Discover The War Lab: Exploring the Future of Conflict
The War Lab: Exploring the Future of Conflict

The War Lab: Exploring the Future of Conflict
Author: CJH
Subscribed: 11Played: 51Subscribe
Share
© CJH
Description
Warfare is evolving at an unprecedented pace. From autonomous weapons and cyber warfare to artificial intelligence and next-generation battle strategies, the future of conflict is being shaped by groundbreaking research and technological advancements. The War Lab is a deep-dive podcast that explores the cutting-edge innovations, strategic theories, and geopolitical forces that will define how wars are fought in the near future. research into the shifting landscape of modern warfare.
83 Episodes
Reverse
Episode SummaryIn this episode of The War Lab, we analyze what is arguably the most significant intellectual shift in modern military thought: the metamorphosis of Operational Art. For over a century, operational art—the "conductor" bridging high-level strategy and tactical execution—was defined by geometry, physical maneuver, and kinetic force. Today, that paradigm is collapsing. We trace the evolution from Napoleon’s corps system to the AI-driven, system-shattering doctrines of 2035, revealing how the modern commander must evolve from a field marshal into a systems architect.We explore how the battlefield has moved beyond maps and arrows into a domain defined by systemic disruption, cognitive paralysis, and decision advantage. The discussion unpacks historical pivot points—from the stalemate of WWI to the precision of Desert Storm—and projects forward to a future where victory is determined not by seizing terrain, but by hacking the enemy’s decision cycle and breaking their will to fight before the first shot is fired.The Geometric Age (Napoleon to Desert Storm):The Corps System: How Napoleon solved the "logistics vs. concentration" paradox by splitting armies to march and uniting them to fight.Soviet Deep Battle: The revolutionary concept (Tukhachevsky/Svechin) of striking the enemy throughout their entire depth simultaneously to induce "operational shock"—the intellectual ancestor of modern maneuver.AirLand Battle & Desert Storm: The apex of geometric warfare, where synchronization and precision allowed the U.S. to dismantle Iraqi forces with a perfect "left hook."The Shift to Systems Warfare:Multi-Domain Operations (MDO): The U.S. shift from guaranteed dominance to creating temporary "windows of advantage" against peer adversaries like China and Russia.Systems Destruction Warfare (China): A doctrine focused on paralyzing the enemy by targeting key information nodes (C2, logistics, sensors) rather than destroying units—aiming for total system collapse.Reflexive Control (Russia): The use of information warfare and nuclear signaling to manipulate an adversary's perception and compel them to make decisions favorable to you (e.g., self-deterrence).The Future: AI & The Systems Architect:JADC2 & The Kill Web: Moving from linear "kill chains" to resilient "kill webs," where any sensor can link to any shooter, powered by AI that reroutes around damage instantly.Mosaic Warfare: The shift from expensive "exquisite" platforms (like the F-35) to swarms of low-cost, expendable, and reconfigurable autonomous systems to overwhelm enemy targeting.The Cognitive Domain: The ultimate battleground is no longer land or sea, but the mind. Future warfare aims to "hack" the enemy commander’s decision cycle, forcing them to face complexity they cannot process.Victory is Abstract: Modern objectives are no longer about physical attrition but informational paralysis. The goal is to sever the enemy's nervous system (C4ISR) so their physical limbs become useless.The Automation Paradox: As we rely on AI to speed up the OODA loop (Observe-Orient-Decide-Act), we face the risk of "automation bias"—uncritically trusting flawed or poisoned algorithms that could lead to catastrophic escalation.Logistics is the New Maneuver: In a transparent world where "to be seen is to be killed," logistics is no longer a support function; it is the primary maneuver element. Future success depends on Quantum Logistics to survive contested environments.
War Lab — Episode: “Recon-Strike Since Desert Storm: Speed, Sensors, and the Logistics That Win (or Lose) Wars”How do you turn sensors into strikes fast enough to matter — and keep them flying when the runway’s been cratered? In this episode we trace four decades of hard lessons: from the U-2 shootdown and Vietnam’s Lightning Bug to the long bureaucratic battle over drones, then forward into today’s race for JADC2, AI-enabled kill chains, quantum timing, and the brittle logistics that could grind modern power projection to a halt. We unpack why technical brilliance won’t save you if the organization, doctrine, and supply chain can’t move at the same tempo.What you’ll hear:A clear narrative of how unmanned reconnaissance evolved — and why organizational culture, not just tech, repeatedly stalled progress.How JADC2 and agentic AI aim to collapse the OODA loop, and the real limits that keep the “decide” and “act” stages slow.The brutal operational reality in the Indo-Pacific: missile salvos, anti-runway submunitions, tanker closure times, and what REDR + Agile Combat Employment can (and can’t) fix.Concrete logistics fixes the transcript argues for: push-based buffers, forward pre-positioning, delegated sustainment authorities, and redesigning supply doctrine for contested, degraded comms.Why listen: if you care about whether America’s ISR-to-strike edge actually holds up in a peer fight — and how to stop brilliant sensors from becoming useless paper promises — this episode stitches history, doctrine, and hard operational math into a single, urgent argument.Subscribe to War Lab for deep, source-driven episodes on the future of conflict.
