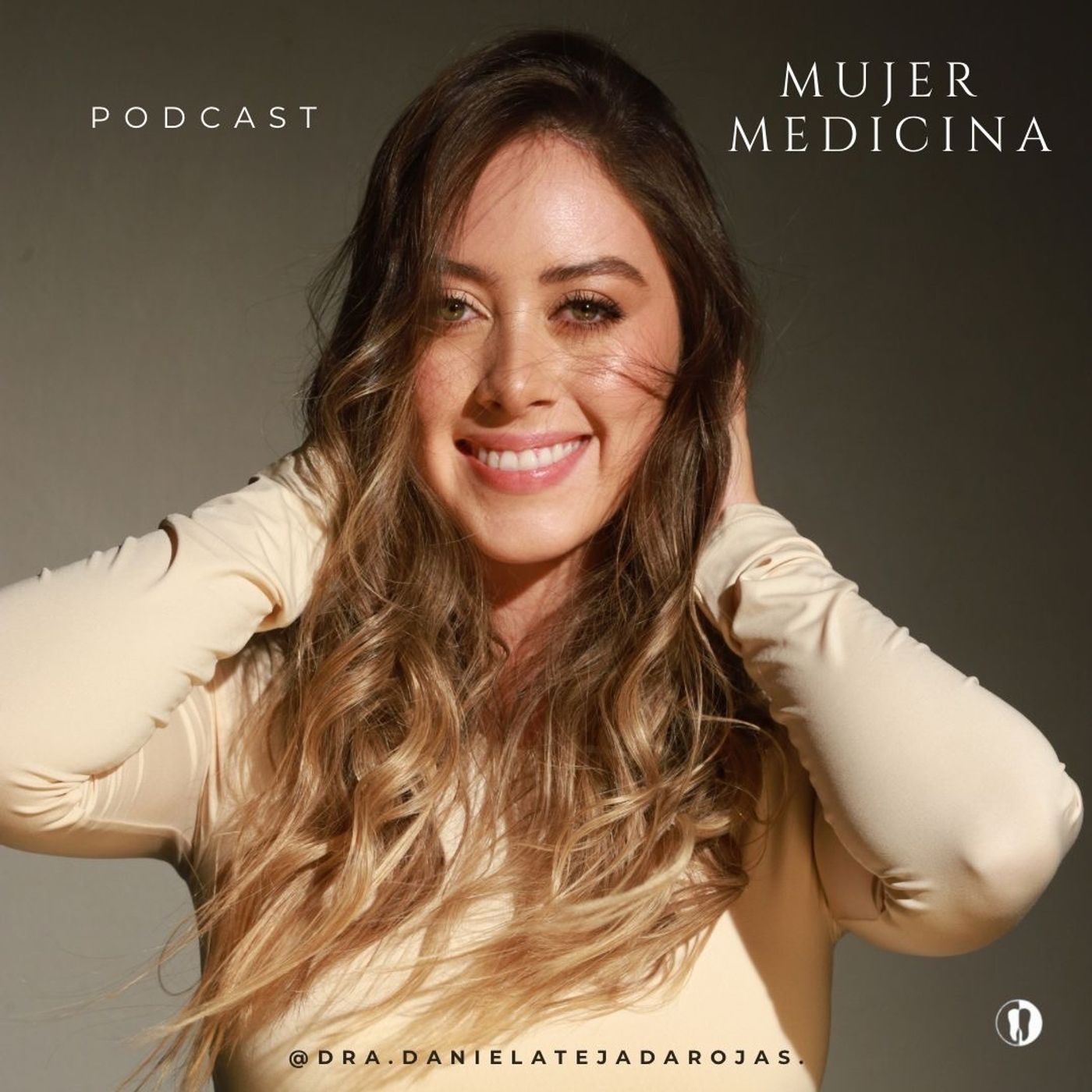
Ground Truths: Lotte Bjerre Knudsen: The Scientist Who Drove GLP-1 Drugs For Obesity and Alzheimer's
Description
The Chief Scientific Advisor at Novo Nordisk, Lotte Bjerre Knudsen, was the key force who pushed hard to develop GLP-1 drugs for treating obesity and subsequently for Alzheimer’s. She was recently recognized by the 2024 Lasker Medical Research Award, and the 2024 AAAS Bhaumik Breakthrough of the Year Award. That recognition is richly deserved, since it is unclear if the GLP-1 drug path to obesity treatment, and all of the associated benefits, would have been seen at this time without her influence. That’s especially true given the mystery for why people with Type 2 diabetes (for which these drugs were used for many years) did not exhibit much in the way of weight loss. We discussed that and the future of these drugs, including their potential to prevent neurodegenerative diseases. And about dressing up in pink!
The Ground Truths podcasts are also available on Apple and Spotify.
Our entire conversation can also be seen by video at YouTube along with all of the Ground Truths podcasts. If you like the video format, please subscribe to this channel. Even if you prefer video, please take a look at the transcript with graphics and useful links to citations.
A Video Clip below on the barriers of a woman scientist to push Novo Nordisk to develop GLP-1 for obesity.
