Create an Offline-first React Native App Using WatermelonDB
Description

React Native has different database storage mechanisms for different mobile app purposes. Simple structures — such as user settings, app settings, and other key-value pair data — can be handled easily using async storage or secure storage.
Other applications — such as Twitter clones — fetch data from the server and directly show it to the user. They maintain a cache of data, and if a user needs to interact with any document, they call the APIs directly.
So not all the applications require a database.
When We Need a Database
Applications such as the Nozbe (a to-do app), Expense (a tracker), and SplitWise (for in-app purchases), need to work offline. And to do so, they need a way to store data locally and sync it up with the server. This type of application is called an offline first app. Over time, these apps collect a lot of data, and it becomes harder to manage that data directly — so a database is needed to manage it efficiently.
Options in React Native
When developing an app, choose the database that best fits your requirements. If two options are available, then go with the one that has better documentation and quicker response to issues. Below are some of the best known options available for React Native:
- WatermelonDB: an open-source reactive database that can be used with any underlying database. By default, it uses SQLite as the underlying database in React Native.
- SQLite (React Native, Expo): the oldest, most used, battle-tested and well-known solution. It’s available for most of the platforms, so if you’ve developed an application in another mobile app development framework, you might already be familiar with it.
- Realm (React Native): an open-source solution, but it also has an enterprise edition with lots of other features. They have done a great job and many well-known companies use it.
- FireBase (React Native, Expo): a Google service specifically for the mobile development platform. It offers lots of functionality, storage being just one of them. But it does require you to stay within their ecosystem to utilize it.
- RxDB: a real-time database for the Web. It has good documentation, a good rating on GitHub (> 9K stars), and is also reactive.
Prerequisites
I assume you have knowledge about basic React Native and its build process. We’re going to use react-native-cli to create our application.
I’d also suggest setting up an Android or iOS development environment while setting up the project, as you may face many issues, and the first step in debugging is keeping the IDE (Android Studio or Xcode) opened to see the logs.
Note: you can check out the official guide for installing dependencies here for more information. As the official guidelines are very concise and clear, we won’t be covering that topic here.
To set up a virtual device or physical device, follow these guides:
Note: there’s a more JavaScript-friendly toolchain named Expo. The React Native community has also started promoting it, but I haven’t come across a large-scale, production-ready application that uses Expo yet, and Expo port isn’t currently available for those using a database such as Realm — or in our case, WatermelonDB.
App Requirements
We’ll create a movie search application with a title, poster image, genre, and release date. Each movie will have many reviews.
The application will have three screens.
Home will show two buttons — one to generate dummy records, and a second to add new movie. Below it, there will be one search input that can be used to query movie titles from the database. It will show the list of movies below the search bar. If any name is searched, the list will only show the searched movies.