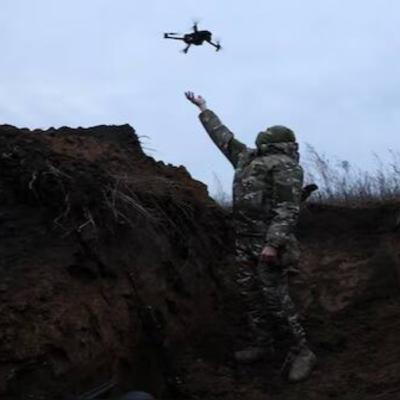
The War Lab — Episode: Task Force Dragon & the Algorithmic StrikeWhat actually happens when AI meets the battlefield? In this episode we move past sci-fi and panic and walk the ground truth: how data integration, human-machine teaming, and a new “military-tech complex” produced real operational effects in Ukraine. Using Task Force Dragon — the 18th Airborne Corps’ deployed experiment in algorithmic targeting — as our crucible, we test the claim that AI will either replace commanders or transform warfare. Spoiler: the tech didn’t erase human judgment — it amplified the need for better teams, new organizations, and sharper moral responsibility.You’ll hear a careful, empirically grounded account of:How Task Force Dragon fused satellites, SIGINT, OSINT and cyber feeds into an accelerated targeting cycle.Why the decisive innovation was organizational (human + civilian tech teams), not a single autonomous weapon.Concrete battlefield effects: faster verification, strikes on command nodes and logistics, and the operational concept called the “algorithmic strike.”The rise of a military-tech complex that looks nothing like the old hardware-focused industrial model.The persistent inhibitors: procurement law, talent and data costs, and the cultural gap between military hierarchies and Silicon Valley.The ethical and command problem — automation bias, AI “black boxes,” and why commanders must remain the final moral arbiters.Who should listen: military planners, policy wonks, technologists, and anyone trying to separate the hype from the practical reality of AI in war.By the end we ask a hard question: if the biggest danger isn’t autonomous robots but human complacency — commanders trusting opaque algorithms like soothsayers — how must professional military education, acquisition, and oversight change? Tune in for a rigorous, skeptical, and actionable look at what winning with AI actually requires.
How do you measure the largest battle in human history — by bodies, by firepower, or by the consequences that change the map forever? In this episode of War Lab we tackle a terrifying but vital project: a “calculus of annihilation” that weighs troop density, casualty intensity, and strategic weight to rank the mega-engagements that defined eras and reshaped nations. We cut through propaganda, bad data, and the fog of statistics to ask the hard question: what does scale really mean — and what does it tell us about the future of war?Listen as we test our framework against the great turning points of history: the urban hell of Stalingrad, the 872-day agony of Leningrad, Kursk’s armored maelstrom, the crushing blow of Operation Bagration, and the final furnace of Berlin. We rewind further — from Verdun and the Somme to ancient catastrophes like Changping and hydraulic ambushes at Salsu — to show how pre-industrial ambition can match industrial lethality. Then we zoom out to maritime and operational extremes — Leyte Gulf, Jutland, Kiev’s vast encirclement — and the Chinese civil war campaigns that rivaled World War II in scale and logistics.This is more than history: it’s a primer for policymakers and security thinkers. If industrialization moved the metric from men to materiel, what replaces troop density in an age of algorithmic war? Is systemic collapse of an electrical grid or financial system the next “largest battle”? We close by mapping the moral and strategic lessons national leaders must learn if they hope to limit the next generation’s capacity for annihilation.Tune in for a rigorous, evidence-driven episode that blends archival revision, operational analysis, and a hard look at how scale shapes strategy — and subscribe so you don’t miss the next deep dive from War Lab.
War Lab — Episode: "Fire, Systems, and Surprise: Russia vs. China — Doctrine, Tools, and the Future of High-End War"How do two of the world’s biggest militaries imagine winning the next great war? In this episode we open the doctrinal blueprints of the Russian Ground Forces (SV) and the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) and show how very different strategic logics produce equally dangerous results.We start with the core question: what does victory look like to Moscow and Beijing? For Russia the answer is overwhelming strike — make the battlefield uninhabitable for an adversary before close combat ever begins, and retain a low threshold for escalation (including tactical nuclear, chemical and thermobaric options) to coerce de-escalation on Moscow’s terms. For China the answer is system paralysis — use a whole-of-state approach (Comprehensive National Power) and tightly integrated “system warfare” to collapse an opponent’s command, reconnaissance and sustainment nodes, while shaping the information and cognitive environment around the fight.What we cover• Doctrinal foundations — “new generation” Russian ideas vs. PLA system warfare and CNP.• Force design — why Russia still leverages divisions, echelons and modular BTGs while China built fire-heavy, self-sufficient combined-arms brigades.• The centrality of fires and C2 — how both doctrines converge on destroying an enemy’s ability to see, decide and act.• Information, EW and reconnaissance — aggressive Russian Razvedka and counter-reconnaissance vs. continuous PLA information operations and psychological warfare.• Protection and escalation — layered air defenses, anti-tank approaches, thermobaric and RHBZ capabilities, and the strategic logic behind escalation choices.• The critical vulnerability both face: massive dependence on automated, networked C2 — what happens if networks fail on Day 1?Why this episode mattersIf you want to understand how future high-intensity fights might begin, what will be targeted first, and how escalation dynamics differ across rivals, this episode lays out the conceptual maps decision-makers and defense planners use — and the blunt tradeoffs those maps create.Who should listenPolicymakers, defense planners, regional specialists, and anyone who wants a clear, doctrine-level briefing on what a modern large-scale confrontation could actually look like — beyond equipment lists and headlines.Listen for a focused, source-driven walkthrough of the mechanics that matter in a peer fight — and a final, provocative question: both militaries assume near-perfect information and automated command; how resilient are their plans when the networks that power them start to fail?Tune in to War Lab — the future of conflict explained in plain terms.
