Masters of Mess Making and Meaning
Description
Hello Interactors,
My wife and I recently started watching the mini-series 100 Foot Wave, which follows extreme surfer Garrett McNamara’s quest to ride the mythical 100-foot breaker. The show has put Nazaré, Portugal on the map — not just as a place, but as a symbol of human daring against forces far larger than ourselves.
At the same time, I’ve been listening to physicist-philosopher Sean Carroll’s recent “solo” podcast on the emergence of complexity, tracing how the universe began in simplicity and blossomed into stars, life, and consciousness. These two threads — towering waves and cosmic arcs — collided in my mind, stirring something that has been swelling in me for years: how to reconcile wonder at life’s improbable flourishing with despair at its accelerated unraveling on Earth.
Should despair be the only response? Or is it possible, like the surfers at Nazaré, to recognize the peril without surrendering to it — to ride, however briefly, the wave that could also destroy us?
THE COSMIC WAVE
Beneath the lighthouse bluff at Nazaré, Portugal opens a canyon 140 miles long and three miles deep — three times deeper than the Grand Canyon. Born of tectonic fractures and sculpted over millions of years, it is less a static feature than a force in its own right: a conduit that gathers the ocean’s momentum and hurls it shoreward. Swells that elsewhere would pass unnoticed are here magnified into walls of water, indifferent to whether they become playground or grave. Geography conspires — wind, current, and rock — but the canyon itself is an accomplice, a reminder that Earth is never merely stage but actor. For today’s surfers, this is possibility. For centuries of fishermen, it was peril. The waves have not changed, but the stance we take toward them has — and that, too, becomes part of the story the canyon tells.
So it is with complexity. Every wave begins simple, a long low swell born of distant winds, that crescendos into chaos at the shoreline. It swirls and curls into turbulent foam piqued in curious but dangerous beauty, only to dissolve back into undertow, bubbles, and silence. Our own cosmos follows the same rhythm, driven by the logic of entropy — the tendency of energy to spread, of order to give way to disorder. In the beginning, we know the universe was astonishingly simple and ordered: a hot, uniform plasma, almost featureless in its smoothness.
Imagine the origin of life sitting at origin of a graph. It exists orderly in low entropy and low complexity. But entropy is restless. As it advanced diagonally up and to the right disorder increases in a straight line. This opens space for complexity to emerge. Early on in the cosmos tiny quantum fluctuations stretched into patterns, atoms gathered into stars, stars fused new elements as galaxies spun, coalesced, and collided. Imagine this as the complexity line on our graph. It also grows with time but takes the shape of a parabolic wave climbing upward to a smooth crest as it increases in complexity. Meanwhile, entropy ticks steadily up and to the right as a straight arrow of time forever growing in disorder as our universe continues to increase in complexity.
We are now somewhere on this complexity curve. And this is the paradox of our middle epoch. Entropy never reverses course — disorder always increases — yet along that trajectory the complexity within we live crests, like a wave gathering its final height. For a sliver of cosmic time, the universe has been rich, complex, and with structure. On at least one world in the cosmos, life emerges and even creates complex organisms like us. But if entropy pushes inexorably forward, complexity will not hold indefinitely. Stars will exhaust their fuel, galaxies will drift into darkness, and matter itself may decay. This diagram reminds us that complexity rises only to fall again, tracing an arc back toward simplicity even as entropy continues its steady climb.
In this framing, the universe is not a march from order to chaos but a cycle of simple-to-complex-to-simple played out against entropy’s one-way slope. We live in a fleeting middle where complexity momentarily flourishes. Like the wave at Nazaré, born as a long low swell, steepening into a towering wall of water, then dissolving again into foam, undertow, and silence, our cosmos crests only once. The question is not whether entropy wins — it does — but how we dwell, and what we make of meaning, within the brief surge of complexity it permits.
It took a lot to get us to this point. This complex space that entropy has carved within cosmic time leaves room for novelty. Complexity flourishes locally even as disorder deepens globally. Out of this novel initial imbalance, life emerged — fragile metabolisms harvesting energy from their surroundings, weaving temporary order against the grain of entropy. From single-celled organisms to multicellular bodies, from photosynthesis to predation, biology layered new strategies of survival atop older ones. Evolution diversified life into forests and reefs, wings and fins, neural nets and circulatory systems. These proliferations multiplied niches where order could briefly hold, even as the larger cosmos drifted toward disorder.
Only much later did consciousness arise, one of evolution’s rarest experiments: a capacity not merely to metabolize energy but to reflect upon the arc of complexity itself. With awareness came memory, imagination, culture — tools for navigating the turbulence of entropy’s middle chapter. Entropy still holds the reins: the universe will drift back toward simplicity, whether into a thin uniform haze or some other quiet ending. Yet here, in the middle, entropy’s detour has produced extravagant complexity — including beings capable of gazing back at the wave that carries them and wondering what it means.
