android), Native App Distribution (Play Store), and Mobile Browser and Browser Engine (Chrome and Blink).Market Dominance: CMA findings confirmed that almost all UK mobile device holders use either Apple or Google's platform. Users are unlikely to switch between them, reinforcing their dominance. Furthermore, to reach both user bases, businesses must distribute their content through both platforms, effectively making them "must-have" channels.Market Entrenchment: The CMA concluded that competitive constraints are currently limited. Despite the rapid deployment of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), these developments are deemed unlikely to eliminate Apple or Google’s market power over the five-year designation period.Economic Impact: The designation acknowledges the crucial role of these platforms, noting that the UK app economy generates an estimated 1.5% of the UK’s GDP and supports about 400,000 jobs, encompassing sectors like FinTech and mobile gaming.What Happens Next? The SMS designation itself is not a finding of wrongdoing and does not introduce immediate new requirements. However, it acts as the gateway for the CMA to introduce targeted and proportionate interventions, such as Conduct Requirements or Pro-Competition Interventions, designed to ensure open choices, fair dealing, and trust and transparency within these vital digital activities. This action mirrors regulatory efforts globally, including the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) and legal actions in the US and Japan. 🎧 Sponsored by Approov We are entering a "pivotal era for mobile technology" where regulatory interventions like the CMA’s SMS designation and the EU's DMA are weakening the centralized control over app distribution held by Apple and Google. This shift "opens the floodgates for alternative app stores, sideloading, and direct-to-consumer models". As mobile security risks move beyond platform constraints, secure your applications and APIs with a truly cross-platform, developer-centric solution. Visit approov.io for more information on how to implement modern app and API protection. 🔗 Useful Links & ResourcesCMA Final Decision on Apple’s Mobile Platform (22 October 2025): [www.gov.uk/cma]CMA Final Decision on Google’s Mobile Platform (22 October 2025): [www.gov.uk/cma]CMA Press Release: CMA confirms Apple and Google have strategic market status in mobile platforms: [www.gov.uk/cma]💡 Keywords CMA, Strategic Market Status (SMS), Digital Markets Competition and Consumers Act 2024 (DMCCA), Apple Mobile Platform, Google Mobile Platform, mobile platform, app distribution, mobile browser, mobile security, iOS, Android, App Store, Play Store, WebKit, Blink, API protection, sideloading, app economy, tech regulation. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
API Security Under Fire: F5's Zero-Day Roadmap and the Unacceptable Risk to Mobile AppsThe F5 BIG-IP Breach and What It Means for Developers This week on Upwardly Mobile, we dive into the fallout from the catastrophic security breach at F5 Networks, where a sophisticated nation-state adversary compromised the integrity of the critical BIG-IP product line. We discuss why this incident poses an imminent and unacceptable risk to organizations—especially mobile app developers who rely on F5 devices for critical API security infrastructure like load balancing and firewalling. The Compromise: Source Code, Credentials, and Zero-Day Roadmaps The threat actor maintained long-term, persistent access to F5’s internal systems, specifically the BIG-IP product development environment and engineering knowledge platforms. This sophisticated attack led to the theft of crucial materials:Proprietary Source Code: Portions of the proprietary source code for the flagship BIG-IP product line were exfiltrated. While F5 confirmed the actor did not inject malicious code, possessing the source code allows adversaries to analyze it for vulnerabilities or backdoor opportunities.Vulnerability Roadmap: Attackers gained access to internal documentation detailing undisclosed (zero-day) vulnerabilities that F5 engineers were investigating or fixing. This provides the adversaries with a virtual roadmap, enabling them to rapidly develop exploits for unpatched flaws.Customer Configuration Data: A small portion of customer-specific data was stolen, including network topologies, device configurations, or deployment details. For developers managing mobile APIs, this stolen information increases the risk that sensitive credentials can be abused and attackers can target specific deployment setups.Urgent Action Required: The CISA Emergency Directive The severity of the incident prompted the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to issue an Emergency Directive for federal agencies, underscoring the potential for widespread exploitation. Developers and organizations using F5 devices must take immediate action:Patch Immediately: Install the latest security updates, particularly the Quarterly Security