War Lab — Logistics Under Fire: How the U.S. Army Plans to Survive a Contested WarIn this episode of The War Lab, we open the command-planning documents and step deep inside one of the most consequential transformations underway in modern warfare: the total redesign of U.S. Army sustainment for large-scale combat operations. This isn’t a tweak to doctrine or a marginal efficiency gain—it’s a philosophical reset driven by a single hard truth: in a war against a peer adversary, logistics will be hunted, disrupted, deceived, and destroyed.We break down the rise of contested logistics, where every movement across land, sea, air, space, cyber, and the electromagnetic spectrum is under persistent surveillance and precision threat. The era of safe rear areas, massive stockpiles, and predictable resupply is over. Survival now depends on dispersion, deception, speed, and data.At the heart of this episode is the Army’s radical organizational shift: the Light Support Battalion (LSB) and its three-node cluster concept, which shatters the traditional brigade support area into mobile, redundant logistics launch centers designed to survive missile strikes, drone swarms, and deep fires. We explain why forward support companies were eliminated, how maintenance and distribution were centralized, and the real risks this places on junior leaders tasked with managing brigade-wide sustainment under fire.From there, we dive into the technological backbone of the transformation. You’ll learn how predictive sustainment, powered by item-level tracking, unified data architecture, and AI-assisted analytics, is moving logistics from reactive to anticipatory—fixing equipment before it fails and allocating supplies before shortages emerge. We examine how enterprise systems are being rebuilt, why data integrity is now a warfighting requirement, and how sustainment leaders are using commercially available tools to generate a single trusted operational picture.The episode also explores the physical fight to move supplies when roads, ports, and airfields are contested. We cover autonomous resupply vessels, cargo drones, last-mile aerial delivery systems, and the growing role of additive manufacturing—where soldiers can fabricate critical parts at the point of need instead of waiting on fragile global supply chains. Logistics, in this model, is no longer passive support—it’s a maneuver element.We then turn to the human dimension: how logistics officers are now trained as sensors, drone operators, and base defenders; how reconstitution models like Iron Forge regenerate combat power in hours instead of weeks; and where dangerous capability gaps remain—from expeditionary port opening in the Pacific to sustainment in the Arctic and amphibious medical evacuation under A2/AD threat.Finally, we confront the most controversial idea of all: offensive logistics. Sustainment forces using their own signatures, data, and mobility to deceive, fix, and destroy the enemy’s ability to fight—turning logistics into a weapon in the deep battle.This episode is a deep, unflinching look at how wars are actually won—or lost—before the first maneuver unit ever reaches the objective. If you want to understand the future of conflict, you have to understand how armies will feed, fuel, repair, and regenerate under fire.Welcome to The War Lab.
Skirmishing Mist — How Infantry Must Learn to Vanish to Survive 2030Description:In this episode of War Lab we dismantle a startling prescription for the future of light infantry: become a professional ghost. Based on the Australian DSTG’s “Skirmishing Mist” concept, we trace a radical body-and-soul redesign of dismounted warfare driven by one grim insight — in a world of ubiquitous sensors, precision strike, and AI-fast decision loops, surviving by incremental upgrades to rifles and optics is no longer an option. You either change the whole force, or you get wiped out.We walk through the concept’s core logic: dispersion, autonomy, and signature denial. Skirmishing Mist (SM) insists on the D3 imperative — disconnected, disaggregated, decentralized — building small autonomous teams that operate systematically below the adversary’s detection threshold. These teams aren’t designed to seize and hold terrain; they exist to fragment enemy command, expose critical nodes, and cue remote killers. Think of them as vapor: they form, strike surgically, and evaporate, leaving the heavy brigade free to exploit the resulting chaos.Episode highlights:• Why the battlefield’s “perfect storm” of sensors + precision + AI makes traditional platoon formations existentially vulnerable, and why stealth must become doctrine rather than an add-on.• The D5 principle of kinetic restraint: skirmishers are explicitly tasked to disrupt — destroy, degrade, deny, deceive — not to slug it out. Major fires are remotely procured by a supporting strike regiment and UCAV mother ships; the forward team’s job is to sense, tag, and vanish.• Anatomy of the force: the 20-soldier baseline (and the expert preference for a 12-soldier survivable team) organized into five cells — command, reconnaissance, pioneer, SEMA (cyber/electromagnetic), and strike — with modular augmentation for HUMINT, PSYOPS, medics, or air defense.• The technology suite that enables invisibility: passive multispectral sensing, ubiquitous unattended ground sensors, smart dust tagging, hydrogen fuel cells for near-silent power, meta-materials for thermal and radar masking, and AI-enabled C2 that predicts team movement and allocates remote fires while minimizing radio traffic.• The comms paradox and the UAV courier: how operational security forces a one-way broadcast and physical data couriers, imposing latency that makes local decision-making mandatory and warps command relationships.• Logistics as the concept’s Achilles’ heel: the “logistical paradox” — an invisible, dispersed D3 force still depends on vulnerable aerial resupply and sustainment networks — and why resilient low-signature sustainment is the next design imperative.• Legal and ethical seams: the controversial “AI judge” that vets proportionality and ROE in near-real time, and the enormous human capital demands placed on decentralized commanders required to make legally and ethically fraught decisions at machine speed.• War-gamed strengths and limits: where SM excels (complex jungle, distributed urban pressure) and where it struggles (fixed subterranean networks, chemical ambushes, and mass casualty scenarios).We close by asking the hard questions every defense planner faces: can you realistically train and trust a generation of small-unit commanders to operate in isolation, juggle legal accountability, and act with near-total autonomy? Can a society accept the logistics and ethical costs of a force designed to be unseen? And if stealth becomes the new baseline for survival, how will that reshape doctrine, procurement, and military culture?Join us for a demanding, forensic look at a concept that may not be science fiction for long — and at the very real choices it forces on the way we organize, equip, and morally govern our soldiers in the age of lethal transparency.
