A Smarter Way to Set Goals
Description
Are you looking for smarter, more sustainable improvements? In this episode, John Dues joins Andrew Stotz to challenge the way schools - and businesses - set goals. Instead of chasing stretch targets that often frustrate teachers and students alike, John shows how to use data and systems thinking to create real improvement.
TRANSCRIPT
0:00:02 .2 Andrew Stotz: My name is Andrew Stotz, and I'll be your host as we dive deeper into the teachings of Dr. W. Edwards Deming. Today, I'm continuing my discussion with John Dues, who is part of the new generation of educators striving to apply Dr. Deming's principles to unleash student joy in learning. The topic for today is how to set educational goals. Take it away, John.
0:00:25 .6 John Dues: Hey, Andrew. It's good to be back. Yeah. So the thing that I see just over and over again is that goal setting in schools is just really ineffective. And not only that, but it's often counterproductive. So I thought it'd be good to talk about a different approach to how to set educational goals. I think most typically what I see, and this is probably not just true in schools, but in other places too, you get some result, and then you set a goal to increase by 10 or 15 or 20%. But I think that what often is missed is that without certain conditions in place, these stretch goals end up disconnected from reality. And so what I wanted to do in this session is to teach three conditions that I believe will lead to much more effective goal setting.
0:01:20 .8 Andrew Stotz: It's interesting because goal setting seems really simple, like, just set a goal and go get it.
0:01:29 .1 John Dues: Yeah.
0:01:29 .5 Andrew Stotz: And yet when you're... You say that it's simple as an individual that I'm going to go walking every morning. That's my goal. It seems simple as an individual, but when it gets to a company level, it can get really complex, or a school level. And also there's this... What did you call it? Like aspirational... Or what was the word? Stretch, stretch goal. It's so common, particularly when business is not going great. Like, I want this from this team, and it's just so common to say, to lay down demands. I want 20% revenue growth. I want students passing this by 70% or whatever. And yet it just doesn't work that way. And so I'm looking forward to hearing from you about your three conditions. So let's go.
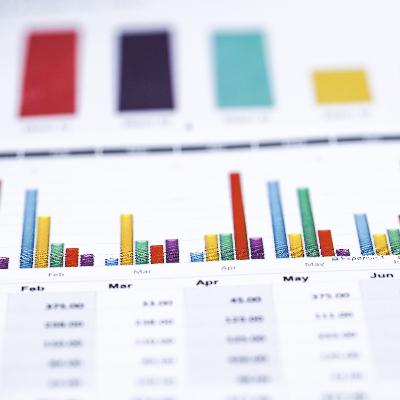
0:02:23 .1 John Dues: Yeah, sounds good. So let's start by looking at why I don't think stretch goals are helpful. And since I'm working in schools, I like using data that people are familiar with. So I'll use this third grade reading state test score data. It's very common. It's really important. There's often some guarantee around third grade reading scores or there's often high stakes attached to third grade reading. So I'll use that. And so let's say in year one, and this is actually real data, 54.9% of third graders scored proficient or higher on that test. And then in the next year, they score 63.8% of the third graders scored proficient or higher. So in most places, leaders and teachers would celebrate because that represents an 8.9% increase in proficiency rates. And so then they do something like set a stretch goal of, well, next year we're going to grow by 20%. So you think, well, we grew by nearly 9%, so we can surely hit 20%. But then what often happens in a situation like this is that the next year's data comes out and actually goes down.
0:03:41 .4 John Dues: And that's exactly what happened in year three of this data. Now, in this third year, only 61.2% of the students scored proficient or higher. And so then you think to yourself, well, what stretch goal would I set next? Would you change that 20% goal because of the decreased rates in the most recent year? So it actually is an interesting exercise. If you're listening to this, actually get a number in your head. You're the school leader, you're the superintendent, you're the principal or whatever, think about what goal then would you set for this group. So they grew by almost 9% and they went down by a couple percent. Between year one and two, they set the goal of 20%. Now what are you going to do? What's the goal? What are you going to say?
0:04:36 .2 Andrew Stotz: And I'm thinking about the tampering concept that Dr. Deming talks about, constantly adjusting based upon where you're at. And it's interesting because in that case, you may say, you know, a disappointing year, but we've got to stick to our 20%. We got to stick to our strong, we can't give up. Remember that celebration we had?
0:05:01 .0 John Dues: Yeah, this is a one year blip. We had increased by nearly 10. I know we can do it if we just double down. Let's keep that 20% goal in place. Yeah, that's definitely what a lot of people would do. So let me show you the results for those three years and then what happened for the next several years after that. So I'll share my screen for those that are watching so they can see this actual data in chart form.
0:05:27 .7 Andrew Stotz: Great. Yep, we can see that.
0:05:29 .8 John Dues: You can see it. All right. So now we have nine years of test data, and we can see that setting that early stretch goal had no effect whatsoever on outcomes. And so in year one, we had that 54.9% of those third graders were proficient. Then we went up to 63.8 like we said. Then we dipped back down in year three to 61.2, and then in the subsequent years that we're looking at now, it jumped up to 60.7, and then it fell to 51.9, and then it jumped up to 59.8, and then it rose again to 62.3, and then it rose again to 64.5, and then it fell again to 61.3. So again, between year one and two is when we set that stretch goal of 20%, and we can see again that it had no effect on outcome. So really, in all likelihood, the goal was not only ineffective back there between year one and two, but it was likely counterproductive. Because if you're thinking about, if you're a teacher in this school, you're teaching third grade or you're the principal of the school, year after year, this team didn't come close to approaching that 20% stretch goal that had been set.
0:06:52 .8 John Dues: Year one, year two, year three, all the way through year nine. Some years the scores go up, some years the scores go down. It's pretty demoralizing if you think about it. I think the good news is, and the reason we're having this conversation is I think there's a better method for understanding your data and then using that data to set school goals in a smarter way. So I'll introduce these three conditions. I think about them as three conditions of healthy goal setting. So the first thing that you want to do is gather baseline data in the area that you're interested in improving. So this could be historical results if you have data, or it might be new data that you need to collect if this is a new focus area. But either way, you need some type of baseline as a starting point, and then you can work to understand these three conditions.
0:07:55 .9 John Dues: So the first condition, condition one is what I call the capability of the system under study. And by system under study, in this case, I just mean the third grade reading test data. So how capable is it? Condition two is the variation of that system under study. And then condition three is the stability of that system under study. So those are the three conditions that I'm interested in taking a look at. And this focus could be on any data that occurs across time. It could be like state test scores, like we're looking at here. Could be attendance rates, could be oral reading fluency rates for those elementary teachers. It could be the number of office referrals that are coming into the principal's office or assistant principal's office on a daily or weekly basis. For this example, I'll just keep using the third grade state testing data.
0:08:52 .8 Andrew Stotz: And let's just go through that just to review. So you talked about gathering baseline data. So you got to figure out what's happening here. The second thing, the first thing then you talked about, step one is capability of the system under study. And what does the word capability mean?
0:09:10 .5 John Dues: Yeah, we'll get into each of them and then define each one.
0:09:12 .0 Andrew Stotz: And then the second one is the variation of that system. Okay. Now what I noticed in all of these as you're talking about system, third one is stability of the system. So I guess a big part of this is basically saying if you're not looking at it as a system, you're not going to have the success that you want to have. So that's certa