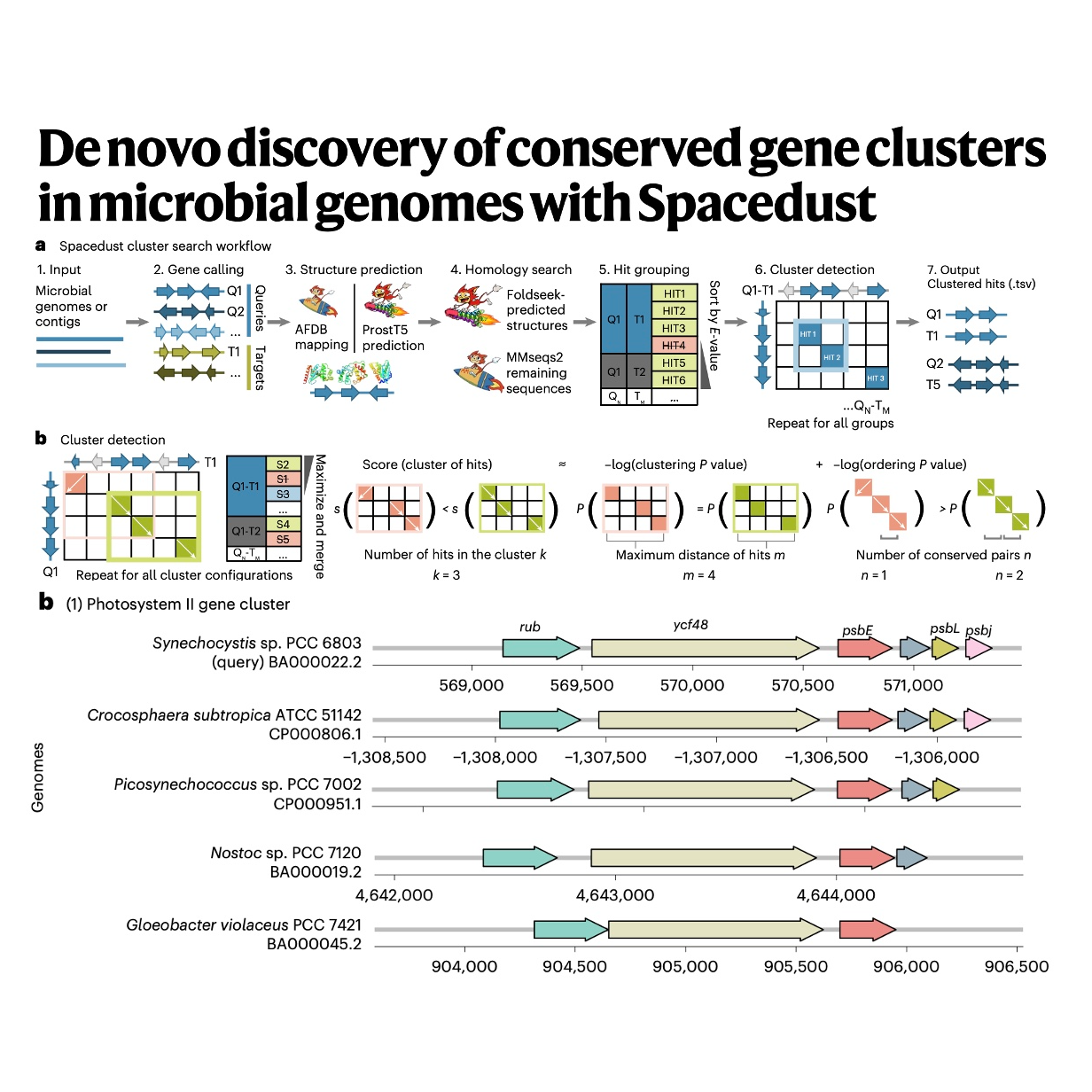
316-TIRTL-seq: Deep Paired TCR Repertoire Sequencing
Update: 2025-12-14
Description
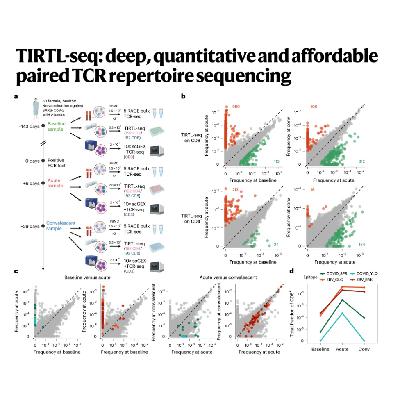
The paper introduces TIRTL-seq (throughput-intensive rapid TCR library sequencing), a novel experimental and computational methodology designed to address the trade-offs between affordability and detailed data collection in T cell receptor sequencing. This new approach combines the high throughput and quantitative precision of older bulk sequencing methods with the critical capacity for acquiring paired TCR alpha and beta chain sequences, a feature traditionally limited to expensive single-cell technologies. TIRTL-seq is highly affordable and scalable, operating in a 384-well plate format to analyze millions of T cells at a fraction of the cost of current commercial kits, enabling large-scale cohort studies. Furthermore, the methodology introduces the T-SHELL algorithm to overcome computational limitations, allowing successful pairing of both high-frequency and low-frequency TCR clones. Benchmarking confirmed its accuracy and depth, and its utility was demonstrated in a longitudinal cohort study of a SARS-CoV-2 infected individual, which simultaneously revealed distinct clonal dynamics associated with an acute viral response and a concurrent expansion of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-specific clones.
References:
- Pogorelyy M V, Kirk A M, Adhikari S, et al. TIRTL-seq: deep, quantitative and affordable paired TCR repertoire sequencing[J]. Nature Methods, 2025: 1-9.
Comments
In Channel