Dynamic Space: The Fight for Orbital Supremacy Has Already BegunIn this episode of The War Lab, we take you inside the most important strategic transformation underway in modern warfare: the shift from a static, predictable space architecture to a fully maneuverable, combat-ready orbital force. What the U.S. built for peaceful dominance in the late 20th century is now a glaring vulnerability—and China is exploiting that gap faster than many policymakers realize.We explore why Dynamic Space Operations (DSO) are no longer an abstract concept but a hard requirement for preserving space superiority. That means sustained maneuver, refueling and repair in orbit, modular payload swaps, rapid launch, and a logistics network that turns space into a fluid operational domain rather than a graveyard of satellites locked into Keplerian orbits.You’ll hear how China’s Shijian satellites are already demonstrating refueling, proximity operations, coordinated multi-vehicle maneuvers, and robotic arms capable of grabbing or disabling U.S. assets—evidence of a real, ongoing campaign to master orbital warfare. And you’ll learn why U.S. systems, despite their sophistication, behave like predictable blimps in space—easily tracked, easily targeted, and unable to maneuver without exhausting precious fuel.From here, we walk through the pillars required to flip the script:• On-orbit refueling, servicing, and modular upgrades that radically extend satellite life and utility.• Nuclear thermal and nuclear electric propulsion, the key to escaping the tyranny of the rocket equation and achieving real maneuver warfare in space.• Distributed, mobile command-and-control, optical cross-links, and spectrum agility that eliminate single points of failure.• Responsive launch, including allied “Starlift” concepts, that allow the U.S. and NATO to replace or augment constellations within hours—not years.• In-space assembly and deception, creating unpredictable spacecraft, surprise payload deployments, decoys, and mission ambiguity that force adversaries to spend enormous resources tracking shadows.But DSO comes with its own challenges: the complexity of continuous maneuver, authority to expend fuel in wartime, gaps in ISR during service windows, and a legal and regulatory vacuum that has allowed commercial mega-constellations to accelerate an orbital debris crisis approaching Kessler-syndrome levels.We close by examining what may be the most controversial shift of all: the potential need for a future human guardian in space. As repair, troubleshooting, and combat interaction grow more complex, the U.S. may face a strategic cost if it cedes human spaceflight experience to a competitor already gaining operational reps.This is one of our most comprehensive deep dives yet—an essential briefing for anyone trying to understand the future character of war and why space, more than any other domain, will define who holds strategic advantage in the decades ahead.Tune in to The War Lab and step into the frontier where orbital mechanics meet military necessity, and where the race for competitive endurance in space is already underway.
In this episode of The War Lab, we conduct a rigorous examination of the most high-risk operational profile in modern conflict: the Singleton. We trace the brutal doctrinal evolution of the solitary operator—the individual soldier placed deep inside enemy-controlled territory, where survival is often secondary to mission execution.We explore the history, tradecraft, and future of the operator who works in total isolation, including:The Origins of Calculated Sacrifice: We analyze the "suicide squad" mentality of WWII’s British Auxiliary Units—human tripwires hidden in underground bunkers with a projected life expectancy of just 12 days.Cold War Stay-Behind Networks: A deep dive into the clandestine world of Detachment A in West Berlin and the "Green Light" teams tasked with the ultimate one-way mission: detonating backpack nuclear weapons (SADMs) to stop a Soviet advance.Modern Manhunting & AFO: How units like Delta Force’s G Squadron and the Intelligence Support Activity (ISA) industrialized the "Grey Man" concept to fix high-value targets in Iraq and Afghanistan.The Legal Gray Zone: The crushing personal risk of operating between Title 10 military status and Title 50 covert action, where a captured operator faces execution as a spy rather than protection as a prisoner of war.The Future of the Hyper-Enabled Operator: We look at the pivot to "cognitive overmatch," where single soldiers control autonomous drone swarms via AR headsets. We ask the critical question: Does this technology make the operator a lethal tactical headquarters, or just an illuminated electronic target for the enemy?.Join us as we dissect the continuous thread of calculated risk that connects the desperate saboteurs of 1940 to the digital ghost warriors of 2040.
