Behind the Study: Social and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Adults with Prediabetes
Update: 2025-10-08
Description
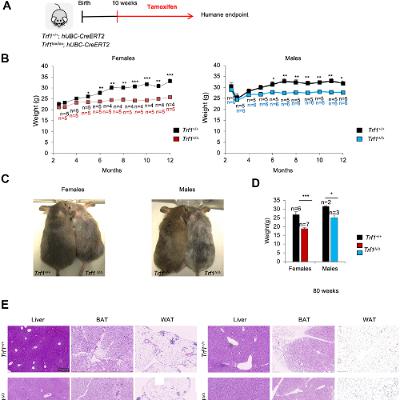
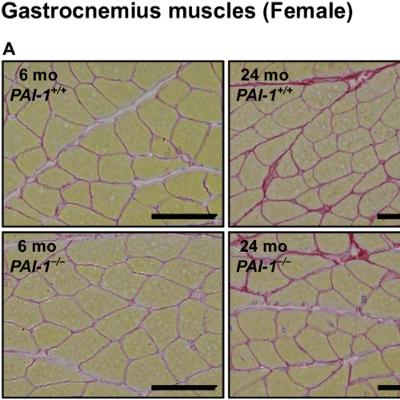
Dr. Leonard Egede, Dr. Rebekah Walker, and Dr. Obinna Ekwunife from the Department of Medicine at the University of Buffalo, NY, describe their #research paper #published in Volume 17, Issue 8 of Aging-US, entitled “Longitudinal relationship between social and CVD risk factors in older adults with prediabetes: the HRS 2006-2016.”
#interview #authorinterview #aging #prediabetes #cardiovascular #health #openaccess #openscience #peerreviewed #journal #publication #publishing #meded
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206308
Corresponding author - Leonard E. Egede - legede@buffalo.edu
Video interview - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1MSTk3GQAGA
Video transcript - https://aging-us.net/2025/10/08/behind-the-study-social-and-cardiovascular-risk-factors-in-older-adults-with-prediabetes/
Abstract
Background: This study examines how multiple social risk factors influence cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk control over time in older adults with prediabetes using a nationally representative cohort.
Methods: Data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) included 5,086 U.S. adults aged 50+ with prediabetes. Five social risk domains (economic stability, environment, education, healthcare, and social context) were examined as independent variables, while CVD risk factors included glycemic control (HbA1c), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and cholesterol ratio (total cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein). Mixed-effects models assessed relationships between social risk factors and CVD outcomes, adjusting for age, gender, race, and marital status.
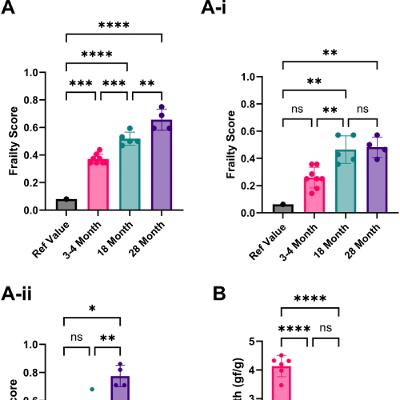
Results: The sample had an average age of 68.6 years, with 60.2% female, and 70.97% identifying as non-Hispanic Black. Average HbA1c was 5.7, SBP 129.4, and cholesterol ratio 3.85. Limited education was consistently associated with increased CVD risk—HbA1c (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.01–0.06, p < 0.001), SBP (β = 4.34, 95% CI: 2.96–5.71, p < 0.001), and cholesterol ratio (β = 0.08, 95% CI: 0.01–0.16, p < 0.05) —in the fully adjusted model. Medication cost-related non-adherence was significantly associated with higher HbA1c levels (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.002–0.06, p < 0.05). Difficulty paying bills and lack of health insurance were both significantly associated with higher cholesterol levels (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.002–0.06, p < 0.05) and (β = 0.22, 95% CI: 0.15–0.30, p < 0.001), respectively.
Conclusions: Social risk factors, particularly limited education, significantly impact CVD risk in older adults with prediabetes.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article -
https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.206308
Subscribe for free publication alerts from Aging - https://www.aging-us.com/subscribe-to-toc-alerts
Keywords - aging, prediabetes, social determinants of health, health equity, cardiovascular health, population health
To learn more about the journal, visit https://www.Aging-US.com and connect with us on social media at:
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
X - https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/@AgingJournal
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
Bluesky - https://bsky.app/profile/aging-us.bsky.social
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
Spotify - https://open.spotify.com/show/1X4HQQgegjReaf6Mozn6Mc
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
#interview #authorinterview #aging #prediabetes #cardiovascular #health #openaccess #openscience #peerreviewed #journal #publication #publishing #meded
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206308
Corresponding author - Leonard E. Egede - legede@buffalo.edu
Video interview - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1MSTk3GQAGA
Video transcript - https://aging-us.net/2025/10/08/behind-the-study-social-and-cardiovascular-risk-factors-in-older-adults-with-prediabetes/
Abstract
Background: This study examines how multiple social risk factors influence cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk control over time in older adults with prediabetes using a nationally representative cohort.
Methods: Data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) included 5,086 U.S. adults aged 50+ with prediabetes. Five social risk domains (economic stability, environment, education, healthcare, and social context) were examined as independent variables, while CVD risk factors included glycemic control (HbA1c), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and cholesterol ratio (total cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein). Mixed-effects models assessed relationships between social risk factors and CVD outcomes, adjusting for age, gender, race, and marital status.
Results: The sample had an average age of 68.6 years, with 60.2% female, and 70.97% identifying as non-Hispanic Black. Average HbA1c was 5.7, SBP 129.4, and cholesterol ratio 3.85. Limited education was consistently associated with increased CVD risk—HbA1c (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.01–0.06, p < 0.001), SBP (β = 4.34, 95% CI: 2.96–5.71, p < 0.001), and cholesterol ratio (β = 0.08, 95% CI: 0.01–0.16, p < 0.05) —in the fully adjusted model. Medication cost-related non-adherence was significantly associated with higher HbA1c levels (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.002–0.06, p < 0.05). Difficulty paying bills and lack of health insurance were both significantly associated with higher cholesterol levels (β = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.002–0.06, p < 0.05) and (β = 0.22, 95% CI: 0.15–0.30, p < 0.001), respectively.
Conclusions: Social risk factors, particularly limited education, significantly impact CVD risk in older adults with prediabetes.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article -
https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.206308
Subscribe for free publication alerts from Aging - https://www.aging-us.com/subscribe-to-toc-alerts
Keywords - aging, prediabetes, social determinants of health, health equity, cardiovascular health, population health
To learn more about the journal, visit https://www.Aging-US.com and connect with us on social media at:
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
X - https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/@AgingJournal
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
Bluesky - https://bsky.app/profile/aging-us.bsky.social
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
Spotify - https://open.spotify.com/show/1X4HQQgegjReaf6Mozn6Mc
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
Comments
In Channel