Longevity & Aging Series (S3, E6): Girish Harinath
Update: 2025-09-26
Description
In this episode of the Longevity & Aging Series, Girish Harinath from AgelessRx joins host Dr. Evgeniy Galimov to discuss a research paper he co-authored in Volume 17, Issue 4 of Aging-US, titled “Influence of rapamycin on safety and healthspan metrics after one year: PEARL trial results.”
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206235
Corresponding author - Stefanie L. Morgan - stefanie@agelessrx.com
Video interview - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-NvskI8Ve0
Longevity & Aging Series - https://www.aging-us.com/longevity
Abstract
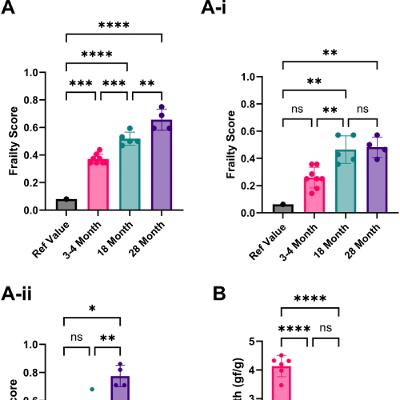
Design: This 48-week decentralized, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04488601) evaluated the long-term safety of intermittent low-dose rapamycin in a healthy, normative-aging human cohort. Participants received placebo, 5 mg or 10 mg compounded rapamycin weekly. The primary outcome measure was visceral adiposity (by DXA scan), secondary outcomes were blood biomarkers, and lean tissue and bone mineral content (by DXA scan). Established surveys were utilized to evaluate health and well-being. Safety was assessed through adverse events and blood biomarker monitoring.
Results: Adverse and serious adverse events were similar across all groups. Visceral adiposity did not change significantly (ηp2 = 0.001, p = 0.942), and changes in blood biomarkers remained within normal ranges. Lean tissue mass (ηp2 = 0.202, p = 0.013) and self-reported pain (ηp2 = 0.168, p = 0.015) improved significantly for women using 10 mg rapamycin. Self-reported emotional well-being (ηp2 = 0.108, p = 0.023) and general health (ηp2 = 0.166, p = 0.004) also improved for those using 5 mg rapamycin. No other significant effects were observed.
Conclusions: Low-dose, intermittent rapamycin administration over 48 weeks is relatively safe in healthy, normative-aging adults, and was associated with significant improvements in lean tissue mass and pain in women. Future work will evaluate benefits of a broader range of rapamycin doses on healthspan metrics for longevity, and will aim to more comprehensively establish efficacy.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article -
https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.206235
Subscribe for free publication alerts from Aging - https://www.aging-us.com/subscribe-to-toc-alerts
Keywords - aging, rapamycin, geroscience, longevity, healthspan
To learn more about the journal, please visit our website at https://www.Aging-US.com and connect with us on social media at:
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
X - https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/@AgingJournal
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
Bluesky - https://bsky.app/profile/aging-us.bsky.social
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
Spotify - https://open.spotify.com/show/1X4HQQgegjReaf6Mozn6Mc
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206235
Corresponding author - Stefanie L. Morgan - stefanie@agelessrx.com
Video interview - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-NvskI8Ve0
Longevity & Aging Series - https://www.aging-us.com/longevity
Abstract
Design: This 48-week decentralized, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04488601) evaluated the long-term safety of intermittent low-dose rapamycin in a healthy, normative-aging human cohort. Participants received placebo, 5 mg or 10 mg compounded rapamycin weekly. The primary outcome measure was visceral adiposity (by DXA scan), secondary outcomes were blood biomarkers, and lean tissue and bone mineral content (by DXA scan). Established surveys were utilized to evaluate health and well-being. Safety was assessed through adverse events and blood biomarker monitoring.
Results: Adverse and serious adverse events were similar across all groups. Visceral adiposity did not change significantly (ηp2 = 0.001, p = 0.942), and changes in blood biomarkers remained within normal ranges. Lean tissue mass (ηp2 = 0.202, p = 0.013) and self-reported pain (ηp2 = 0.168, p = 0.015) improved significantly for women using 10 mg rapamycin. Self-reported emotional well-being (ηp2 = 0.108, p = 0.023) and general health (ηp2 = 0.166, p = 0.004) also improved for those using 5 mg rapamycin. No other significant effects were observed.
Conclusions: Low-dose, intermittent rapamycin administration over 48 weeks is relatively safe in healthy, normative-aging adults, and was associated with significant improvements in lean tissue mass and pain in women. Future work will evaluate benefits of a broader range of rapamycin doses on healthspan metrics for longevity, and will aim to more comprehensively establish efficacy.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article -
https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.206235
Subscribe for free publication alerts from Aging - https://www.aging-us.com/subscribe-to-toc-alerts
Keywords - aging, rapamycin, geroscience, longevity, healthspan
To learn more about the journal, please visit our website at https://www.Aging-US.com and connect with us on social media at:
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
X - https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/@AgingJournal
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
Bluesky - https://bsky.app/profile/aging-us.bsky.social
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
Spotify - https://open.spotify.com/show/1X4HQQgegjReaf6Mozn6Mc
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
Comments
In Channel