Podcast #219: Mount Bohemia Owner Lonie Glieberman
Description
The Storm explores the world of lift-served skiing year-round. Join us.
Who
Lonie Glieberman, Founder, Owner, & President of Mount Bohemia, Michigan
Recorded on
November 19, 2025
About Mount Bohemia
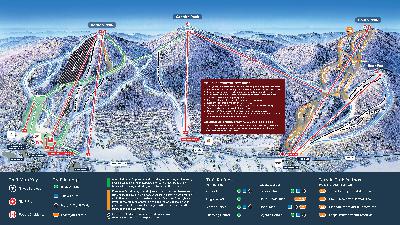
Click here for a mountain stats overview
Owned by: Lonie Glieberman
Located in: Lac La Belle, Michigan
Year founded: 2000, by Lonie
Pass affiliations: None
Reciprocal partners: Boho has developed one of the strongest reciprocal pass programs in the nation, with lift tickets to 34 partner mountains. To protect the mountain’s more distant partners from local ticket-hackers, those ski areas typically exclude in-state and border-state residents from the freebies. Here’s the map:
And here’s the Big Dumb Storm Chart detailing each mountain and its Boho access:
Closest neighboring ski areas: Mont Ripley (:50)
Base elevation: 624 feet
Summit elevation: 1,522 feet
Vertical drop: 898 feet
Skiable acres: 585
Average annual snowfall: 273 inches
Trail count: It’s hard to say exactly, as Boho adds new trails every year, and its map is one of the more confusing ones in American skiing, both as you try analyzing it on this screen, and as you’re actually navigating the mountain. My advice is to not try too hard to make the trailmap make sense. Everything is skiable with enough snow, and no matter what, you’re going to end up back at one of the two chairlifts or the road, where a shuttlebus will come along within a few minutes.
Lift count: 2 (1 triple, 1 double)
Why I interviewed him
For those of us who lived through a certain version of America, Mount Bohemia is a fever dream, an impossible thing, a bantered-about-with-friends-in-a-basement-rec-room-idea that could never possibly be. This is because we grew up in a world in which such niche-cool things never happened. Before the internet spilled from the academic-military fringe into the mainstream around 1996, We The Commoners fed our brains with a subsistence diet of information meted out by institutional media gatekeepers. What I mean by “gatekeepers” is the limited number of enterprises who could afford the broadcast licenses, printing presses, editorial staffs, and building and technology infrastructure that for decades tethered news and information to costly distribution mechanisms.
In some ways this was a better and more reliable world: vetted, edited, fact-checked. Even ostensibly niche media – the Electronic Gaming Monthly and Nintendo Power magazines that I devoured monthly – emerged from this cubicle-in-an-office-tower Process that guaranteed a sober, reality-based information exchange.
But this professionalized, high-cost-of-entry, let’s-get-Bob’s-sign-off-before-we-run-this, don’t-piss-off-the-advertisers world limited options, which in turn limited imaginations – or at least limited the real-world risks anyone with money was willing to take to create something different. We had four national television networks and a couple dozen cable channels and one or two local newspapers and three or four national magazines devoted to niche pursuits like skiing. We had bookstores and libraries and the strange, ephemeral world of radio. We had titanic, impossible-to-imagine-now big-box chain stores ordering the world’s music and movies into labelled bins, from which shoppers could hope – by properly interpreting content from box-design flare or maybe just by luck – to pluck some soul-altering novelty.
There was little novelty. Or at least, not much that didn’t feel like a slightly different version of something you’d already consumed. Everything, no matter how subversive its skin, had to appeal to the masses, whose money was required to support the enterprise of content creation. Pseudo-rebel networks such as ESPN and MTV quickly built global brands by applying the established institutional framework of network television to the mainstream-but-information-poor cultural centerpieces of sports and music.
This cultural sameness expressed itself not just in media, but in every part of life: America’s brand-name sprawl-ture (sprawl culture) of restaurants and clothing stores and home décor emporia; its stuff-freeways-through-downtown ruining of our great cities; its three car companies stamping out nondescript sedans by the millions.