Notification F5 released simultaneously, which addressed 44 new vulnerabilities.Isolate Management Interfaces: Identify all F5 resources and critically, isolate management interfaces from the internet to prevent initial access and investigate any exposure.Adopt Zero Trust: Implement a zero trust architecture to reduce the attack surface and block lateral movement. Prioritize connecting users directly to applications, not the underlying network.Change Credentials: Change all default credentials immediately.Sponsor Segment Securing mobile APIs from threats that target application logic and device integrity is paramount. To fortify your defenses against sophisticated adversaries like the one in the F5 breach, explore approov.io. Approov provides crucial mobile app and API protection by verifying the authenticity of mobile apps and ensuring only legitimate, untampered clients can access your APIs.Relevant LinksF5 Security Advisory: CISA Emergency Directive: Sponsor Website: approov.ioKeywords: F5, BIG-IP, API Security, Mobile App Security, Zero-Day Vulnerability, Source Code Theft, Nation-State Hacking, CISA, Emergency Directive, Zero Trust, Load Balancer, Firewall, Patching, UNC5221, BRICKSTORM, Cybersecurity, Network Topology, Credential Abuse, Upwardly Mobile🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
Corporate Extortion and the Fall of BreachForums: Tracking ShinyHuntersIn this episode of "Upwardly Mobile," we dive into the world of high-stakes corporate extortion, focusing on the sophisticated cybercriminal group ShinyHunters (also tracked as UNC6040) and the subsequent takedown of their infamous platform, BreachForums. The sources detail how the FBI, in collaboration with French law enforcement authorities, seized the Breachforums.hn domain, which the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters (a gang linked to ShinyHunters, Scattered Spider, and Lapsus$) were using as a data leak and extortion site. This action involved switching the domain’s nameservers to ns1.fbi.seized.gov and ns2.fbi.seized.gov. ShinyHunters confirmed the seizure, noting that law enforcement gained access to BreachForums database backups dating back to 2023 and escrow databases since the latest reboot, effectively declaring that "the era of forums is over". Despite the clearnet site takedown, the threat actors maintained that their Tor dark web site was still accessible and that the seizure would not affect their campaign. The Massive Salesforce Extortion Campaign The core focus of the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters’ recent activity was an extensive Salesforce extortion campaign. This campaign originated in May 2025 when ShinyHunters launched a social engineering campaign using voice phishing to trick targets into connecting a malicious app to their organization’s Salesforce portal. The hackers claimed to have stolen more than one billion records containing customer information. The long list of affected companies included major corporations such as FedEx, Disney/Hulu, Home Depot, Marriott, Google, Cisco, Toyota, Gap, McDonald's, Walgreens, and Chanel. Salesforce has publicly stated that they will not engage, negotiate with, or pay any extortion demand. Beyond Salesforce: Discord and Red Hat The criminal group also claimed responsibility for other significant intrusions:Red Hat Data Theft: The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters took credit for compromising a Red Hat GitLab server, stealing more than 28,000 Git code repositories and sensitive internal documents, including customer secrets and infrastructure details.Discord Breach: ShinyHunters claimed responsibility for an incident affecting Discord users. Discord confirmed that an unauthorized party compromised a third-party customer service provider (5CA), impacting a limited number of users who had contacted Customer Support or Trust & Safety teams. Critically, the unauthorized party gained access to a small number of government-ID images submitted for age verification appeals, as well as usernames, emails, limited billing info, and IP addresses.Tactics and Targets The group employs sophisticated tactics, including exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, such as a critical flaw in Oracle’s E-Business Suite software (CVE-2025-61882). Furthermore, members of the group have been known to distribute malware—specifically the commercially available ASYNCRAT backdoor—disguised as a Windows screensaver file (.scr) via menacing, targeted emails. This highlights the constant pressure faced by security professionals, often from threat actors derisively called "Advanced Persistent Teenagers" (APTs). Links & ResourcesLaw Enforcement Takedown: Nameservers used in the FBI seizure: ns1.fbi.seized.gov and ns2.fbi.seized.gov.Publications Cited: Information confirmed by BleepingComputer and reported by KrebsOnSecurity.Discord Security Incident: Discord confirmed they would contact impacted users via noreply@discord.com.Security Validation: Join the Picus BAS Summit to experience the future of security validation.ASYNCRAT Analysis: Virustotal analysis on the ASYNCRAT malware provided via link.🛡️ Sponsor: approov.io To ensure your mobile and web applications are secure against sophisticated attacks, trust the experts. Learn more about enhanced security measures and API protection at approov.io.Keywords ShinyHunters, BreachForums, Salesforce Extortion, FBI Takedown, Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters, Data Breach, Red Hat, Discord Hack, Voice Phishing, Cybercrime, Hacking Forum, ASYNCRAT, UNC6040, CVE-2025-61882, Security Validation. Relevant 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
