Chapter Fourteen, part 2. Hypovolemic States
Description
Outline Chapter 14 — Treatment
- Treatment
- Both oral and IV treatment can be used for volume replacement
- The goal of therapy are to restore normovolemia
- And to correct associated acid-base and electrolyte disorders
- Oral Therapy
- Usually can be accomplished with increased water and dietary sodium
- May use salt tablets
- Glucose often added to resuscitation fluids
- Provides calories
- Promotes intestinal Na reabsorption since there is coupled Na and Glucose similar to that seen in the proximal tubule
- Rice based solutions provide more calories and amino acids which also promote sodium reabsorption
- 80g/L of glucose with rice vs 20 g/L with glucose alone
- IV therapy
- Dextrose solutions
- Physiologically equivalent to water
- For correcting hypernatremia
- For covering insensible losses
- Watch for hyperglycemia
- Footnote warns against giving sterile water
- Saline solutions
- Most hypovolemic patients have a water and a sodium deficit
- Isotonic saline has a Na concentration of 154, similar to that of plasma see page 000
- Half-isotonic saline is equivalent to 550 ml of isotonic saline and 500 of free water. Is that a typo?
- 3% is a liter of hypertonic saline and 359 extra mEq of Na
- Dextrose in saline solutions
- Give a small amount of calories, otherwise useless
- Alkalinizing solutions
- 7.5% NaHCO3 in 50 ml ampules 44 mEq of Na and 44 mEq of HCO3
- Treat metabolic acidosis or hyperkalemia
- Why 44 mEq and not 50?
- Do not give with calcium will form insoluble CaCO3
- Polyionic solutions
- Ringers contains physiologic K and Ca
- Lactated Ringers adds 28 mEq of lactate
- Spreads myth of LR in lactic acidosis
- Potassium chloride
- Available as 2 mEq/mL
- Do not give as a bolus as it can cause fatal hyperkalemia
- Plasma volume expanders
- Albumin, polygelastins, hetastarch are restricted to vascular space
- 25% albumin can pull fluid into the vascular space
- 25% albumin is an albumin concentration of 25 g/dL compare to physiologic 4 g/dL
- Says it pulls in several times its own volume
- 5% albumin is like giving plasma
- Blood
- Which fluid?
- Look at osmolality, give hypotonic fluids to people with high osmolality
- Must include all electrolytes
- Example of adding 77 mEw of K to 0.45 NS and making it isotonic
- DI can be replaced with dextrose solutions, pure water deficit
- Case 14-3
- Diarrhea with metabolic acidosis
- He chooses 0.25 NS with 44 mEq of NaCl and 44 NaHCO3
- Talks about blood and trauma
- Some studies advocate delaying saline until penetrating trauma is corrected APR about to. Keep BP low to prevent bleeding. Worry about diluting coagulation factors
- Only do this if the OR is quickly available
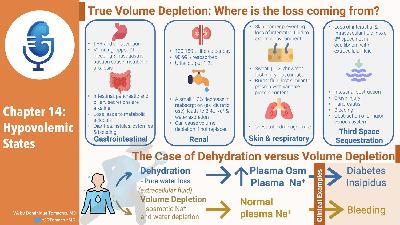
- Volume deficit
- Provides formula for water deficit and sodium deficit
- Do not work for isotonic losses
- Provides a table to adjust fluid loss based on changes in Hgb or HCTZ
- Says difficult to estimate it from lab findings and calculations
- Follow serial exams
- Serial urine Na
- Rate of replacement
- Goal is not to give fluid but to induce a positive balance
- Suggests 50-100 ml/hr over what is coming out of the body
- Urine
- Insensibles 30-50
- Diarrhea
- Tubes
- Hypovolemic shock
- Due to bleeding
- Sequesting in third space
- Why shock?
- Progressive volume depletion leads to
- Increased sympathetic NS
- Increased Ang 2
- Initially this maintains BP, cerebral and coronary circulation
- But this can decrease splanchnic, renal and mucocutaneous perfusion
- This leads to lactic acicosis
- This can result in intracellular contents moving into circulation or translocation of gut bacteria
- Early therapy to prevent irreversible shock
- In dogs need to treat with in 2 hours
- In humans may need more than 4 hours
- Irreversible shock associated with pooling of blood in capillaries
- Vasomotor paralysis
- Hyperpolarization of vascular smooth muscle as depletion of ATP allows K to flowing out from K channels opening. Ca flows out too leading to vasodilation
- Glyburide is an K-ATP channel inhibitor (?) caused increased vasoconstriction and BP
- Pluggin of capillaries by neutrophils
- Cerebral ischemia
- Increased NO generation
- Which Fluids?
- Think of what is lost and replace that.
- Bleeding think blood
<p cla