Skiing has long acted as a rebel’s escape from staid American culture, but it has also been hemmed in by it. Yes, said Skiing Incorporated circa 1992, we can allow a photo of some fellow jumping off a cliff if it helps convince Nabisco Bob fly his family out to Colorado for New Year’s, so long as his family is at no risk of actually locating any cliffs to jump off of upon arrival. After all, 1992 Bob has no meaningful outlet through which to highlight this advertising-experience disconnect.
The internet broke this whole system. Everywhere, for everything. If I wanted, say, a Detroit Pistons hoodie in 1995, I had to drive to a dozen stores and choose the least-bad version from the three places that stocked them. Today I have far more choice at far less hassle: I can browse hundreds of designs online without leaving the house. Same for office furniture or shoes or litterboxes or laundry baskets or cars. And especially for media and information. Consumer choice is greater not only because the internet eliminated distance, but also because it largely eliminated the enormous costs required to actualize a tangible thing from the imagination.
There were trade-offs, of course. Our current version of reality has too many options, too many poorly made products, too much bad information. But the internet did a really good job of democratizing preferences and uniting dispersed communities around niche interests. Yes, this means that a global community of morons can assemble over their shared belief that the planet is flat, but it also means that legions of Star Wars or Marvel Comics or football obsessives can unite to demand more of these specific things. I don’t think it’s a coincidence that the dormant Star Wars and Marvel franchises rebooted in spectacular, omnipresent fashion within a decade of the .com era’s dawn.
The trajectory was slightly different in skiing. The big-name ski areas today are largely the same set of big-name ski areas that we had 30 years ago, at least in America (Canada is a very different story). But what the internet helped bring to skiing was an awareness that the desire for turns outside of groomed runs was not the hyper-specific desire of the most dedicated, living-in-a-campervan-with-their-dog skiers, but a relatively mainstream preference. Established ski areas adapted, adding glades and terrain parks and ungroomed zones. The major ski areas of 2025 are far more interesting versions of the ski areas that existed under the same names in 1995.
Dramatic and welcome as these additions were, they were just additions. No ski area completely reversed itself and shut out the mainstream skier. No one stopped grooming or eliminated their ski school or stopped renting gear. But they did act as something of a proof-of-concept for minimalist ski areas that would come online later, including avy-gear-required, no-grooming Silverton, Colorado in 2001, and, at the tip-top of the American Midwest, in a place too remote for anyone other than industrial mining interests to bother with, the ungroomed, snowmaking-free Mount Bohemia.
I can’t draw a direct line between the advent of the commercial internet and the rise of Mount Bohemia as a successful niche business within a niche industry. But I find it hard to imagine one without the other. The pre-internet world, the one that gave us shopping malls and laugh-track sitcoms and standard manual transmissions, lacked the institutional imagination to actualize skiing’s most dynamic elements in the form of a wild and remote pilgrimage site. Once the internet ordered fringe freeskiing sentiments into a mainstream coalition, the notion of an extreme ski area seemed inevitable. And Bohemia, without a basically free global megaphone to spread word of its improbable existence, would struggle to establish itself in a ski industry that dismissed the concept as idiotic and with a national ski media that considered the Midwest irrelevant.
Even with the internet, Boho took a while to catch on, as Lonie detailed in his first podcast appearance three years ago. It probably took the mainstreaming of social media, starting around 2008, to really amp up the online echo-sphere and help skiers understand this gladed, lake-effect-bombed kingdom at the end of the world.
Whatever drove Boho’s success, that success happened. This is a good, stable business that proved that ski areas do not have to cater to all skiers to be viable. But those of us who wanted Bohemia before it existed still have a hard time believing that it does. Like superhero movies or video-calls or energy drinks that aren’t coffee, Boho is a thing we could, in the ‘80s and early ‘90s, easily imagine but just as easily dismiss as fantasy.
Fortunately, our modern age of invention and experimentation includes plenty of people who dismiss the dism