In this episode of The War Lab, we unpack one of the least understood but most consequential transformations underway in China’s military ecosystem: the sweeping overhaul of its nationwide militia system. Far from a relic of Maoist “people’s war,” the militia is being re-engineered into a modern, specialized reserve force tied directly into the PLA’s joint warfighting architecture—and the implications for regional conflict are profound.We trace the origins of Beijing’s 2018 reform campaign, driven by a blunt internal assessment: before China could build a strong militia, it had to build a real one. That meant rooting out fake enlistments, hollow units, bureaucratic double-counting, and peacetime dysfunction. Only after that cleanup could the transition to “getting strong” begin—a transition aimed squarely at wartime readiness.From cyber specialists embedded in major tech firms, to maritime militia units operating alongside the China Coast Guard in contested waters, China’s once-disparate militia forces are now being shaped into a highly structured support arm for PLA operations across every domain: air, land, sea, space, and the electromagnetic spectrum. We break down how this new force is organized, what missions it’s being trained for, and how Beijing is using financial incentives, civilian–military partnerships, new training bases, and joint exercises with the PLA to hardwire militia units into campaigns that could shape the opening hours of a Taiwan or South China Sea conflict.But the reforms also face friction: limited budgets, uneven implementation, short training cycles, and the inherent challenge of turning civilian professionals—often available for only 7–12 days a year—into reliable wartime assets. We examine these limitations honestly, while highlighting pockets of real capability that Beijing is clearly proud of, from advanced UAV reconnaissance teams to elite cyber units providing security during major political events.Finally, we explore what indicators analysts should watch as China moves toward the next Five-Year Plan: whether rhetoric shifts beyond the “real-to-strong” phase, whether training days increase, and whether militia units appear more consistently in full-scale PLA joint exercises. Because taken together, these reforms represent something far larger than a reserve-force tune-up—they reveal how China is mobilizing its entire national base of talent, technology, and industry for modern conflict.If you want to understand China’s real mobilization power—and the strategic warning signs hidden in plain sight—this is an episode you won’t want to miss.
Today on War Lab: Exploring the Future of Conflict — we unpack one of the sharpest, most consequential confrontations in the Western Hemisphere: an unprecedented concentration of U.S. military power off Venezuela and the legal, clandestine, and diplomatic campaign built to force regime change.In this episode we trace how a carrier strike group, an amphibious readiness group with a Marine Expeditionary Unit, resurrected Cold-War infrastructure at Roosevelt Roads, and a layered ISR/strike architecture (F-35Bs, B-52s, MQ-9s, BACN, and ~200 Tomahawks at sea) combine with novel legal doctrine and covert action to create a pressure campaign unlike anything the region has seen in decades. We detail the administration’s controversial legal move — treating major trafficking syndicates as FTOs and declaring a non-international armed conflict — and how that reclassification permits lethal military strikes at sea instead of traditional law-enforcement interdictions. What you’ll learn:• What the force posture actually looks like, why it’s historically extreme, and what it can — and can’t — do.• How the NIA legal framework converts a criminal problem into a military targeting problem, and why that matters for due process and international law.• The secret war: CIA, FBI/HSI covert ops, a failed rendition plot, and a public campaign designed to fracture Maduro’s inner circle.• Diplomatic play and regional alignments — why Trinidad & Tobago’s pivot is a strategic coup for Washington.• The likely endgames: a psychological campaign that forces an internal collapse, or a grim choice to escalate (targeted air strikes, SOF capture/kill, or conventional seizures) — and the catastrophic risks of miscalculation.Crisp, sourced, and unflinching — this episode is a must-listen for anyone tracking the future of coercion, law, and war in America’s backyard. Tune in and ask: if coercion fails, what is the next step — and who will pay the price?
In this episode of War Lab, we step into the shattered world of modern espionage — a world where invisibility has vanished, tradecraft has collapsed, and every action leaves a permanent trace in the digital ether. The romantic era of Cold War spying — coded drops, shadowed meetings, and whispered secrets — is over. Welcome to the Glass House, where ubiquitous technical surveillance makes hiding nearly impossible.Host Chris Hedgecock dissects how the very foundations of intelligence — cover and tradecraft — have been obliterated by a planet blanketed in sensors, cameras, cell towers, and AI-driven analytics. In the Glass House, trying to hide isn’t stealth — it’s suspicious. Algorithms can now detect silence itself, flagging any deviation from the endless hum of normal digital life.From CIA networks burned by their own operational patterns to the collapse of non-official cover in the age of LinkedIn and social media, this episode explores how the spy’s greatest skillset has become their greatest liability. Physical disguise is obsolete; gait recognition, body-shape analysis, and multimodal biometric fusion can identify a person from a kilometer away — even with their face hidden.But this isn’t just a story of loss — it’s a story of transformation. Hedgecock traces the rise of advertising intelligence (AdINT), where vast streams of commercial data — geolocation, app telemetry, genomic profiles — have become the new battlefield. He unpacks how a civilian data scientist once uncovered a top-secret JSOC base in Syria using nothing more than open-market ad data, and how this revelation forced the U.S. to redefine personal data as a matter of national security.We also enter the age of agentic AI, where autonomous reasoning systems now compress the intelligence cycle from collection to action at machine speed. Platforms like Scale AI’s Donovan and Vanavar Labs’ Archer are reshaping espionage itself — but they also expose a dangerous truth: America’s most advanced intelligence infrastructure may no longer be sovereign. When the Pentagon’s critical AI tools are owned and shaped by private tech giants, what does that mean for national power in an era of “rented superpowers”?Finally, War Lab returns to the human element — the one domain AI still can’t replicate. In a world where machines collect every fact, the new spy’s mission is no longer to gather information, but to verify it and understand intent — the thoughts, motives, and plans still locked inside human minds.Themes explored:The collapse of traditional espionage under ubiquitous technical surveillanceAI-driven biometric tracking and the death of anonymityThe commercialization of intelligence and rise of AdINTAgentic AI and the “rented superpower” problemThe enduring human role: validating machine intelligence and uncovering intentListen to learn: why the future of espionage may depend not on hiding better — but on redefining what it means to know anything at all.