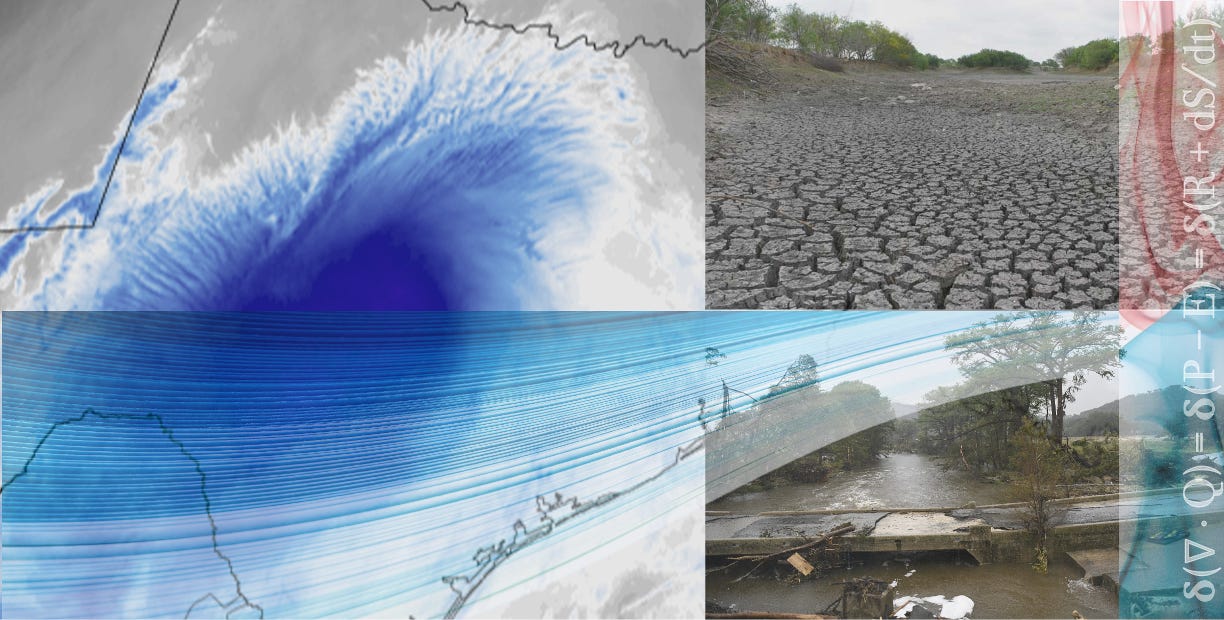
THE INDIFFERENT EARTH
This same gaze can also induce speculation. Like speculative realism. Emerging in the early 2000s as a reaction against a tendency to keep reality tethered to human thought and language, its central claim is stark: the world is indifferent to us. Planets orbit, tectonic plates shift, and waves break whether or not anyone is there to see them. From this view, complexity arises from imbalances in matter and energy, from unfinished processes that unfold far beyond human agency. The wave doesn’t care whether it is surfed or feared; it builds from wind, water, and terrain, cresting and dissolving with no meaning to maintain.
Animated globe of tectonic plates shifting across hundreds of millions of years, reminding us that Earth’s movements unfold indifferent to human presence or perception. Source: Reddit. And below is where we go from here:
This speculation hits another conscious reality — optimism. Human optimism is as hard to contain as its constant refrain. Born of the Enlightenment but rebirthed amid the industrial expansion, world wars, and scientific breakthroughs of the early 1900s, modernist optimism leaned confidently on reason and science — a conviction that human ingenuity could transcend natural limits and bend uncertainty toward progress. Time and again, human ingenuity has found ways to stretch the boundaries of what seemed natural limits. Agricultural revolutions multiplied food production beyond what Malthus thought possible. Industrialization transformed energy regimes, substituting fossil carbon for dwindling forests. Urban innovations — from sanitation to electrification — allowed cities to grow far past the thresholds that once doomed them to collapse. Each leap suggested that collapse was not destiny but averted through cleverness.
This pattern sustains modernist faith: that humans can intervene wisely in the unfolding of complexity. Where speculative realism emphasizes the indifference of natural forces — entropy driving stars and systems toward disorder regardless of our designs — modernist thought wagers otherwise. It insists that ingenuity allows us not merely to endure the swell but to ride it, to carve temporary stability out of turbulence. In this view, the challenge of complexity is not simply to recognize its inevitabilities but to cultivate the foresight, restraint, and imagination that let human life persist in its fragile middle.
That is if humans “don’t do dumb things.” In other words, humans can and should preserve the conditions that let life and intelligence persist locally, even as the universal drift of entropy continues.
Armed with the mathematical models that fuel both scientific confidence and human hubris, the world can appear elegant — even in its ugliness. Amidst entropy following a relentless trajectory we see scaling laws enfold organisms, cities, and civilizations alike. The planet itself is rendered as a singular complex system drifting through cosmic time. The physicist’s gaze simplifies this by design — reducing frictions, stripping away differences, until only lawlike arcs remain. As the polymath Heinz von Foerster once put it, “Hard sciences are successful because they deal with the soft problems; soft sciences are struggling because they deal with the hard problems.”
Geography, by contrast, cannot ignore what falls through those cracks. The sweep of cosmology may remind us that complexity is not uniquely human — stars ignite, galaxies cluster, black holes churn — but such vistas stretch horizons so far that human lifetimes blur into insignificance. Civilizations, like waves, crest and crash in an instant against the span of cosmic time.
To move closer in, at a planetary scale, complexity narrows to the thin envelope where oceans, land, and atmosphere intertwine. It is within this fragile band that agriculture took root, cities rose, and civilizations flourished. Yet scientists, equipped with hard science, warn that this Holocene balance has already been breached. The “safe operating space” is n