Chapter Two: Renal Circulation and Glomerular Filtration Rate
Description
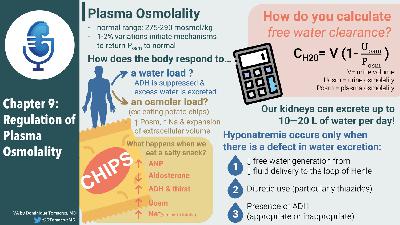
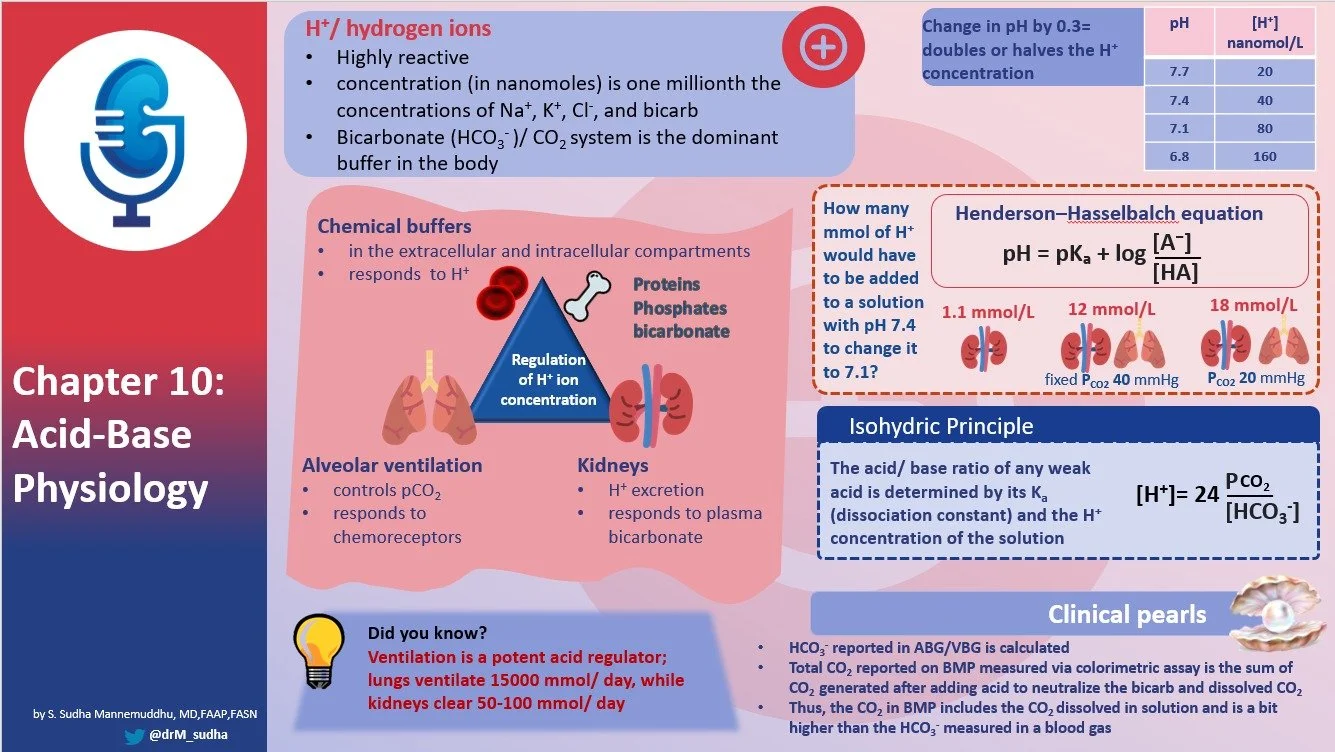
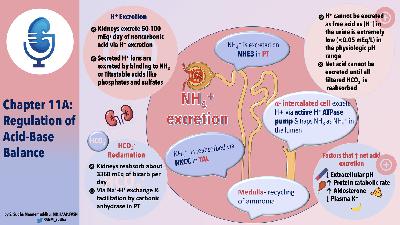
Back by popular demand…all two of you…the second chapter of The Clinical Physiology of Acid Base and Electrolyte Disorders.
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">

