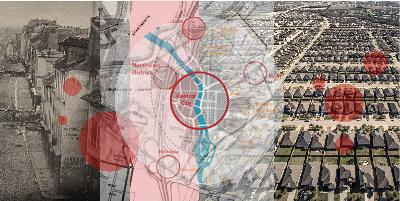
You Are Here. But Nowhere Means Anything
Description
Hello Interactors,
This week, the European Space Agency launched a satellite to "weigh" Earth's 1.5 trillion trees. It will give scientists deeper insight into forests and their role in the climate — far beyond surface readings. Pretty cool. And it's coming from Europe.
Meanwhile, I learned that the U.S. Secretary of Defense — under Trump — had a makeup room installed in the Pentagon to look better on TV. Also pretty cool, I guess. And very American.
The contrast was hard to miss. Even with better data, the U.S. shows little appetite for using geographic insight to actually address climate change. Information is growing. Willpower, not so much.
So it was oddly clarifying to read a passage Christopher Hobson posted on Imperfect Notes from a book titled America by a French author — a travelogue of softs. Last week I offered new lenses through which to see the world, I figured I’d try this French pair on — to see America, and the world it effects, as he did.
PAPER, POWER, AND PROJECTION
I still have a folded paper map of Seattle in the door of my car. It’s a remnant of a time when physical maps reflected the reality before us. You unfolded a map and it innocently offered the physical world on a page. The rest was left to you — including knowing how to fold it up again.
But even then, not all maps were neutral or necessarily innocent. Sure, they crowned capitals and trimmed borders, but they could also leave things out or would make certain claims. From empire to colony, from mission to market, maps often arrived not to reflect place, but to declare control of it. Still, we trusted it…even if was an illusion.
I learned how to interrogate maps in my undergraduate history of cartography class — taught by the legendary cartographer Waldo Tobler. But even with that knowledge, when I was then taught how to make maps, that interrogation was more absent. I confidently believed I was mediating truth. The lines and symbols I used pointed to substance; they signaled a thing. I traced rivers from existing base maps with a pen on vellum and trusted they existed in the world as sure as the ink on the page. I cut out shading for a choropleth map and believed it told a stable story about population, vegetation, or economics. That trust was embodied in representation — the idea that a sign meant something enduring. That we could believe what maps told us.
This is the world of semiotics — the study of how signs create meaning. American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce offered a sturdy model: a sign (like a map line) refers to an object (the river), and its meaning emerges in interpretation. Meaning, in this view, is relational — but grounded. A stop sign, a national anthem, a border — they meant something because they pointed beyond themselves, to a world we shared.
But there are cracks in this seemingly sturdy model.
These cracks pose this question: why do we trust signs in the first place? That trust — in maps, in categories, in data — didn’t emerge from neutrality. It was built atop agendas.
Take the first U.S. census in 1790. It didn’t just count — it defined. Categories like “free white persons,” “all other free persons,” and “slaves” weren’t neutral. They were political tools, shaping who mattered and by how much. People became variables. Representation became abstraction.
Or Carl Linnaeus, the 18th-century Swedish botanist who built the taxonomies we still use: genus, species, kingdom. His system claimed objectivity but was shaped by distance and empire. Linnaeus never left Sweden. He named what he hadn’t seen, classified people he’d never met — sorting humans into racial types based on colonial stereotypes. These weren’t observations. They were projections based on stereotypes gathered from travelers, missionaries, and imperial officials.
Naming replaced knowing. Life was turned into labels. Biology became filing. And once abstracted, it all became governable, measurable, comparable, and, ultimately, manageable.
Maps followed suit.
What once lived as a symbolic invitation — a drawing of place — became a system of location. I was studying geography at a time (and place) when Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and GIScience was transforming cartography. Maps weren’t just about visual representations; they were spatial databases. Rows, columns, attributes, and calculations took the place of lines and shapes on map. Drawing what we saw turned to abstracting what could then be computed so that it could then be visualized, yes, but also managed.