Mobile is officially the digital default. In this episode of Upwardly Mobile, we explore the staggering statistics showing mobile devices dominating global internet usage and discuss the critical security challenges that arise from this mobile-first environment. We then delve into the cutting-edge solution offered by our sponsor, Approov, and their latest platform update, Approov 3.5, designed to secure brands against evolving threats, including AI-driven attacks and new regulatory pressures.The Mobile Tipping Point: 64% and RisingThe mobile landscape is at an inflection point. As of 2025, over 64% of all website traffic comes from mobile devices. This dominance is driven by the fact that nearly 96.3% of internet users access the internet using a mobile phone.• This shift is not just a trend; it is the new normal.• Mobile traffic reached 64.1% in Q2 2025, marking eight consecutive quarters of growth.• Developing regions are leading the surge, with Africa having the highest proportion of mobile internet traffic at 69.13%, and Asia seeing 72.3% of all web traffic coming from smartphones.• The most common activities performed on smartphones include playing a game (68%), listening to music (67%), and using social media (63%).The Security Gap in a Mobile-First WorldThe widespread adoption of mobile creates significant security vulnerabilities. Automated threats make it easier for bad actors to clone legitimate apps, steal data, and commit fraud, which can cause irreparable damage to a brand's reputation and financially devastate users. Furthermore, new security gaps are emerging due to regulations like the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA), which mandates support for third-party app stores, increasing the risk of fraudulent apps.Approov 3.5: Protecting the Critical ConnectionApproov, the leader in mobile API security, addresses these threats by acting as a digital gatekeeper. Approov protects the critical connection between a mobile app and a company's backend servers (APIs). It ensures that only genuine, untampered apps running in a secure environment can access sensitive services, blocking automated bots, modified apps, and cloned apps before they can compromise data.The latest platform update, Approov 3.5, delivers next-generation attestation:• Ready for the DMA and Open App Stores: Approov’s cloud-based verification ensures only genuine app instances—regardless of their distribution source—can access a company’s APIs.• Hardware-Backed Security (Android): Cryptographic keys are stored in a secure, isolated “vault” on the device’s hardware, making cloning an app’s identity virtually impossible.• Defense Against AI-Powered Attacks: The platform provides real-time threat analytics, allowing security teams to dynamically issue over-the-air (OTA) updates to block emerging AI threats without requiring an app update.• Immutable App Signature: This feature creates a unique fingerprint upon installation, continuously verifying the app’s integrity against tampering or repackaging with malware.• Memory Dump Detection: A new defense actively blocks attackers attempting to scrape sensitive information, such as AI secrets or user credentials, directly from the device’s memory.Approov has proven that robust security can be achieved without compromising user experience, offering fast and responsive cross-platform security checks for iOS, Android, and HarmonyOS. By verifying API requests, Approov reduces API attacks by over 95%.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------KeywordsMobile traffic, API security, Approov 3.5, mobile app security, Digital Markets Act (DMA), hardware-backed security, 64% web traffic, AI-powered attacks, mobile-first, app cloning, fraud prevention, mobile API.Sponsor LinkFor more information on securing your mobile application and APIs, please visit our sponsor: www.approov.io.🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
