Episode 400: Four no wait Five Mysteries!
Description
To donate to help victims of Hurricane Helena:
Day One Relief – direct donation link
World Central Kitchen – direct donation link
It’s the big 400th episode! Let’s have a good old-fashioned mystery episode! Thanks to Richard from NC for suggesting two of our animal mysteries today.
Further reading:
A 150-Year-Old Weird Ancient Animal Mystery, Solved
The Enigmatic Cinnamon Bird: A Mythical Tale of Spice and Splendor
First ever photograph of rare bird species New Britain Goshawk
Scientists stumbled onto toothy deep-sea “top predator,” and named it after elite sumo wrestlers
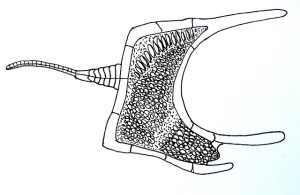
A stylophoran [drawing by Haplochromis – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10946202]:
A cinnamon flycatcher, looking adorable [photo by By https://www.flickr.com/photos/neilorlandodiazmartinez/ – https://www.flickr.com/photos/neilorlandodiazmartinez/9728856384, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30338634]:

The rediscovered New Britain goshawk, and the first photo ever taken of it, by Tom Vieras:

The mystery fish photo:
The yokozuna slickhead fish:

The Biotwang maker, Bryde’s whale:

Show transcript:
Welcome to Strange Animals Podcast. I’m your host, Kate Shaw.
We’ve made it to the big episode 400, and also to the end of September. That means monster month is coming up fast! To celebrate our 400th episode and the start of monster month, let’s have a good old-fashioned mysteries episode.
We’ll start with an ancient animal called a stylophoran, which first appears in the fossil record around 500 million years ago. It disappears from the fossil record around 300 million years ago, so it persisted for a long time before going extinct. But until recently, no one knew what the stylophoran looked like when it was alive, and what it could possibly be related to. It was just too weird.
That’s an issue with ancient fossils, especially ones from the Cambrian period. We talked about the Cambrian explosion in episode 69, which was when tiny marine life forms began to evolve into much larger, more elaborate animals as new ecological niches became available. In the fossil record it looks like it happened practically overnight, which is why it’s called the Cambrian explosion, but it took millions of years. Many of the animals that evolved 500 million years ago look very different from all animals alive today, as organisms evolved body plans and appendages that weren’t passed down to descendants.
As for stylophorans, the first fossils were discovered about 150 years ago. They’re tiny animals, only millimeters long, and over 100 species have been identified so far. The body is flattened and shaped sort of like a rectangle, but two of the rectangle’s corners actually extend up into little points, and growing from those two points are what look like two appendages. From the other side of the rectangle, the long flat side, is another appendage that looks like a tail. The tail has plates on it and blunt spikes that stick up, while the other two appendages look like they might be flexible like starfish arms.
Naturally, the first scientists to examine a stylophoran decided the tail was a tail and the flexible appendages were arm-like structures that helped it move around and find food. But half a billion years ago, there were no animals with tails. Tails developed much later, and are mainly a trait of vertebrates.
That led to some scientists questioning whether the stylophoran was an early precursor of vertebrates, or animals with some form of spinal cord. The spikes growing from the top of the tail actually look a little bit like primitive vertebrae, made of calcite plates. That led to the calcichordate hypothesis that suggested stylophorans gave rise to vertebrates.
Then, in 2014, scientists found some exceptionally well preserved stylophoran fossils in the Sahara Desert in Africa. The fossils dated to 478 million years ago and two of them actually had soft tissue preserved as the mineral pyrite. Pyrite is also called fool’s gold because it looks like gold but isn’t, so these were shiny fossils.
When the soft tissue was observed through electron microscopes in the lab, it became clear that the tails weren’t actually tails. Instead, they were more like a starfish arm, with what may be a mouth at the base. The arm was probably the front of the animal, not the back like a tail, and the stylophoran probably used it to grab food and maybe even to crawl around.
Most scientists today agree that stylophorans are related to modern echinoderms like starfish and urchins, but there is one big difference. Echinoderms show radial symmetry, but no stylophoran found so far does. It doesn’t really even show bilateral symmetry, since the two points aren’t really symmetrical to each other. We’re also not sure what the points wer