Chris Perkins, writing on the philosophy of mapping, argued that digital cartographies didn’t just depict the world — they constituted it. The map was no longer a surface to interpret, but a script to execute. As critical geographers Sam Hind and Alex Gekker argue, the modern “mapping impulse” isn’t about understanding space — it’s about optimizing behavior through it; in a world of GPS and vehicle automation, the map no longer describes the territory, it becomes it.
Laura Roberts, writing on film and geography, showed how maps had fused with cinematic logic — where places aren’t shown, but performed. Place and navigation became narrative. New York in cinema isn’t a place — it’s a performance of ambition, alienation, or energy. Geography as mise-en-scène.
In other words, the map’s loss of innocence wasn’t just technical. It was ontological — a shift in the very nature of what maps are and what kind of reality they claim to represent. Geography itself had entered the domain of simulation — not representing space but staging it. You can simulate traveling anywhere in the world, all staged on Google maps. Last summer my son stepped off the train in Edinburgh, Scotland for the first time in his life but knew exactly where he was. He’d learned it driving on simulated streets in a simulated car on XBox. He walked us straight to our lodging.
These shifts in reality over centuries weren’t necessarily mistakes. They unfolded, emerged, or evolved through the rational tools of modernity — and for a time, they worked. For many, anyway. Especially for those in power, seeking power, or benefitting from it. They enabled trade, governance, development, and especially warfare. But with every shift came this question: at what cost?
FROM SIGNS TO SPECTACLE
As early as the early 1900s, Max Weber warned of a world disenchanted by bureaucracy — a society where rationalization would trap the human spirit in what he called an iron cage. By mid-century, thinkers pushed this further.
Michel Foucault revealed how systems of knowledge — from medicine to criminal justice — were entangled with systems of power. To classify was to control. To represent was to discipline. Roland Barthes dissected the semiotics of everyday life — showing how ads, recipes, clothing, even professional wrestling were soaked in signs pretending to be natural.
Guy Debord, in the 1967 The Society of the Spectacle, argued that late capitalism had fully replaced lived experience with imagery. “The spectacle,” he wrote, “is not a collection of images, but a social relation among people, mediated by images.”
Then came Jean Baudrillard — a French sociologist, media theorist, and provocateur — who pushed the critique of representation to its limit. In the 1980s, where others saw distortion, he saw substitution: signs that no longer referred to anything real. Most vividly, in his surreal, gleaming 1986 travelogue America, he described the U.S. not as a place, but as a performance — a projection without depth, still somehow running.
Where Foucault showed that knowledge was power, and Debord showed that images replaced life, Baudrillard argued that signs had broken free altogether. A map might once distort or simplify — but it still referred to something real. By the late 20th century, he argued, signs no longer pointed to anything. They pointed only to each other.
You didn’t just visit Disneyland. You visited the idea of America — manufactured, rehearsed, rendered. You didn’t just use money. You used confidence by handing over a credit card — a symbol of wealth that is lighter and moves faster than any gold.
In some ways, he was updating a much older insight by another Frenchman. When Alexis de Tocqueville visited America in the 1830s, he wasn’t just studying law or government — he was studying performance. He saw how Americans staged democracy, how rituals of voting and speech created the image of a free society even as inequality and exclusion thrived beneath it. Tocqueville wasn’t cynical. He simply understood that America believed in its own image — and that belief gave it a kind of sovereign feedback loop.
Baudrillard called this condition simulation — when representation becomes self-contained. When the distinction between real and fake no longer matters because everything is performance. Not deception — orchestration.
He mapped four stages of this logic:
* Faithful representation – A sign reflects a basic reality. A map mirrors the terrain.
* Perversion of reality – The sign begins to distort. Think colonial maps as logos or exclusionary zoning.
* Pretending to represent – The sign no longer refers to anything but performs as if it does. Disneyland isn’t America — it’s the fantasy of America. (ironically, a car-free America)
* Pure simulation – The sign has no origin or anchor. It floats. Zillow heatmaps, Uber surge zones — maps that don’t reflect the world, but determine how you move through it.
We don’t follow maps as they were once known anymore. We follow interfaces.
And not just in apps. Cities themselves are in various stages of simulation. New York sti