In this episode of Upwardly Mobile, we dive into the significant legal challenges facing major technology companies—Apple, Google (Alphabet), and Meta Platforms—as they are forced to defend themselves against class action lawsuits alleging that they promoted and profited from illegal social casino gambling apps. A recent ruling by U.S. District Judge Edward Davila in San Jose, California, denied the companies' requests to dismiss the lawsuits. The plaintiffs, numbering in the dozens, contend that the companies' platforms—Apple’s App Store, Google’s Play Store, and Meta’s Facebook—promoted an “authentic Vegas-style experience of slot machine gambling” through an allegedly illegal racketeering conspiracy. Key Takeaways from the Litigation:The Liability Claim: The core claim is that the defendants "willingly assist, promote and profit from" allegedly illegal gambling. This is achieved by:Offering users access to the apps through their stores.Taking a substantial percentage of consumer purchases (estimated at 30% commission, totaling over $2 billion) on in-app transactions for items like Game Coins and Sweeps Coins.Processing these allegedly illicit transactions using proprietary payment systems.Using targeted advertising to "shepherd the most vulnerable customers" to the casino apps.The Section 230 Defense Rejected: Apple, Google, and Meta argued that Section 230 of the federal Communications Decency Act protected them from liability because this law shields online platforms from lawsuits over third-party content. Judge Davila rejected this argument, finding that the companies did not act as "publishers" when processing payments. The judge emphasized that the "crux of plaintiffs’ theory is that defendants improperly processed payments for social casino apps"."Neutral Tools" Argument Undercut: The court called it irrelevant that the companies provided "neutral tools" (like payment processing) to support the apps.Damages Sought: The lawsuits seek unspecified compensatory and triple damages, among other remedies.Appeals and Case History: Judge Davila allowed the defendants to immediately appeal his decision to the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals, acknowledging the importance of the Section 230 issues. The litigation against the Silicon Valley-based companies began in 2021.Additional Suits: Separately, a new lawsuit was filed against Apple and Google by lead Plaintiff Bargo (not naming the social casino operators), alleging the distribution of "patently illegal gambling software" in New Jersey and New York. This complaint includes legal claims under NJ and NY gambling loss recovery statutes, consumer protection laws, and RICO laws.Sponsor Message: This episode of Upwardly Mobile is brought to you by our sponsor. Learn how to secure your mobile app business today. Visit approov.io. Relevant Source Materials & Case Information:Article Reference (Legal Analysis): Excerpts from "Apple and Google Hit with New Social Casino Gambling Lawsuit," National Law Review (October 02, 2025). (Article written by James G. Gatto of Sheppard, Mullin, Richter & Hampton LLP).Article Reference (News): "Apple, Google, Meta must face lawsuits over gambling apps," Honolulu Star-Advertiser (Oct. 1, 2025).Article Reference (Judicial Denial): "Judicial Denial for Tech Giants in Casino App Lawsuits" (Sept 30).Amicus Brief Reference: In re: Casino-Style Games Litigation (Nos. 22-16914, 22-16916, 22-16888, 22-16889, 22-16921, 22-16923) U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit.District Court Case Reference (Northern District of California): In re Apple Inc App Store Simulated Casino-Style Games Litigation, No. 21-md-02985; In re Google Play Store Simulated Casino-Style Games Litigation, No. 21-md-03001; and In re Facebook Simulated Casino-Style Games Litigation, No. 21-02777.Sponsor Link: approov.ioKeywords for SEO Optimization: Social Casino Lawsuit, Apple, Google, Meta, Section 230, Gambling Apps, App Store, Play Store, Communications Decency Act, Platform Liability, Edward Davila, Consumer Protection, Racketeering, Illegal Gambling, Tech Litigation, In-App Purchases, RICO.🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
In this critical episode of Upwardly Mobile, we delve into the alarming cybersecurity incident involving massive data exposure stemming from misconfigured Firebase servers. Cybersecurity researchers uncovered a breach that exposed the sensitive information and plaintext passwords of over 1.8 million users. This wasn't the result of sophisticated hacking, but rather "basic negligence" and developers failing to implement standard security settings.We discuss why Firebase, Google's popular backend-as-a-service (BaaS) for mobile apps, has become a liability risk when developers neglect configuration best practices.What was exposed and the devastating scope of the leak:The scope of this data leak is massive, involving publicly accessible Firebase real-time databases used by more than 900 mobile applications, predominantly Android-based. These affected apps spanned categories including health, fitness, education, and finance.The highly sensitive user data exposed included:• Plaintext passwords (unencrypted)• Usernames, email addresses, and phone numbers• Billing information• High-privilege API tokens, AWS root access tokens, and private chat logs• Millions of user ID photos.The Failure of Security as an Afterthought:Experts warn that