In this episode of War Lab we trace a quiet, epochal re-engineering of American national security: how the Cold War continuity-of-government (COG) apparatus was repurposed — legally, operationally, and physically — into a near-permanent “shadow government” designed to survive and sustain a vastly broader set of catastrophes. This isn’t a 9/11 origin story. It’s a story about preparation, policy, and power that began months before the attacks and accelerated in their wake.Hosts take you inside the doctrine, the bunkers, and the personalities — especially Vice President Dick Cheney and his counsel David Addington — who transformed continuity planning from a doomsday contingency into an enduring, executive-led operational system.What you’ll hearA clear, chronological unpacking of COG’s Cold War foundations (Mount Weather, Raven Rock, Greenbrier) and the three-part continuity doctrine (COG / COOP / ECG).The May 2001 policy pivot that put Cheney in charge of preparing for catastrophic WMD terrorism — and why 9/11 was an accelerant, not the origin.How the PEOC bunker moment on 9/11 produced immediate operational orders (including the shoot-down authorization) and the simultaneous birth of expansive legal rationales.The logistics and human cost of a perpetual shadow government: rotating teams of senior officials, 90-day bunker cycles, and constant readiness.The legal architecture that enabled secrecy and executive control: the unitary executive theory, the Addington legal strategy, and NSPD-51’s transformative language (the catastrophic emergency trigger and “cooperation as a matter of courtesy”).The constitutional stakes: how the program reshaped the balance among the branches and what it means for oversight, democratic legitimacy, and the future of emergency governance.Why it mattersThis episode shows that continuity planning is not merely a technical contingency; it’s a political and constitutional project. The structures put in place to ensure survival also concentrated power, shielded policy from oversight, and enshrined a legal framework that grants broad unilateral authority to the executive in “catastrophic” circumstances. Those arrangements remain official policy today — and the questions they raise about sovereignty, accountability, and the resilience of constitutional government are urgent.Listen if you want to understandHow national survival planning became national governance planning.Why secrecy and legal theory matter as much as bunkers and emergency rations.The human and institutional tradeoffs baked into perpetual emergency readiness.The contours of a debate that will shape the next major crisis: who should decide what counts as a catastrophic emergency — and who should run the country when it happens?Tune in for a rigorous, historically grounded, and unflinching look at how continuity became power — and what that means for democracy in an age of new threats.
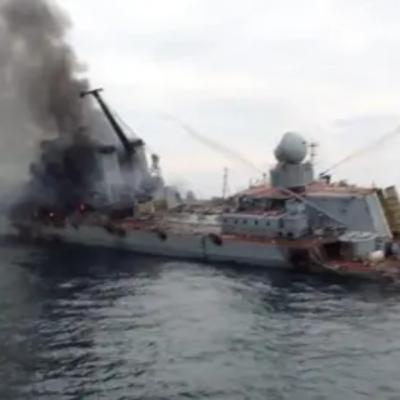
The Black Sea has always been more than a map feature—it’s a crucible of power, a maritime bottleneck where empire, geography, and ambition have collided for millennia. In this episode of War Lab, we dive deep into the evolving struggle for control over this body of water that has once again become one of the most strategically charged frontiers on Earth.From ancient Troy and the Ottoman Empire to the Cold War’s delicate balance and today’s brutal war in Ukraine, the Black Sea has served as the pivot of Eurasian power. Russia’s centuries-long drive for access to warm-water ports has shaped its very identity, and the city of Sevastopol—founded in 1783—became the heart of that ambition. But now, for the first time in history, that bastion of Russian naval dominance is collapsing from within.Through a mix of deep historical analysis and cutting-edge military insight, this episode explores how a war fought with drones, missiles, and data links has rewritten the rules of naval warfare. The once-mighty Russian Black Sea Fleet—rebuilt after the Cold War as a “fortress fleet” bristling with Kalibr cruise missiles and layered defenses—has been systematically dismantled by a nation with almost no navy at all. Ukraine’s mastery of asymmetry—land-based anti-ship missiles, explosive sea drones, and real-time satellite control—has rendered traditional surface fleets obsolete in contested littoral zones.We trace the story from Catherine the Great’s annexation of Crimea to the Montreux Convention that made Turkey the eternal gatekeeper of the straits, from the Moskva’s fiery sinking to the rise of the naval drone swarms that now dominate the western Black Sea. What began as a conventional naval campaign has become a case study in how cheap, networked systems can defeat billion-dollar warships.The implications reach far beyond the region. The Black Sea has become the world’s most consequential testing ground for the future of maritime conflict. Its lessons challenge a century of naval orthodoxy—from Mahan’s “big ship” doctrine to the very idea of sea control itself. Can massive fleets still survive in the age of precision strike and autonomous warfare? Or has the network—the swarm—replaced the ship as the new measure of sea power?Finally, we turn to the geopolitics shaping the next phase. Turkey’s control of the straits, NATO’s evolving posture on its southeastern flank, and the question of whether Russia can ever rebuild its fleet all converge in this episode. The “fortress Crimea” has been breached, the “Soviet lake” drained of its dominance, and a new maritime order is emerging—one defined not by size or tonnage, but by intelligence, adaptability, and distributed power.Shattered Bastion: The Black Sea reveals how one of the world’s oldest naval battlegrounds became the proving ground for the future of war at sea—and why what happens here will define the balance of power far beyond its shores.
