Niacinamide Found to Reduce the Risk of New Skin Cancers
Description
STORY AT-A-GLANCE
Skin cancer affects one in five Americans, with nonmelanoma types like basal and squamous cell carcinoma making up most cases. Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, is found to offer a strong preventive effect
A recent study published in JAMA Dermatology associated niacinamide use with a 14% lower overall risk of developing additional nonmelanoma skin cancers, with the greatest benefit seen after the first cancer diagnosis
Earlier research showed that taking 500 milligrams of niacinamide twice daily reduced new nonmelanoma skin cancers by 23% and precancerous lesions by up to 15%
Niacinamide protects your skin by restoring NAD+ for DNA repair, reducing inflammation, supporting immune defenses, and strengthening the barrier that maintains moisture and resilience against environmental stress
For long-term use, smaller daily doses of 50 milligrams three times per day are safe and sustainable. Combining niacinamide with sensible sun exposure habits and good nutrition strengthens skin defense naturally

Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide.1 In the United States, one in five Americans is expected to develop skin cancer during their lifetime, and roughly 9,500 people receive a diagnosis each day.2 The vast majority of these cases are nonmelanoma skin cancers, which include basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).3
The incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancers is estimated to be 18 to 20 times higher than that of melanoma.4 Although often treatable when detected early, recurrence is common and remains a significant concern.5 This has led researchers to explore better ways to prevent future cases, and one compound that has been recommended by dermatologists is niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3.6
What Is Niacinamide and How Does It Protect Your Skin?
Niacinamide is one of the two main forms of vitamin B3. The other is niacin, or nicotinic acid, which is known for causing flushing due to histamine release. Niacinamide does not produce this effect, which makes it easier to tolerate and suitable for long-term use. It used to be called nicotinamide, but the term niacinamide is now preferred to prevent confusion with nicotine, an entirely unrelated compound.
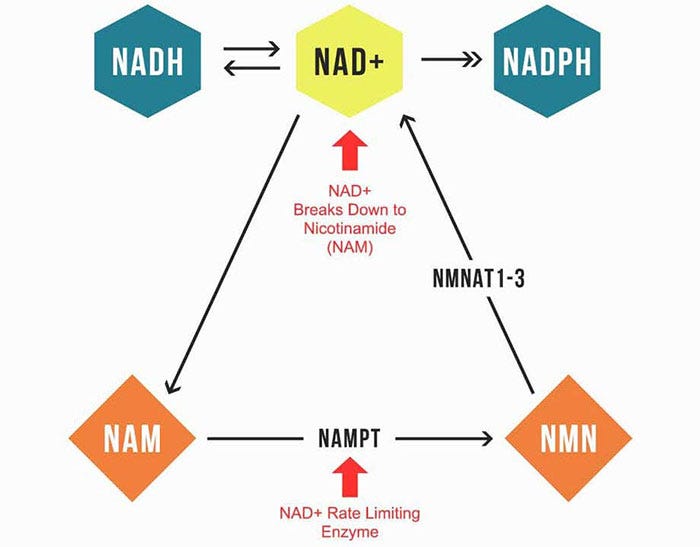
Niacinamide supports the skin at the cellular level — It does this by restoring a vital molecule called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that every cell relies on for energy production, DNA repair, inflammation control, and mitochondrial health.
<label class="hide-text" contenteditable="false">Text within this block will maintain its original spacing when published</label>When prolonged UV exposure, oxidative stress, or aging depletes NAD+ levels, skin cells lose the energy needed to maintain normal repair processes. Niacinamide replenishes this supply, keeping your skin’s repair systems active and resilient.
Inside your cells, niacinamide participates in the NAD+ salvage pathway — When NAD+ breaks down during normal metabolic activity, it forms niacinamide, which the body recycles by converting it into nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and then back into NAD+. This cycle allows your cells to sustain energy production and DNA repair without interruption, ensuring that repair enzymes and antioxidant systems always have the resources they need.
NAD+ fuels key DNA-repair enzymes — These include poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARPs) and sirtuins, which identify and repair DNA strand breaks. When NAD+ levels drop, these enzymes cannot function effectively, leading to the accumulation of damaged DNA. By maintaining NAD+ availability, niacinamide keeps these enzymes working efficiently and supports the genetic stability of your skin cells.
Niacinamide also reinforces your skin’s structural defenses — It stimulates ceramide production, strengthening the barrier that locks in moisture and shields against environmental damage.7 Because of its effects, dermatologists have used niacinamide for decades in both topical and oral forms to manage acne, rosacea, hyperpigmentation, and photoaging.8
Niacinamide’s influence extends far beyond skin health — Clinical studies have shown benefits in conditions linked to metabolic stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, including neurodegeneration,9 glaucoma,<a class="footnote-anchor" href="#