storing plaintext passwords on open cloud databases in 2025 is "reckless". The breach occurred because developers failed to secure their Firebase instances, often by extending insecure "test-mode" configurations or inadvertently leaving production environments vulnerable. Responsibility for this preventable disaster lies with both the developers and Firebase itself, for allowing insecure default settings.We also explore the technical mechanism behind these breaches: Automated scanning tools (like OpenFirebase) are actively exploiting this vulnerability by parsing Android Package Kit (APK) files to extract Firebase project IDs, API keys, and subsequently probing service URLs for unauthenticated access.This incident serves as a strong wake-up call for the tech industry, emphasizing the critical need for mandatory security training and treating security as a core function of software development—not an afterthought.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------🛡️ Sponsor: ApproovProtect your mobile APIs and prevent automated attacks that exploit hardcoded secrets and misconfigurations. Secure your apps from the client-side up.Learn more and protect your platform at https://approov.io.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Source Materials & Links• Article 1: "Massive data leak exposes passwords of 1.8 million users through misconfigured Firebase servers," ZENDATA (May 25, 2025).• Article 2: "Numerous Applications Using Google's Firebase Platform Leaking Highly Sensitive Data," Cyber Security News (September 25, 2025).--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Keywords: Data Leak, Firebase Security, Plaintext Passwords, Cybersecurity, Mobile App Security, Google Firebase, Cloud Misconfiguration, Data Breach, Developer Negligence, API Security, Android Security, BaaS, App Development.🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast
Neon's Data Disaster: How a Viral AI App Exposed 75,000 Users and Went DarkIn this urgent episode of Upwardly Mobile, we break down the spectacular rise and immediate fall of the highly controversial mobile application, Neon. The app, which recently topped the charts and went viral on platforms like TikTok, promised users payment in exchange for recording their phone calls. These recordings were then sold to AI companies for training. However, less than 24 hours after gaining widespread attention, a significant security flaw was discovered. According to reports from TechCrunch, this flaw allowed public access to extremely sensitive user data. The Security Catastrophe The call-recording app had rapidly climbed the App Store ranks, reporting 75,000 downloads in a single day. Despite its rapid growth, Neon was forced offline after the security issue was discovered by TechCrunch. The flaw was so severe that it allowed anyone utilizing a network analysis tool to access private information belonging to other users. Exposed data included:Users' phone numbers.Call recordings and accessible URLs to the raw audio files.Text transcripts of the recorded calls.Detailed metadata connected to the calls, including the phone number of the person called, the time and duration of the call, and the amount earned from the call.The Company Response Following the discovery, Neon founder Alex Kiam sent an email to customers notifying them of the app's temporary shutdown. Kiam stated that they were taking the app down to "add extra layers of security" because "Your data privacy is our number one priority". However, it is crucial to note that the email failed to warn users about the specific security issue or that their phone numbers, call recordings, and transcripts had been exposed. TechCrunch noted that although the app's servers were taken down, rendering the app useless, it remained available in the App Store. If Neon does make a comeback, it will certainly receive increased scrutiny regarding its security protocols. Secure Your Mobile Infrastructure with Our Sponsor In a world where mobile app security flaws can rapidly expose millions of data points, protecting your back-end servers and APIs is non-negotiable. Our episode today highlights the critical importance of mobile app protection from the get-go. Learn how to implement proactive mobile security measures. Visit: approov.io Relevant Source Materials & Further ReadingExcerpts from "Neon, the viral app that pays users to record calls, goes offline after exposing data | Mashable"Excerpts from "Viral call-recording app Neon goes dark after exposing users' phone numbers, call recordings, and transcripts | TechCrunch"Keywords: Neon app security flaw, AI training data, call recording app, data privacy, cybersecurity, mobile app data exposure, Alex Kiam, App Store security, TechCrunch exclusive, data breach, viral app failure, mobile security. 🎙️ Upwardly Mobile is hosted by Skye Macintyre & George McGregor. 🛡️ Sponsored by Approov: The only comprehensive solution for mobile app and API security. 👉 Subscribe & Review: Upwardly Mobile | Podcast