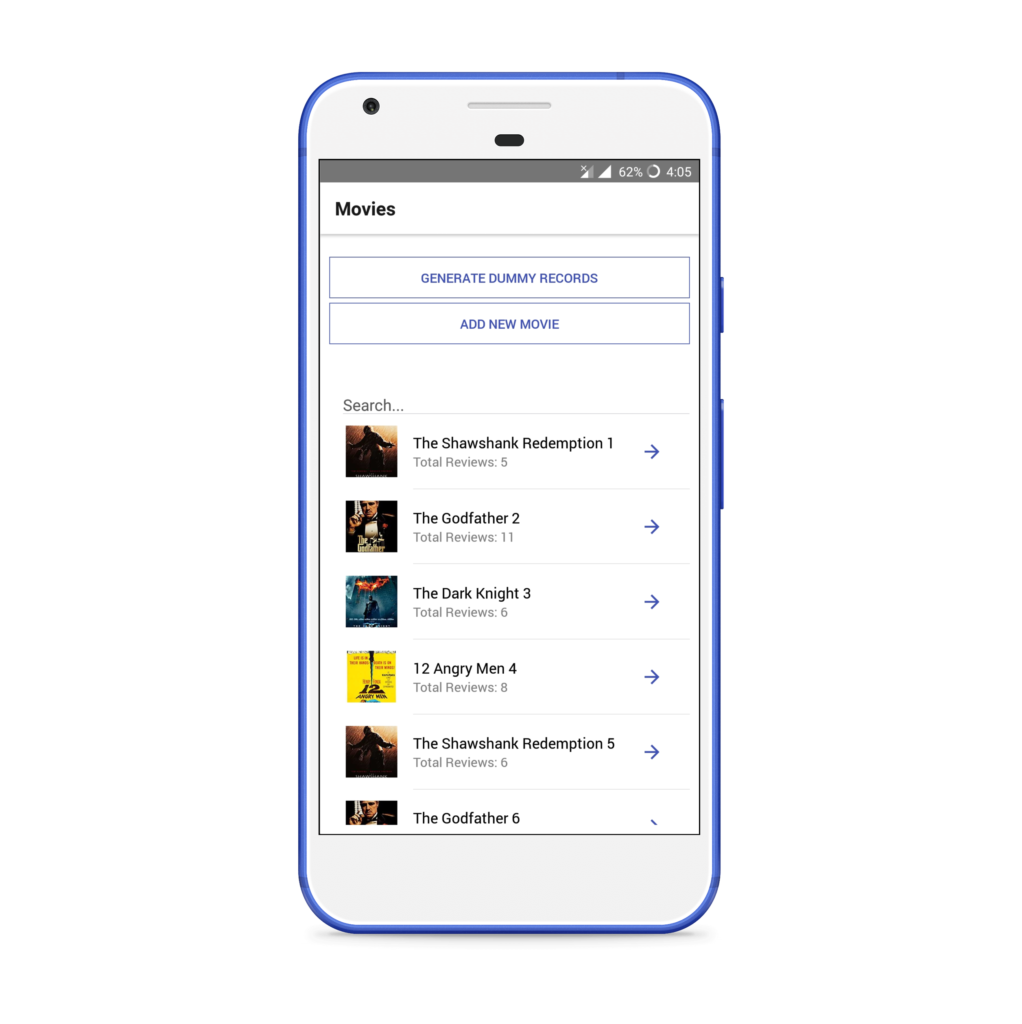
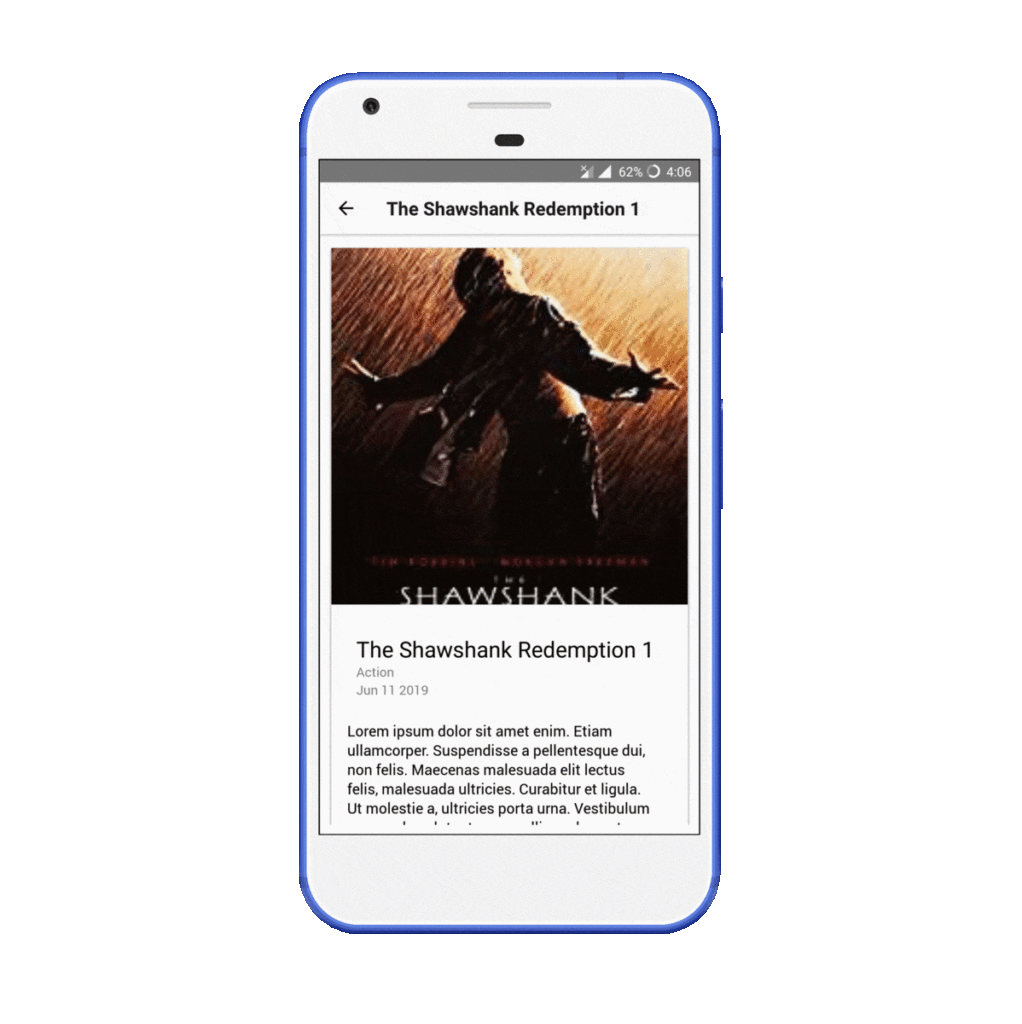
Clicking on any movie will open a Movie Dashboard, from where all its reviews can be checked. A movie can be edited or deleted, or a new review can be added from this screen.
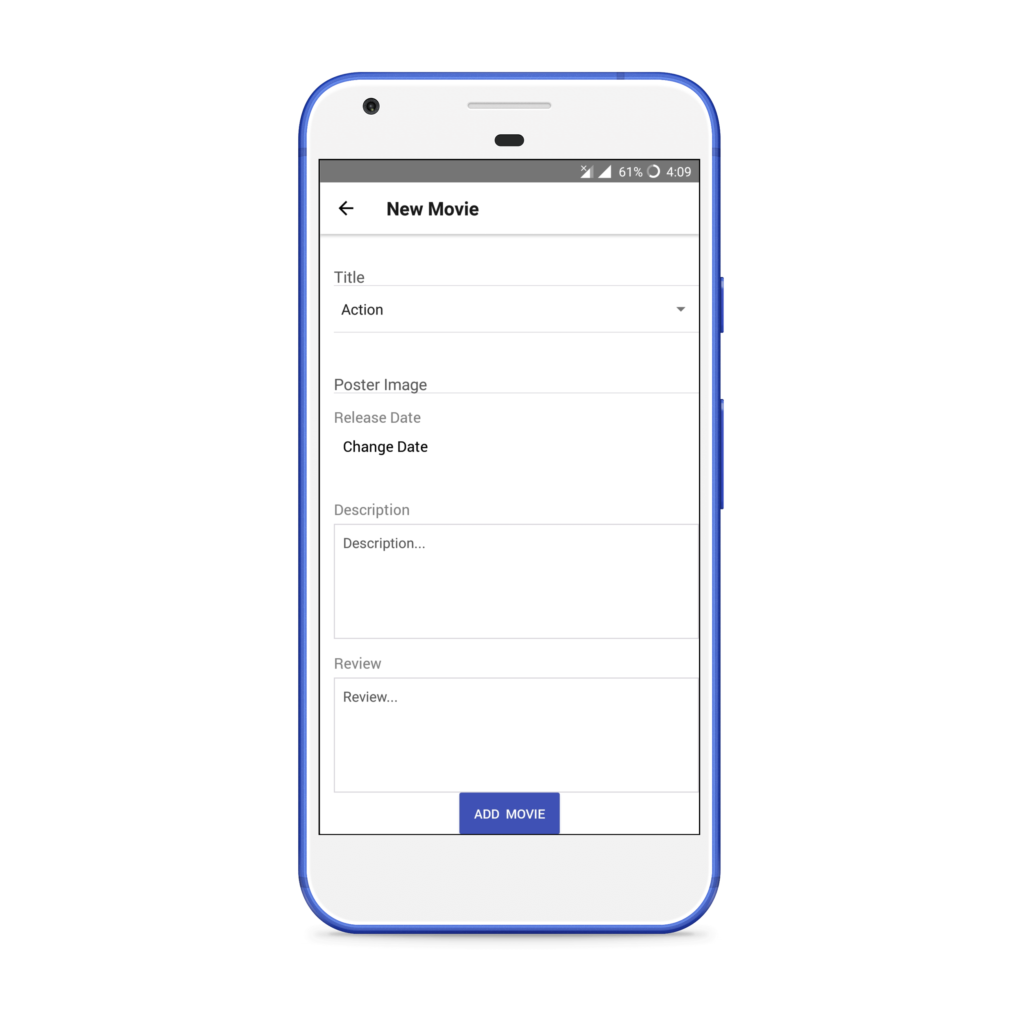
The third screen will be Movie Form, which is used to create/update a movie.
The source code is available on GitHub.
Why We Chose WatermelonDB (features)
We need to create an offline-first application, so a database is a must.
Features of WatermelonDB
Let’s look at some of the features of WatermelonDB.
Fully observable
A great feature of WatermelonDB is its reactive nature. Any object can be observed using observables, and it will automatically rerender our components whenever the data changes. We don’t have to make any extra efforts to use WatermelonDB. We wrap the simple React components and enhance them to make them reactive. In my experience, it just works seamlessly, and we don’t have to care about anything else. We make the changes in the object and our job’s done! It’s persisted and updated at all the places in the application.