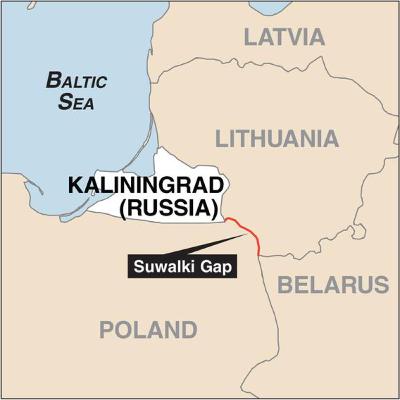
Kaliningrad—Russia’s heavily militarized enclave on the Baltic Sea—is both a sword and a shield, a fortress and a vulnerability. Once envisioned as a “Hong Kong of the Baltic,” it became something very different: Moscow’s forward-deployed bastion in Europe, armed with nuclear-capable missiles, dense air defenses, and naval strike forces capable of threatening NATO’s heartland. But as the tides of war and geopolitics shift, that fortress may now stand on crumbling ground.In this episode of War Lab, we dissect the Kaliningrad Paradox—how Russia’s most formidable outpost has evolved into one of its most exposed liabilities. We explore the anatomy of the exclave’s defenses: from its S-400 “no-fly” envelope and Iskander-M ballistic missiles to the degraded remnants of its once-proud 11th Army Corps. We trace how the war in Ukraine hollowed out its ground forces and how the accession of Finland and Sweden to NATO has turned the Baltic Sea into a “NATO Lake,” surrounding Kaliningrad on all sides.The discussion dives into the doctrine that makes Kaliningrad dangerous—the Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) strategy designed to paralyze NATO’s decision-making and deter reinforcement of the Baltic states. We examine how these systems interact to create an overlapping bubble of air, land, and sea denial—and how NATO can systematically dismantle it by targeting the vulnerable “nervous system” of radars, command posts, and sensor networks that sustain it.At the center of the analysis lies the Suwałki Gap—a 65-kilometer strip of land between Poland and Lithuania that could determine the fate of NATO’s eastern flank. Long seen as the Alliance’s Achilles’ heel, it is also Russia’s lifeline to Kaliningrad. If conflict comes, it could become the most contested corridor in Europe—a kill zone for both sides.Finally, we assess the transformation of the exclave in the wake of Nordic enlargement. With every Baltic coastline now under NATO control, Russia’s once-formidable stronghold has become an isolated, brittle “poison pill”—dangerous in its capacity for coercion and escalation, yet unsustainable in a prolonged war.The episode concludes with the key question for NATO planners: How do you neutralize a fortress without triggering catastrophe? We unpack strategic recommendations—blinding Kaliningrad’s reconnaissance-strike complex, enforcing total maritime isolation, and turning the Alliance’s new geography into an advantage.War Lab brings you inside the evolving architecture of modern deterrence—where military geography, doctrine, and technology converge to shape the balance of power. In this episode, the fortress at Kaliningrad is no longer just a Russian weapon—it’s a strategic riddle for NATO in the age of renewed great-power confrontation.
Episode Description: “The PLA’s Doctrine of Deception: How China Might Strike Taiwan”Surprise has always been a decisive force in warfare. For China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA), deception is not a supporting tactic—it is the very heart of its warfighting philosophy. Xi Jinping has exhorted his commanders to “excel at stratagem,” and modern PLA doctrine treats guile, misdirection, and surprise as the keys to defeating a technologically superior adversary.In this episode of War Lab, we dive deep into the PLA’s doctrine of deception and its application to the most dangerous flashpoint in the world today: a potential invasion of Taiwan. Drawing from historical precedent, doctrinal manuals, and modern capabilities, we explore how China might attempt to paralyze Taipei’s defenses long before the first landing craft reaches shore.From Sun Tzu’s timeless axiom that “all warfare is based on deception” to the PLA’s own case study of the 1955 Yijiangshan amphibious assault, we trace how deception has been institutionalized at every level of Chinese military thinking. We unpack the PLA’s “Information Deception Methodology,” which integrates concealment, confusion, and inducement to overwhelm adversary intelligence and decision-making. And we look at how modern tools—from decoy drones and electronic “ghost armies” to maritime militia disguised as civilian shipping—could be employed to disguise the real invasion force and fracture Taiwan’s defenses.But deception is not just about hiding; it’s about shaping the adversary’s perceptions. The PLA’s goal is not a zero-warning attack, but to create ambiguity, hesitation, and doubt—conditions that can delay a decisive response until it is too late. We analyze how Beijing might engineer a crisis to distract or lull Taiwan, sow chaos through covert infiltration and psychological warfare, and conduct multi-pronged feints designed to overwhelm command and control.Finally, we turn to what this means for the United States and Taiwan. Can modern ISR systems really make the battlefield “transparent,” or will deception once again prove decisive? What would it take for Taiwan to adopt a true “fight tonight” posture? And how can allies flip the script—using deception themselves to complicate PLA planning and blunt its warfighting edge?This is not just an academic debate. The PLA’s doctrine of deception represents one of the greatest challenges to deterrence in the 21st century. Understanding it is the first step in countering it.War Lab takes you inside the architecture of modern military power—where innovation, doctrine, and strategy collide.
