Ep 45 Roshcast Emergency Board Review
Description
There is only one corner of the universe you can be certain of improving, and that’s your own self.
–Aldous Huxley
Welcome back to RoshCast for Episode 45! Let’s start out with a review of rabies before getting to core content Q&A.
<figure class="aligncenter">
 </figure>
</figure>- The most common wild reservoirs of rabies are raccoons, skunks, bats, foxes, and coyotes. Domestic animals like cats, dogs, and cattle can also get rabies. Rodents, reptiles, and birds on the other hand are not carriers and cannot transmit rabies.
- One important factor in deciding if you get rabies postexposure prophylaxis is whether the animal can be found and held for observation.
- The rabies postexposure prophylaxis has two parts: the immunoglobulin and the vaccine.
- When giving rabies postexposure prophylaxis, inject the immunoglobulin into the wound and start the rabies vaccine series which the patient will receive on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28.
Now onto this week’s podcast
Question 1
Which of the following is true regarding acute respiratory distress syndrome?
A. Define as PaO2:FiO2 > 300
B. Empiric corticosteroids should be given
C. Positive end-expiratory pressure should be increased with increases in FiO2
D. Tidal volume should be started at 10 mL/kg in intubated patients
Question 2
A 35-year-old man presents to the ED after being assaulted in a bar fight. He has signs of significant facial trauma. On physical exam, you note a tooth fracture through the enamel and dentin but does not involve the pulp. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of his dental injury?
A. Calcium hydroxide paste
B. Extract the tooth
C. Immediate dental consult
D. Pencillin VK
Question 3
A 62-year-old man presents with acute onset of chest pain with radiation to the shoulders and nausea while walking his dog. On examination, he is diaphoretic with heart rate 94 bpm, respiratory rate 20 bpm, blood pressure 92/59 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation 96% on room air. His ECG reveals 2 mm elevation in aVR. Occlusion of which coronary artery is most likely responsible for this patient’s presentation?
A. Left anterior descending artery
B. Left circumflex artery
C. Left main coronary artery
D. Right coronary artery
Question 4
<figure class="aligncenter">
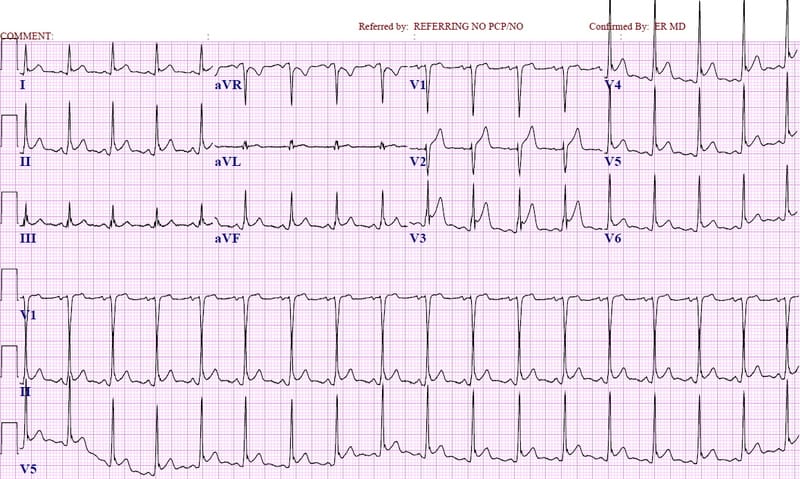 </figure>
</figure>A 62-year-old man presents for evaluation of chest pain. Approximately three weeks ago the patient had a myocardial infarction with stent placement. Last evening he developed pleuritic chest pain and fever. He has no cough and does not feel short of breath. His ECG is shown above. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Dressler syndrome
B. Infarct pericarditis
C. Left ventricular aneurysm
D. ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
Question 5
A 45-year-old man with a history of hypercholesterolemia presents with acute onset of anterior chest pain, nausea, and diaphoresis. His ECG is distinct for upsloping ST elevation in AVR (≥ 1 mm) with ST depressions and tall T waves in the precordial leads. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Occlusion of the left circumflex artery
B. Occlusion of the left main coronary artery
C. Occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery
D. Occlusion of the right coronary artery
Question 6
A 25-year-old man presents the emergency department with knee pain. This morning he slipped on the ice and felt a pop in his knee. On physical exam his left knee appears to have a moderate effusion with limited range of motion and medial joint line tenderness. An X-ray of the left knee is performed. A pedunculated, bony exostosis with well-defined margins is seen along the distal lateral femur on the AP view of the knee. What is the most likely diagnosis of the incidental bone lesion?
A. Aneurysmal bone cyst
B. Osteochondroma
C. Osteoid osteoma
D. Osteosarcoma
<figure class="aligncenter">
 </figure>
</figure>- Intubated patients with ARDS should be started on low tidal volumes of 6–8 cc/kg of ideal body weight, and the PEEP and FiO2 should be titrated up together.
- The PaO2 to FiO2 ratio in patients with ARDS is < 300. The lower the ratio, the worse the disease process.
- There are three classes of dental fractures:
- Ellis Class I involves injury to the enamel alone and is treated by smoothing any rough edges.
- Ellis Class II involves injury to the dentin and enamel. This is treated by covering exposed dentin with calcium hydroxide.
- Ellis Class III involves the pulp along with the dentin and enamel. These usually require antibiotics and immediate dental consult.
- ST segment elevation in aVR greater than 1 mm or greater than the ST segment elevation in V1 is most concerning for occlusion of the left main coronary artery.
- Dressler syndrome is pericarditis occuring one week to several months after an MI.
- A left ventricular aneurysm is a complication of a large anterior wall MI. EKG shows ST segment elevations in the anterior leads.
- De Winter ECG patterns presents with tall, prominent symmetric T waves in the precordial leads with upsloping ST segment depression greater than 1mm at the J point and ST segment elevation may be seen in aVR
- De Winter EKG is a STEMI equivalent and represents acute LAD occlusion.
- Aneurysmal bone cyst, osteochondroma, and osteoid osteoma are benign bone lesions.
- Osteosarcoma is a malignant bone lesion seen on X-ray as a lytic lesion, a blastic lesion, or a heavily ossified mass.
That wraps up RoshCast Episode 45! Be sure to also check out the rest of the Rosh Review Blog