“I was always just been a nerdy little scientist who kind of found home here in this company for 35 years.”—Lotte Bjerre Knudsen, 60 Minutes
Transcript with Links to audio and external references
Eric Topol (00:06 ):
Well, hello, it's Eric Topol with Ground Truths, and I have with me a special guest. She's the Chief Science Officer of Novo Nordisk and it's Lotte Bjerre Knudsen, and we're delighted to have her. She's a recent recipient of the Lasker Award, which I think is considered like the pre-Nobel Award here in the United States. And I was involved with her in terms of researching who was the principal person who brought the GLP-1 drugs to the forefront for obesity, and it turned out to be Lotte. So welcome, Lotte.
Lotte Bjerre Knudsen (00:48 ):
Thank you very much. And also very, very happy to be here. I'm not the Chief Science Officer for Novo Nordisk, I'm the Chief Scientific Advisor of working for the Chief Science Officer of Novo Nordisk, but maybe too many people, not so different, right?
From Laundry Detergents to GLP-1 Drugs
Eric Topol (01:06 ):
Yes. Thank you, I actually meant to say advisor, but yes, I'm glad you cleared that up. I know from speaking to some of your colleagues, I actually spoke to Robin yesterday that you are looked to very highly, the most highly regarded person in science there, so not surprisingly. What I want to do is first talk about the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) that got its legs back in, I guess 1984. So we're going way back. And what's also interesting is that you go way back at Novo Nordisk to 35 years in 1989. And so, there had been this work with this extraordinary hormone and neurotransmitter with a very short half-life that you knew about. But when you first started in Novo Nordisk, you weren't working on this. As I understand it, you're working on laundry detergent enzymes. How did you make this pivot from the laundry enzymes to getting into the GLP-1 world?
Lotte Bjerre Knudsen (02:16 ):
Yeah, thank you for that question. I'm from the technical University of Denmark, so I'm trained in biotechnology, and we're a small country, so not that many companies to work for. And I always had my mind set on, I wanted to work for Novo as it was called back then, and it just happened to be in the industrial enzyme part that I got my foot in first. And then I had a very interesting boss at the time. Unfortunately, he's not alive anymore, but he was both a medical doctor as well as a chemist. So he was actually put in charge of actually, let's see if we can do something new in diabetes. And then since he hired me and I had not been there that long, I simply tagged along as the youngest scientist on the team, and then suddenly I became a diabetes researcher. Around the same time, I think you remember that all of pharma was interested in obesity in the early 90s, everyone wanted to do diabetes as well as obesity, but they were separate teams and they all wanted to do small molecules, but it just happens to be so that the best idea we could find at that time was actually GLP-1, because we actually had clinical data relatively early that GLP-1 was a really good candidate as a treatment for diabetes because of the glucose sensitivity of the actions.
(03:43 ):
So you'd have efficient lowering of glucose through a dual mechanism with increasing insulin, lowering glucagon, and then it was safe because there wasn't this hypoglycemia you get from insulin. But then I had other colleagues who were working on obesity, and I was just kind of listening, right, what's going on there? And then also a colleague that I had, we had, I don’t know if you remember the old Hagedorn Research Institute, but Novo actually had kind of like an academic research institute that was affiliated with us. And there was this group that were working on this glucagon tumor model that produced high levels of glucagon, GLP-1 and PYY. And these rats, they starved themselves to death. And I knew about that from 1994. So that actually inspired my thinking. So when Stephen Bloom's paper came out in January of 1996, and he was the first one to call GLP-1 a neurotransmitter, I think, but I was already way into actually screening these kind of molecules that later then became liraglutide.
No One Else Thought About This [Obesity]
(04:54 ):
And then I thought, why on earth should we not actually do both things at the same time? If we have an idea that can both work in diabetes in a much safer way than in insulin, and then also at the same time work in obesity. But the reality is that no one else thought about this, or if they thought about it, they didn't really think that it would a good idea. But I think I had the luxury of being in a biotech company, so everyone was working with peptides and proteins. So I don't think I got the same challenge that the other people in the other pharma’s got when they all wanted small molecules.
Eric Topol (05:36 ):
Well, also just to set the foundation here, which you alluded to, there had been so many attempts to come up with a drug that would work, not just of course in diabetes where there are many classes of drugs, but moreover, to treat the condition of obesity. Actually, I was involved with one of them, Rimonabant and did the large trial, which as you know, led to having to stop the drug, discontinue it because it was associated with suicidal ideation and actual some suicide. So there had been such a long history of checkered inability to come up with a drug. But what was striking is the challenge, and this is one of the first important questions about, when you had the extended half-life of the first GLP-1 drug, that instead of having to take multiple times a day, you could actually, with liraglutide get to a point where you were starting to get to an extended half-life. This is now going back to 1997 with approval in 2010, still 14 years ago. But when you came up with this drug, because this was certainly one of your great contributions, this drug was just a step along the way in this kind of iterative process, wouldn't you say? It wasn't the long half-life and the potency that eventually got us to where we are today. Is that true?
Lotte Bjerre Knudsen (07:15 ):
Yeah, it was a stepwise process. And what's super interesting about this class of medicines is that they're actually so different. If you talk about a class of