Episode Description — The Violent Overthrow of Reconstruction and the Rise of Jim CrowThe end of Reconstruction was not the result of political drift but the product of a decade-long insurgency. In this episode, we examine how white supremacist paramilitary groups—the Ku Klux Klan, the White League, and the Red Shirts—used organized terror to dismantle biracial democracy in the South and force the federal government into retreat.We trace the violent arc from the Army’s early role in enforcing emancipation to the paramilitary massacres at Colfax and Hamburg that revealed the collapse of federal will. We explore how economic depression, judicial retreat in U.S. v. Cruikshank, and political compromise in 1877 sealed Reconstruction’s fate.The rise of Jim Crow was not a new beginning but the consolidation phase of this insurgency, where victory in the streets became victory in the law. The federal government’s unwillingness to sustain its commitment to Black citizenship turned Reconstruction into a cautionary tale—one that reveals the dangers of half measures, the costs of retreat, and the enduring power of organized violence to reshape democracy.
Episode Description — Future Korean War Scenarios and ImplicationsThe Korean Peninsula stands at its most dangerous moment since the 1953 armistice. In this episode, we explore how a shifting strategic landscape—Kim Jong Un’s abandonment of reunification, a deepening DPRK-Russia alliance, and the emergence of a China-Russia-North Korea bloc—has created the conditions for a second Korean War.Drawing on new analysis, we break down three plausible conflict pathways:The Conventional Gambit — a sudden preemptive strike designed to seize Seoul.Gray Zone Escalation — limited clashes that spiral into full-scale war through miscalculation.The Taiwan Contingency — a U.S.-China conflict that tempts Pyongyang to strike while Washington is distracted.We examine the likely opening moves: cyber warfare, disinformation, a devastating artillery and missile barrage on Seoul, infiltration by special forces, and the catastrophic risk of chemical and biological weapons. From there, the war could spiral into urban combat, massive civilian casualties, and, most dangerously, nuclear escalation in a desperate “gamble for resurrection” by Pyongyang.Finally, we consider the role of China and Russia, the near-certainty of U.S. and allied intervention, and the global consequences—from regional nuclear proliferation to a U.S.-China confrontation. The stakes are nothing less than the future of Northeast Asia and the stability of the international order.
Episode Description — Proactive and Integrated Deterrence: Countering Russian Hybrid WarfareRussia’s campaign against the West isn’t a series of isolated incidents—it’s a continuous, multi-domain hybrid war designed to divide NATO, undermine democracies, and reshape the global order in Moscow’s favor. For too long, the West has relied on a reactive and defensive posture—intercepting provocations, exposing disinformation, and imposing sanctions—without changing the Kremlin’s cost-benefit calculus.In this episode, we introduce a new strategic doctrine: Proactive and Integrated Deterrence. This approach flips the script, moving from passive defense to seizing the initiative through:Proactive Cost Imposition — shaping Russian behavior before it acts by raising the price of aggression.Asymmetric Response — punishing Moscow across economic, cyber, and diplomatic domains, not just on the battlefield.Sealing the Seams — closing the legal, political, and regulatory gaps Russia systematically exploits.We then explore how this doctrine translates into action across five fronts: diplomacy and information, military posturing, economic warfare, cyber operations, and legal reform.The takeaway is clear: to deter hybrid warfare, the West must stop playing defense and take the initiative. Only by making Russian aggression predictably and prohibitively costly can we restore deterrence and stability in the 21st century.
Episode Description — The New Paradigm of 21st-Century Warfare: An Analysis of Battlefield DisruptorsThe character of war is changing before our eyes. From Ukraine to Gaza, the old rules of 20th-century conflict are being dismantled by a new set of “battlefield disruptors” that are reshaping how wars are fought—and won.In this episode, we break down the six disruptors driving this transformation:Transparent Battlespace — where drones, satellites, and sensors make hiding nearly impossible.Decisive First Strike — why whoever fuses data with long-range precision fires first can win outright.AI-Driven Tempo — how algorithms compress decision cycles into milliseconds, outpacing human cognition.Top Attack Dominance — why cheap drones and loitering munitions are destroying tanks and inverting the economics of war.Autonomous Systems — the rise of human-out-of-the-loop weapons and swarming machines.Cognitive Electronic Warfare — AI in the spectrum, autonomously jamming, spoofing, and blinding an enemy’s systems.Drawing on lessons from Nagorno-Karabakh, Ukraine, and Gaza, we explore how these disruptors are converging into a new paradigm of hyper-lethality and decision dominance. The challenge for today’s leaders is clear: adapt doctrine, force structure, and leadership now—or risk repeating the mistake of generals in 1914, who saw change coming but failed to grasp its revolutionary implications.