</figure>
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">

</figure>
Chapter Outline
- Renal Circulation and GFR
- RBF is 20% of cardiac output
- In terms of mL per 100 g organ weight it is 4x the liver and exercising muscle and 8x coronary blood flow!
- After the glomeruli the efferent arteriole have two fates
- Peritubular capillaries in the cortex
- Peritubular capillaries are not necessarily associated with their parent glomeruli. Weird.
- Vasa recta from juxtamedullary glomeruli in the medulla
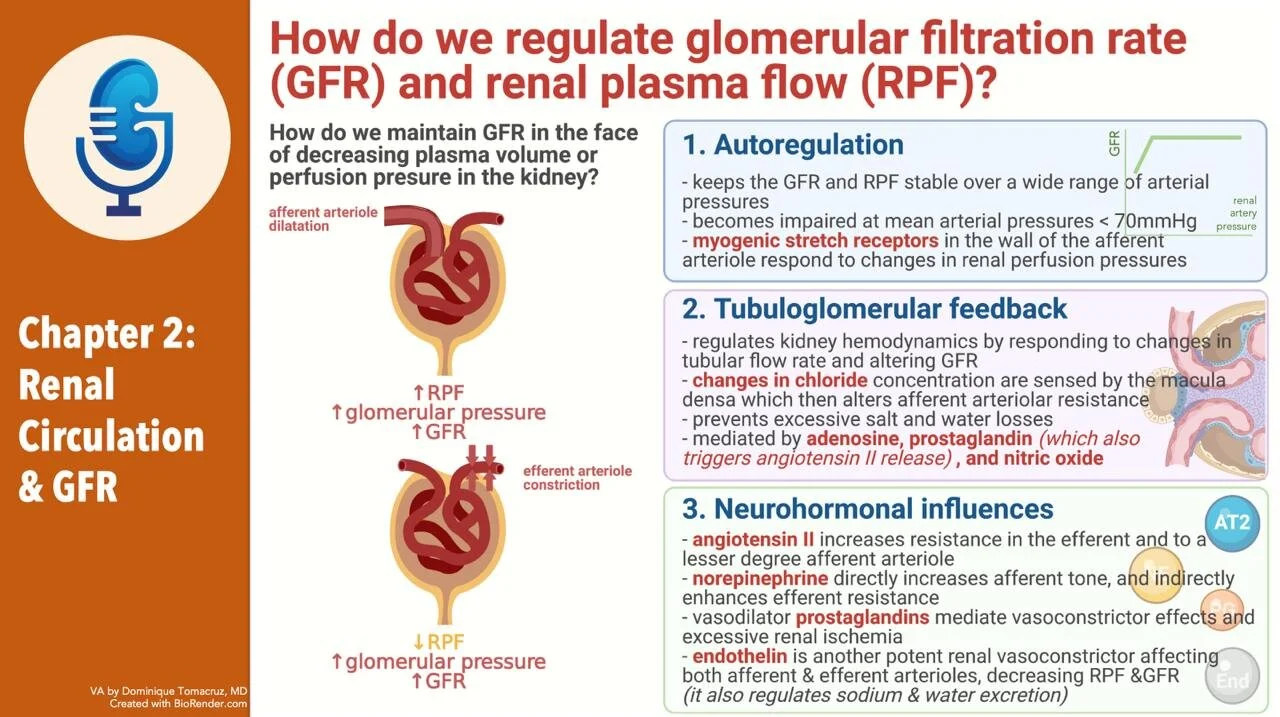
Joel Says: This seems wrong. Solute balance can be maintained down to a very low GFR. The R^2 here would be very low. Prove me wrong.
- States that GFR is an important determinant of solute and water excretion.
- Glomerular anatomy and function
- Structure
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">

<figcaption class="image-caption-wrapper">
Four editions of the Bud Bible up top and a copy of Bud Light on the bottom.
</figcaption>
</figure>
- Glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries
- Enclosed in a capsule of epithelial cells, called Bowman’s capsule
- The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule are continuous with the epithelial cells of the proximal tubule
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">

<figcaption class="image-caption-wrapper">
Looking at scanning EMs of the glomerulus is one of life’s simple pleasures—Josh.
</figcaption>
</figure>
Josh says: Look at the review in Nature Reviews Nephrology from Rachel Lennon’s group
Complexities of the glomerular basement membrane
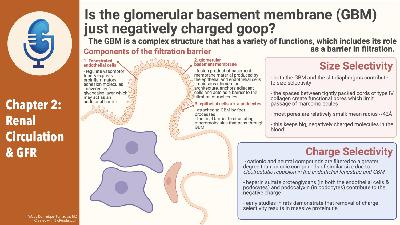
- Filtration barrier
- Epithelial cell (podocyte)
- Epithelial cells adhere to the basement membrane via foot processes and the foot processes have slit diaphragms
- Basement membrane
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">

<figcaption class="image-caption-wrapper">
New Super-resolution structure of the GBM: https://elifesciences.org/articles/01149 Hi res microscopy is really hi-res. Technique is call ed STORM.
</figcaption>
</figure>
Melanie talks about conduits through the glomeruli. Here is a cool review:
Why until just now? Undiscovered uniqueness of the human glomerulus! by L. Gabriel Navar, Owen Richfield
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Nov 1; 315(5): F1345–F1346. Published online 2018 Aug 15. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00369.2018 PMCID: PMC6293291
- Produced by both the endothelial cells and podocytes
- Formed from type IV collagen
- Abnormalities of type 4 collagen cause Alport
- The gene coding for the alpha 5 chain is the culprit
- COL4A5
- Abnormal Alpha 3 and 4 chains can also cause hereditary nephritis
- Has other substances
- Laminin
- Nidogen
- Heparin sulfate proteoglycans
- Provides the negative charge
- Enthothelial cell (fenestrated)
- Protein excretion
- Glomerular function: allow filtration of small solutes (Na and urea) while preventing filtration of larger molecules
- Insulin MW 5,200 is freely filtered (upper range of freely filtered)
- Preventing loss of protein prevents
- Negative nitrogen balance
- Development of hypoalbuminemia
- Infection from loss of immunoglobulin
- Size and charge selectivity of the GBM
- pores are between cords of type 4 collagen
- The epithelial cells and slit diaphragms matter
- Macromolecules that pass through GBM can accumulate underneath the epithelial layer
- Isolated GBM in invitro studies is much more permeable to than intact glomerulus
- There is increased protein filtration in areas where the epithelial cells have detached from the GBM
<figure class="
sqs-block-image-figure
intrinsic
">