SQLite under the hood for React Native
In a modern browser, just-in-time compilation is used to improve speed, but it’s not available in mobile devices. Also, the hardware in mobile devices is slower than in computers. Due to all these factors, JavaScript apps run slower in a mobile application. To overcome this, WatermelonDB doesn’t fetch anything until it’s needed. It uses lazy loading and SQLite as an underlying database on a separate thread to provide a fast response.
Sync primitives and sync adapter
Although WatermelonDB is just a local database, it also provides sync primitives and sync adapters. It makes it pretty easy to use with any of our own back-end databases. We just need to conform to the WatermelonDB sync protocol on the back end and provide the endpoints.
Further features include:
- Statically typed using Flow
- Available for all platforms
Dev Env and WatermelonDB Setup (v0.0)
We’re going to use react-native-cli to create our application.
Note: you may be able to use it with ExpoKit or Ejecting from Expo.
If you want to skip this part then clone the source repo and checkout the v0.0 branch.
Start a new project:
react-native init MovieDirectory
cd MovieDirectory
Install dependencies:
npm i @nozbe/watermelondb @nozbe/with-observables react-navigation react-native-gesture-handler react-native-fullwidth-image native-base rambdax
Below is the list of installed dependencies and their uses:
native-base: a UI library that will be used for look and feel of our app.react-native-fullwidth-image: for showing full-screen responsive images. (Sometimes it can be a pain to calculate the width, height and also maintain aspect ratio. So it’s better to use an existing community solution.)@nozbe/watermelondb: the database we’ll be using.@nozbe/with-observables: contains the decorators (@) that will be used in our models.react-navigation: used





