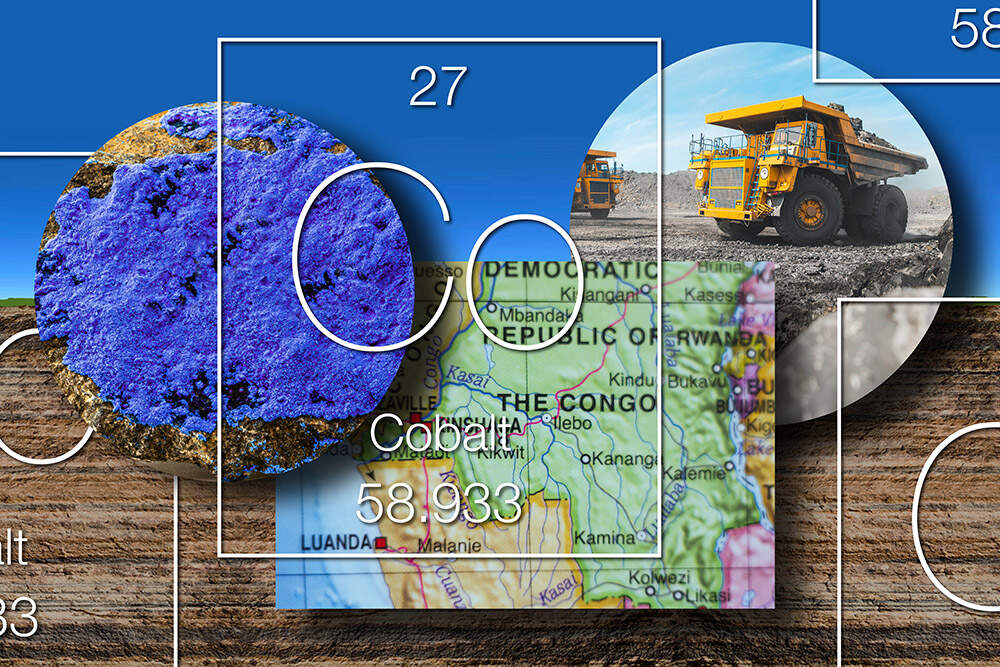
The human cost of cobalt: Modern slavery in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Digest
The podcast delves into the critical role of mining in the transition to clean energy, specifically focusing on the demand for cobalt, a key component in rechargeable batteries. It highlights the environmental and social costs associated with increased mining, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where cobalt is extracted under dangerous and exploitative conditions. The episode explores the history of exploitation in the DRC, tracing it back to the colonial era and highlighting the ongoing violence and instability fueled by the demand for minerals. It examines the role of the Congolese government and the international community in addressing the challenges of ethical and sustainable cobalt mining. The podcast concludes by discussing potential levers for change, emphasizing the need for tech companies to take responsibility for their supply chains and for consumers to be aware of the human cost of their technology.
Outlines

The Clean Energy Transition and Mining
The episode introduces the global shift towards clean energy and the critical role of mining in supplying essential minerals like cobalt, lithium, copper, and nickel. It acknowledges the environmental and social costs associated with increased mining, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of the cobalt mining industry in the Democratic Republic of Congo.

The Human Cost of Cobalt: Exploitation in the Democratic Republic of Congo
This chapter focuses on the human cost of cobalt mining in the DRC, highlighting the dangerous and exploitative conditions faced by artisanal miners, many of whom are children. It explores the use of child labor, lack of safety equipment, and environmental pollution, emphasizing the urgent need for change in the industry.

Congo's History of Exploitation: From Leopold II to the Present
The episode delves into the history of exploitation in the DRC, tracing it back to the reign of King Leopold II of Belgium in the 19th century. It highlights the brutal atrocities committed under Leopold's rule, including forced labor, torture, and murder. The chapter also discusses the ongoing violence in the DRC, fueled by the demand for minerals, and the role of international actors in perpetuating this exploitation.

The Role of the Congolese Government and the International Community
This chapter examines the role of the Congolese government in addressing the exploitation of its mineral resources. It discusses the challenges faced by the DRC in achieving good governance and the impact of colonial interference on its development. The episode also explores the responsibility of the international community, including Western governments and tech companies, in ensuring ethical and sustainable cobalt mining practices.

Leveraging Pressure for Change: The Role of Tech Companies and Consumers
The episode concludes by discussing potential levers for change in the cobalt mining industry. It emphasizes the need for tech companies to take responsibility for their supply chains and ensure ethical sourcing practices. The episode also encourages consumers to be aware of the human cost of their technology and to demand change from companies.
Keywords
Cobalt
A bluish-gray metal that is a key component in rechargeable batteries, particularly for electric vehicles. Cobalt is found in high concentrations in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which accounts for a significant portion of global production.
Artisanal Mining
Small-scale mining operations that are often unregulated and involve manual labor. In the DRC, artisanal miners play a significant role in cobalt extraction, but they often work in dangerous and exploitative conditions.
Supply Chain Transparency
The ability to track the origin and movement of products and materials throughout their journey from raw materials to finished goods. Transparency in supply chains is crucial for ensuring ethical and sustainable sourcing practices.
Human Rights Due Diligence
A process by which companies identify, assess, and mitigate human rights risks associated with their operations and supply chains. Due diligence is essential for ensuring that companies are not contributing to human rights abuses.
Conflict Minerals
Minerals that are extracted from areas where armed conflict is taking place. Cobalt is considered a conflict mineral due to the violence and instability in the DRC.
Green Energy Transition
The shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power. The transition to clean energy requires significant amounts of minerals, including cobalt, which are used in batteries and other technologies.
Post-Colonialism
The period following the end of colonialism, characterized by the ongoing impact of colonial legacies on former colonies. The DRC continues to grapple with the consequences of its colonial past, including exploitation of its resources and political instability.
Geopolitical Tensions
The complex and often strained relationships between countries, often driven by economic, political, or military interests. The demand for cobalt has created geopolitical tensions between countries like the United States and China, which are both seeking to secure access to the mineral.
Q&A
What are the key challenges associated with increasing mining to meet the demand for clean energy?
Increased mining comes with significant environmental and social costs, including habitat destruction, pollution, and potential human rights abuses. The episode highlights the need for responsible mining practices that prioritize sustainability and human well-being.
How does the history of exploitation in the DRC contribute to the current situation in the cobalt mining industry?
The DRC has a long history of being exploited for its resources, dating back to the colonial era. This history has created a legacy of poverty, violence, and weak governance, which makes it difficult to address the challenges in the cobalt mining industry.
What role can tech companies play in ensuring ethical and sustainable cobalt mining practices?
Tech companies that use cobalt in their products have a responsibility to ensure that their supply chains are free from human rights abuses and environmental damage. They can achieve this by conducting due diligence, working with local communities, and supporting responsible mining practices.
What can consumers do to make a difference in the situation for Congolese people?
Consumers can raise awareness about the human cost of cobalt mining, demand transparency from companies, and support organizations working to improve conditions in the DRC. By making informed choices and advocating for change, consumers can contribute to a more ethical and sustainable cobalt industry.
Show Notes
Rebroadcast: Most of the world’s cobalt is extracted in the Democratic Republic of Congo. But to get it, hundreds of thousands of Congolese people labor with no other means to survive. On episode three of On Point’s special series -- cobalt and the human cost of mining.